Embed presentation
Downloaded 153 times


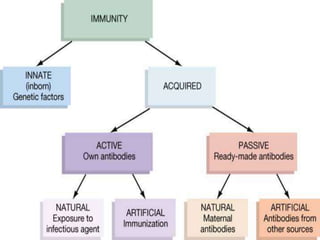
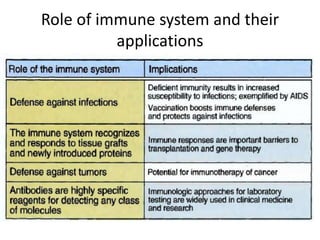
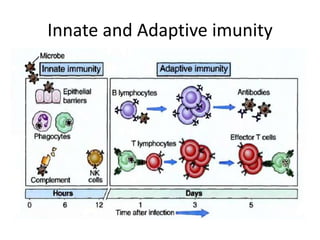

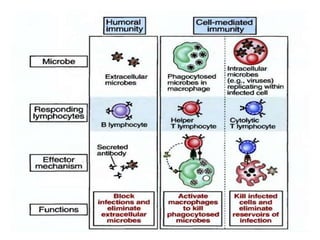
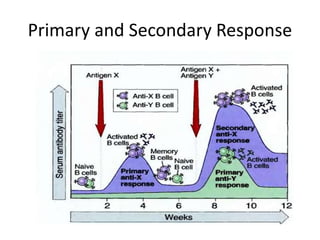
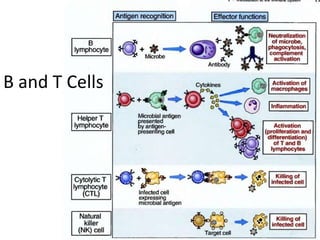
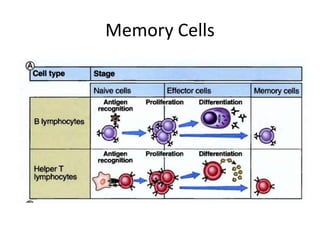
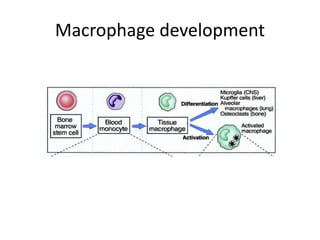
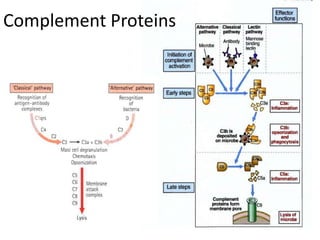
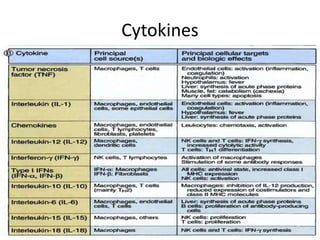
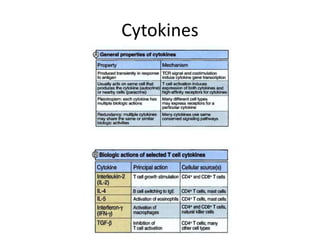
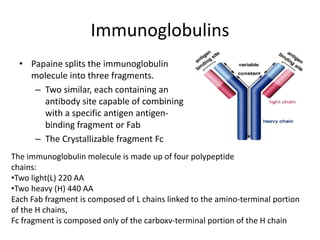

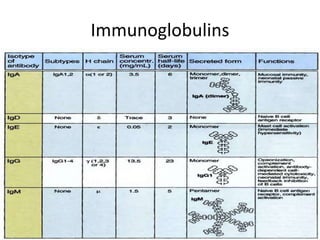
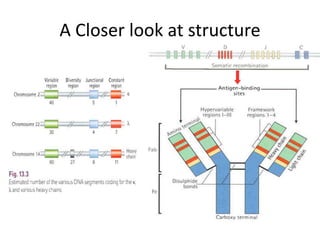
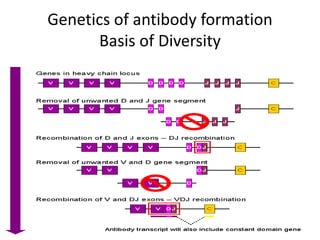
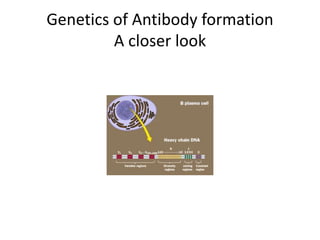
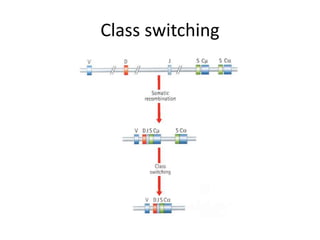
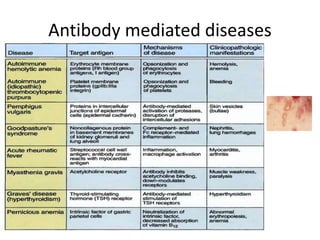
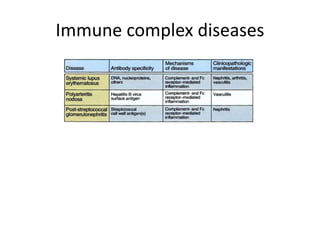
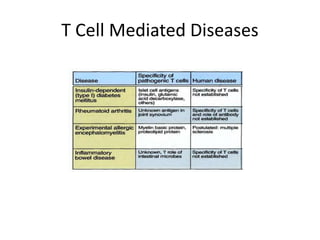
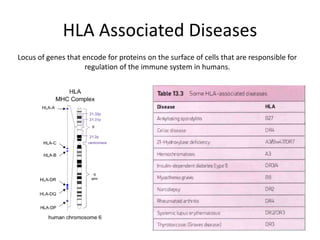
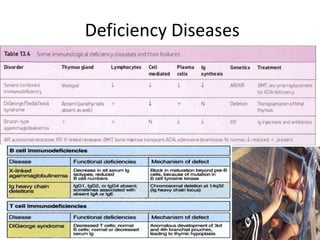


This document provides an overview of immunogenetics and immune disorders. It discusses the organization of the immune system, including innate and adaptive immunity. It describes the roles of natural killer cells, defense proteins, B and T cells, memory cells, macrophages, complement proteins, cytokines, and immunoglobulins. The document examines the structure and genetics of antibody formation, class switching, and diseases associated with antibody- and T cell-mediated responses. It also discusses HLA-associated diseases and immunodeficiency disorders. The overall goal is to help students understand the immune system and immune-related disorders.




























