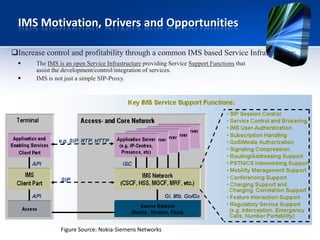
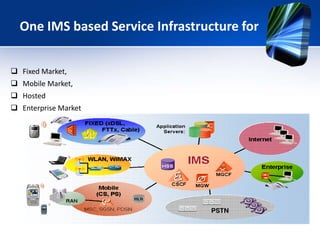
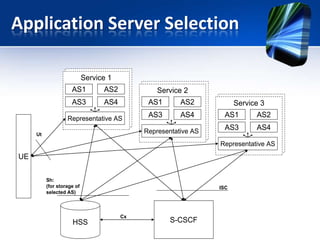
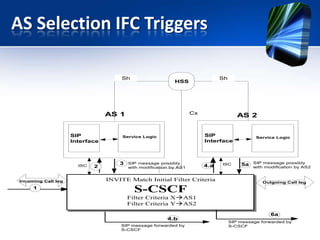
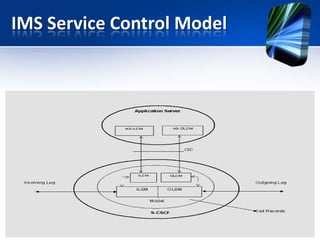
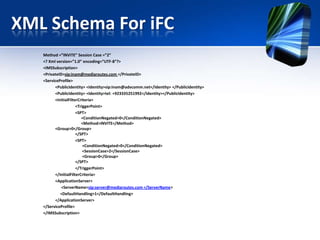
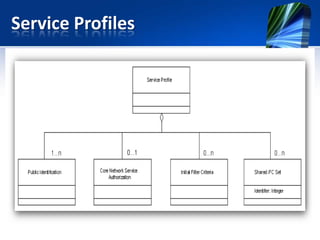
This document provides an overview of the IMS service control model. It discusses why operators are offering more services like IP telephony, presence, and video on demand. It then introduces the IMS as a flexible, standard platform that simplifies developing and deploying new services. The IMS provides a common service infrastructure and increases control and profitability through a unified service environment. Key components of the IMS service control model are also summarized, including service invocation using SIP application servers and initial filter criteria.