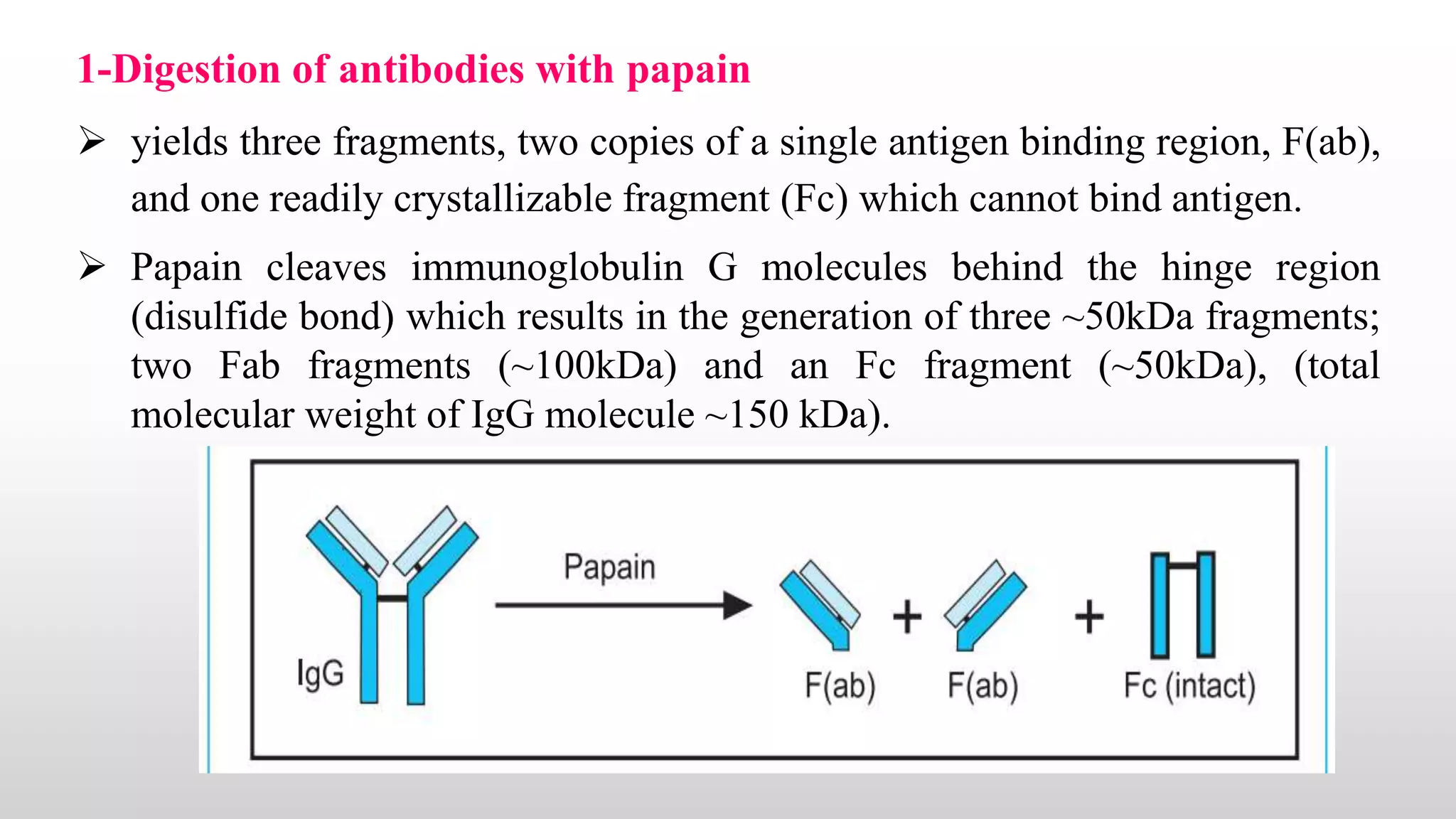
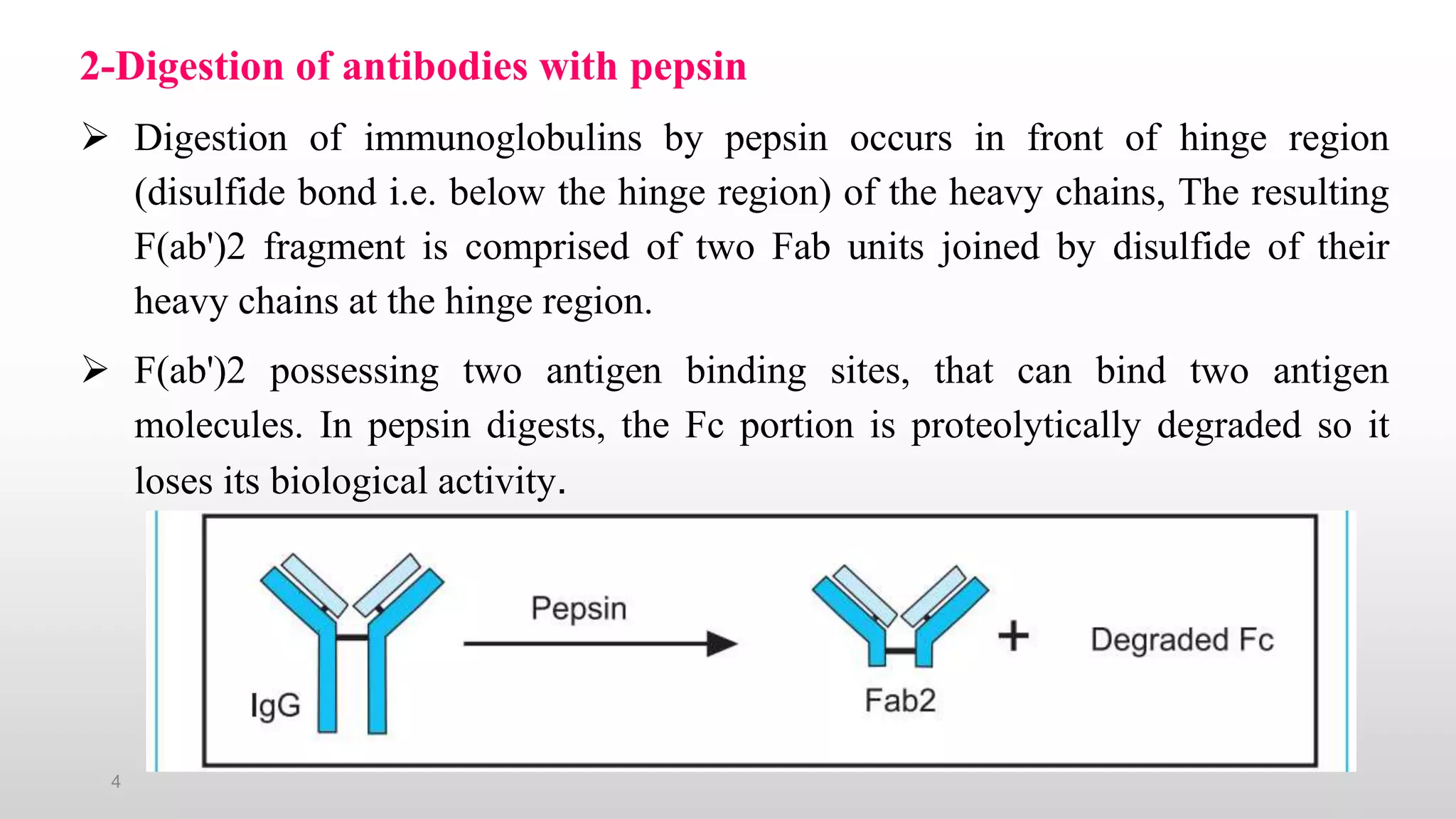
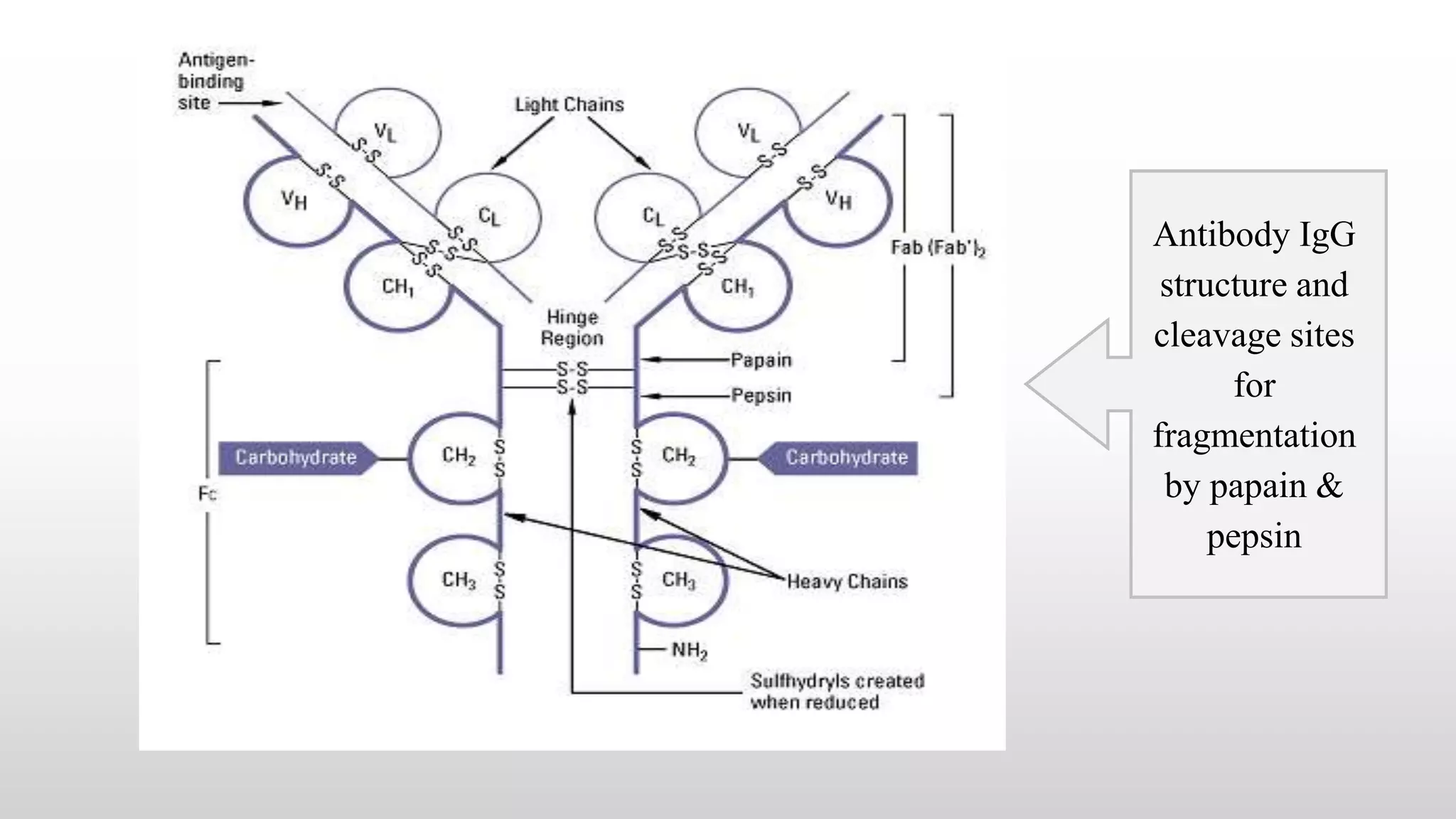
1) Antibodies possess both an antigen binding capacity and a biological activity. Digestion with enzymes like papain and pepsin can yield fragments that retain one or the other function.
2) Papain digestion yields two Fab fragments that retain antigen binding and an Fc fragment that retains biological activity. Pepsin digestion yields an F(ab')2 fragment with two antigen binding sites and degrades the Fc fragment.
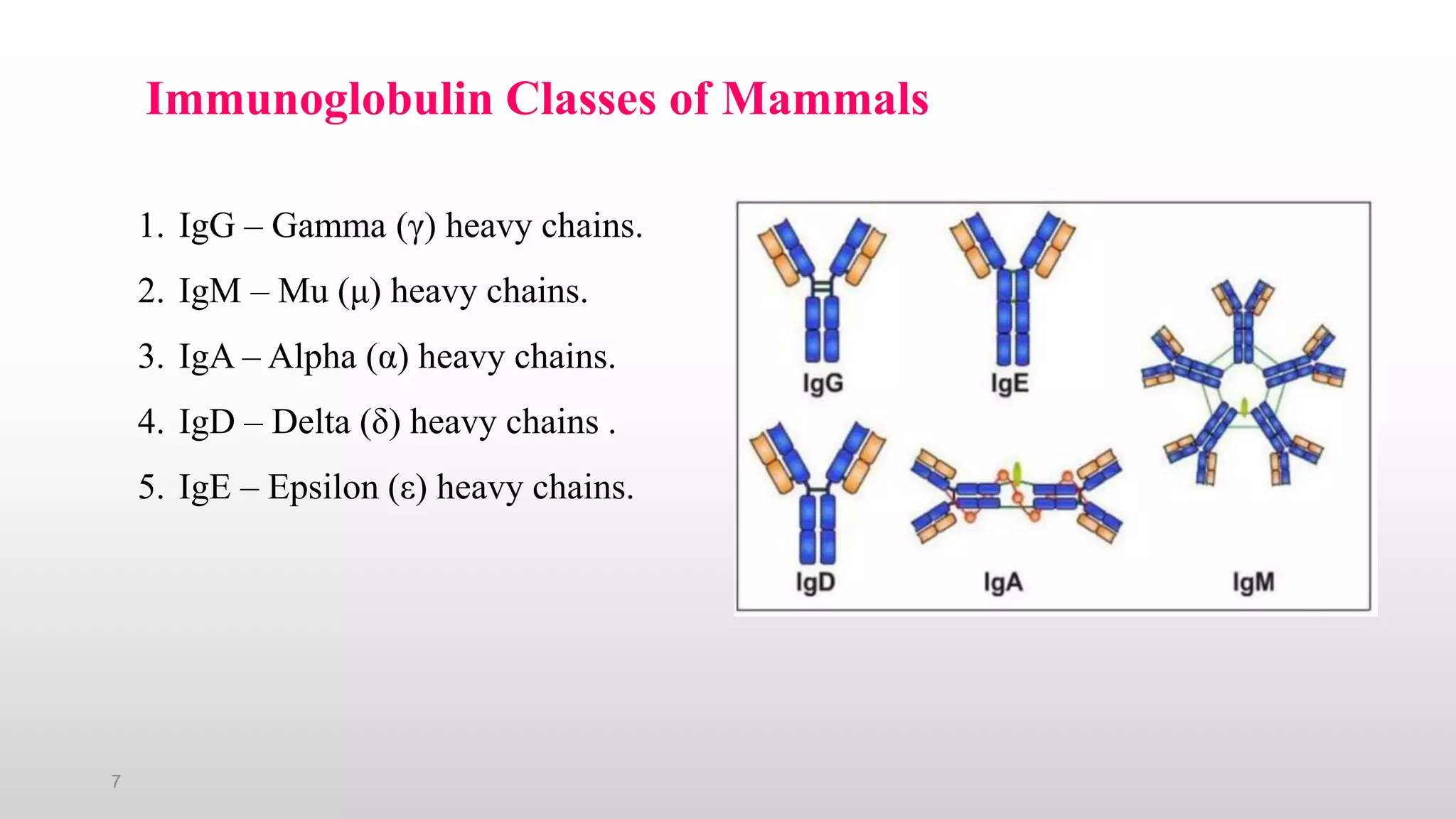
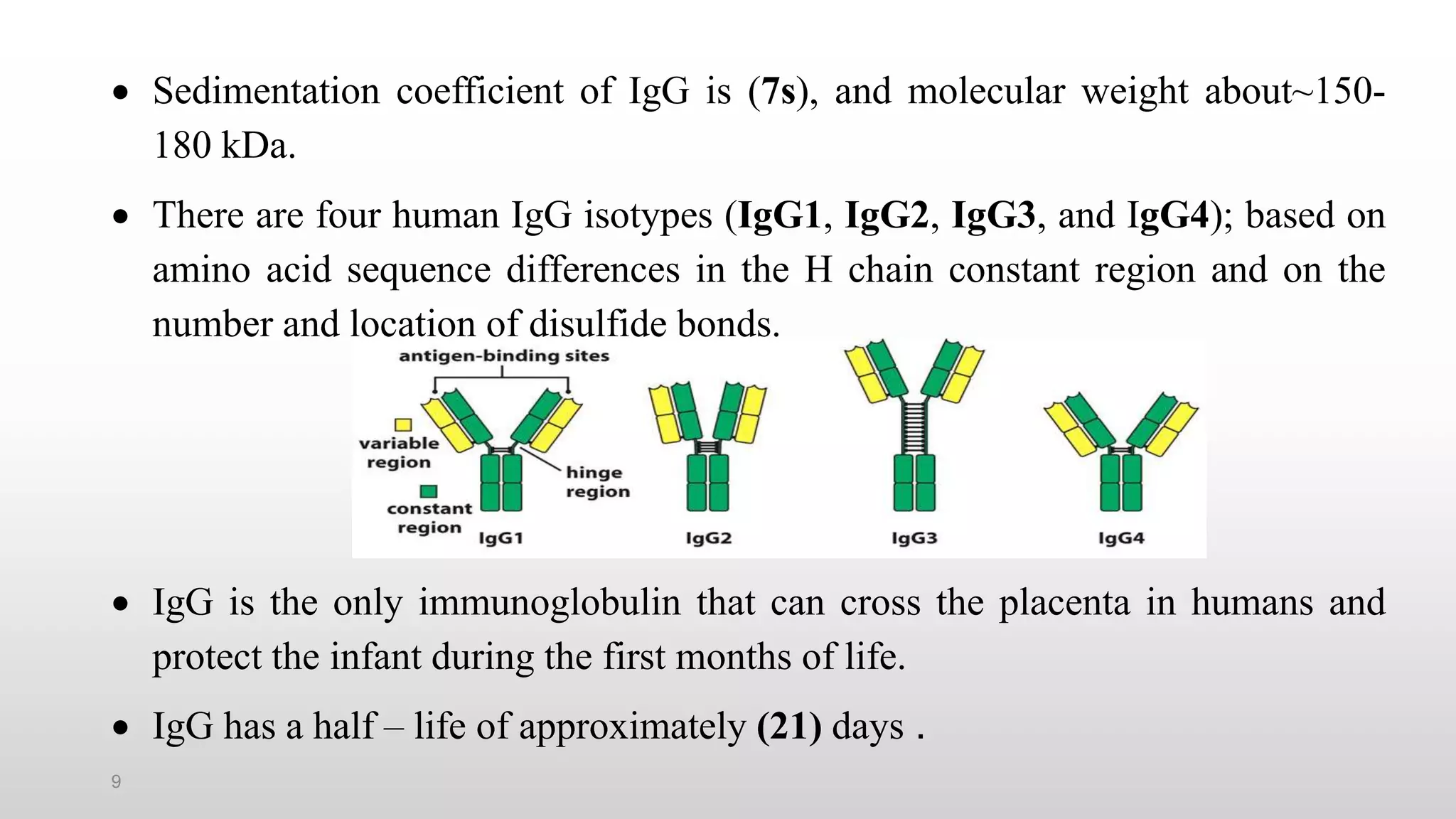
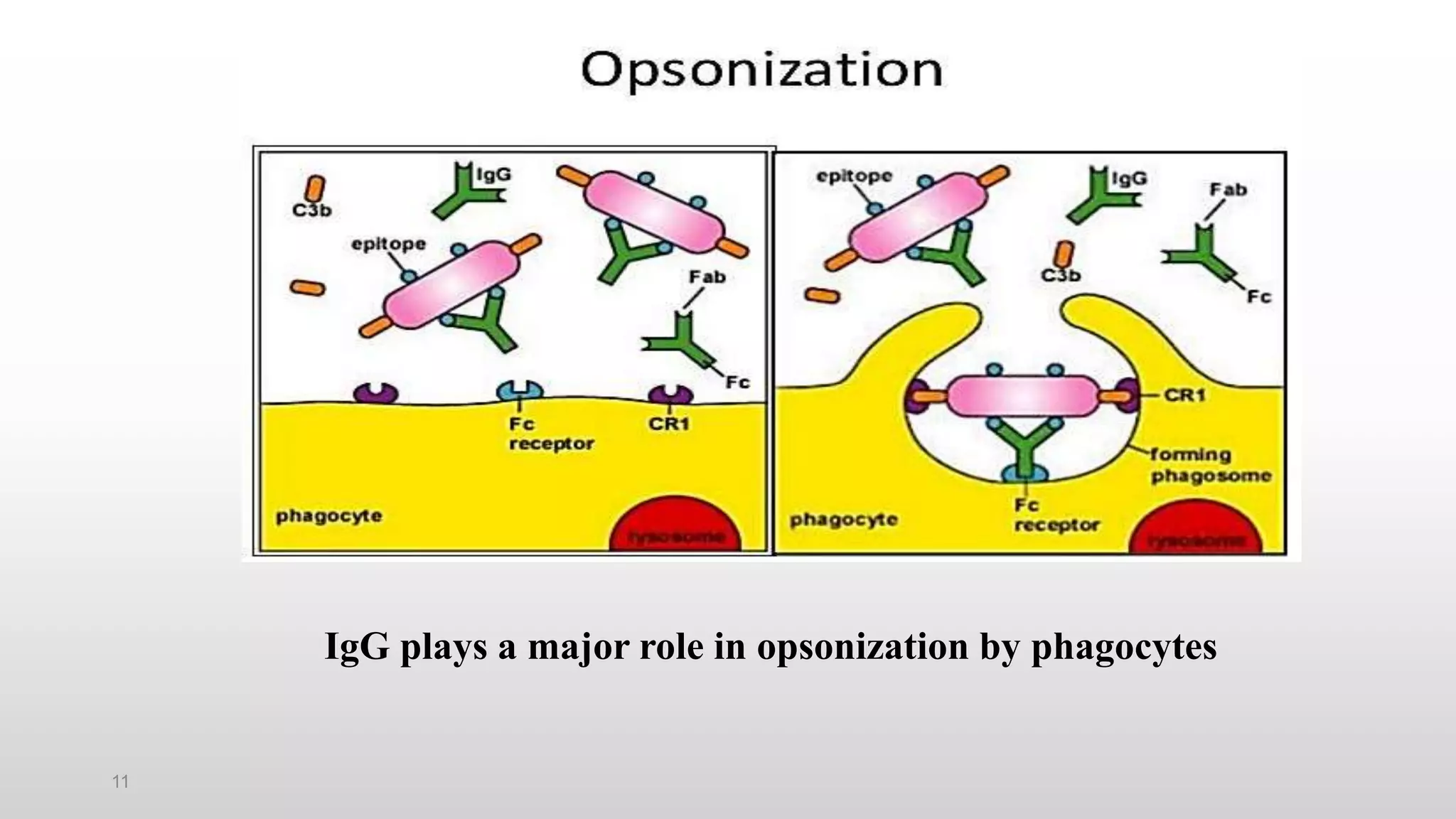
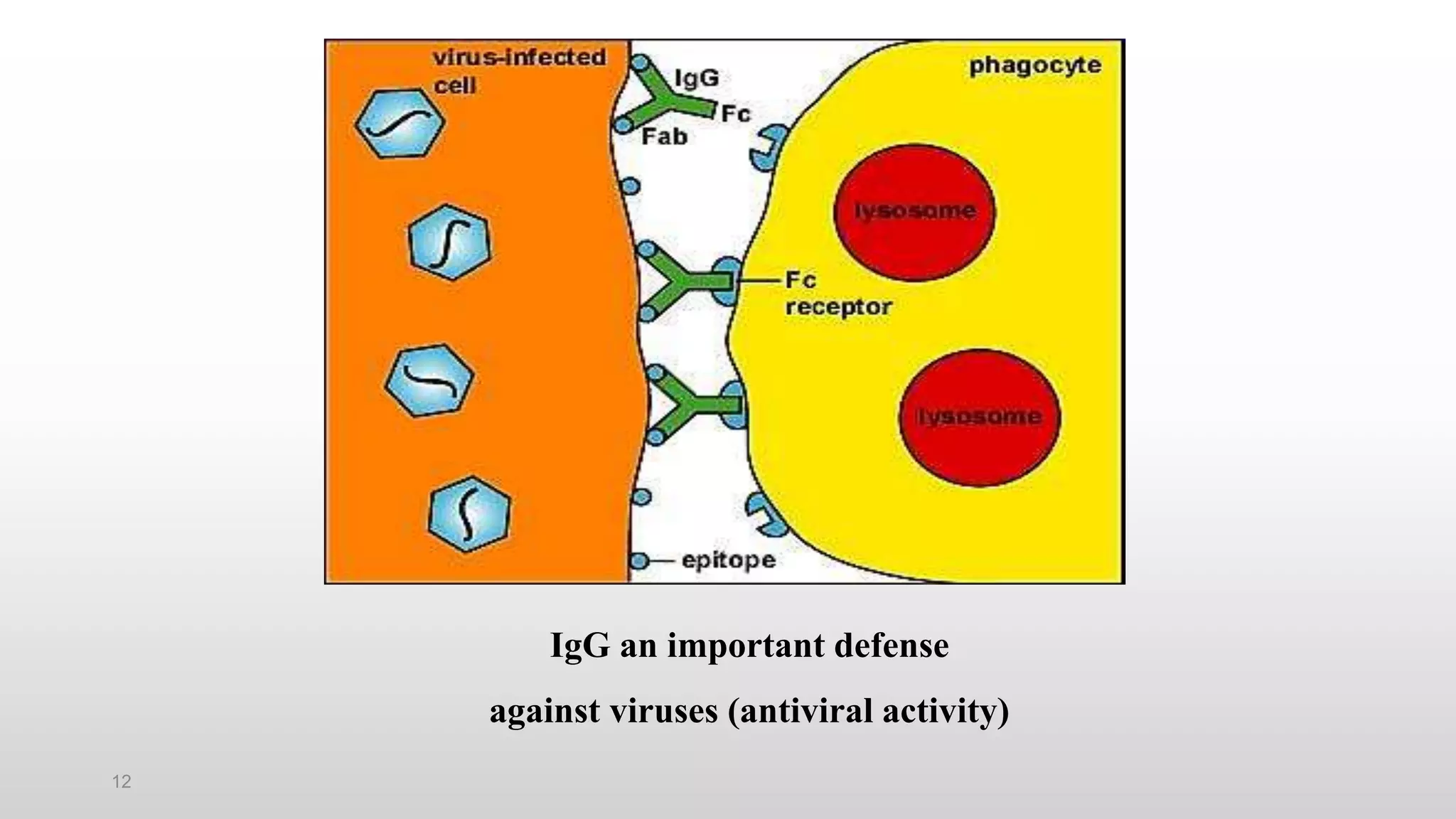
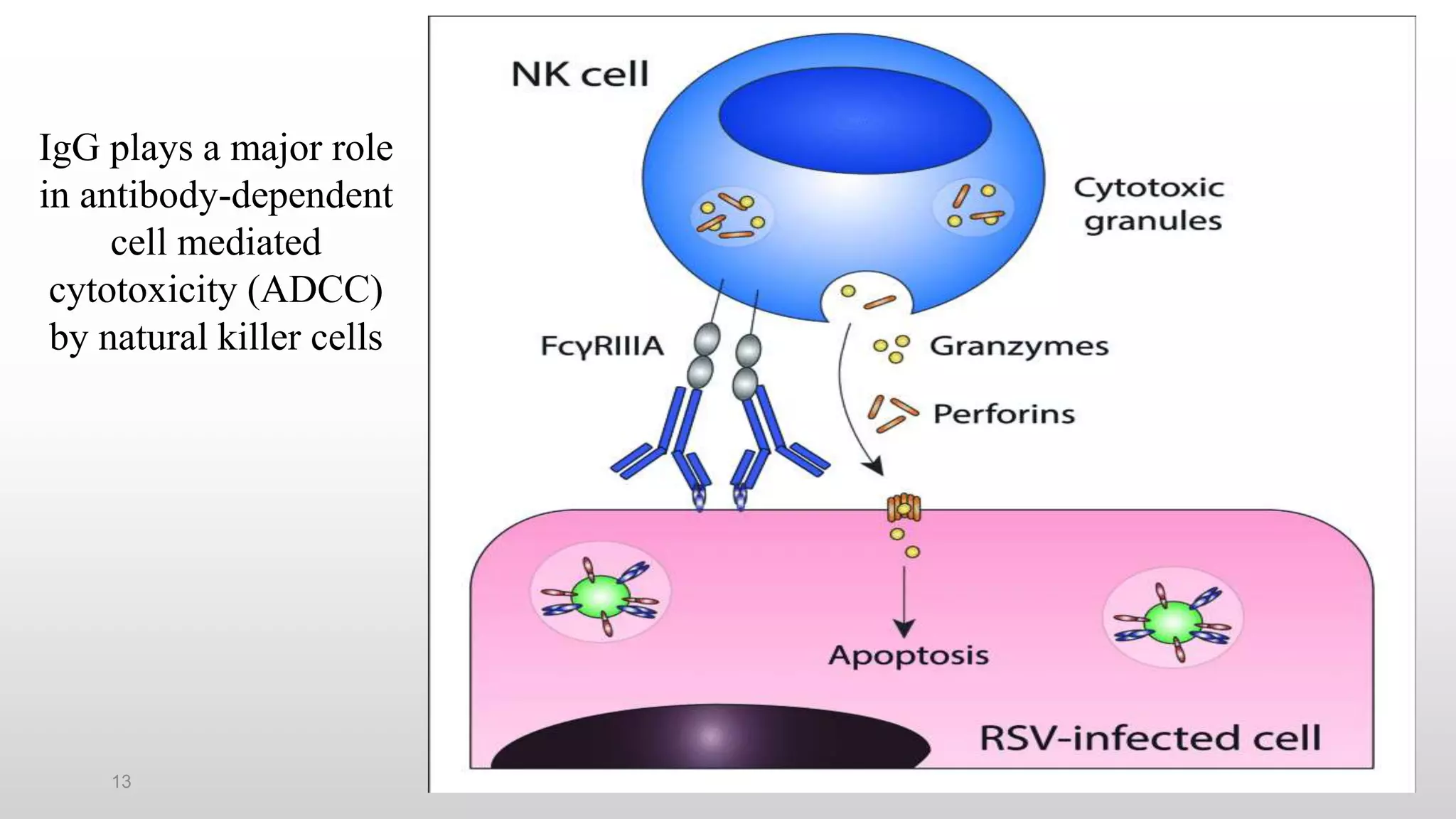
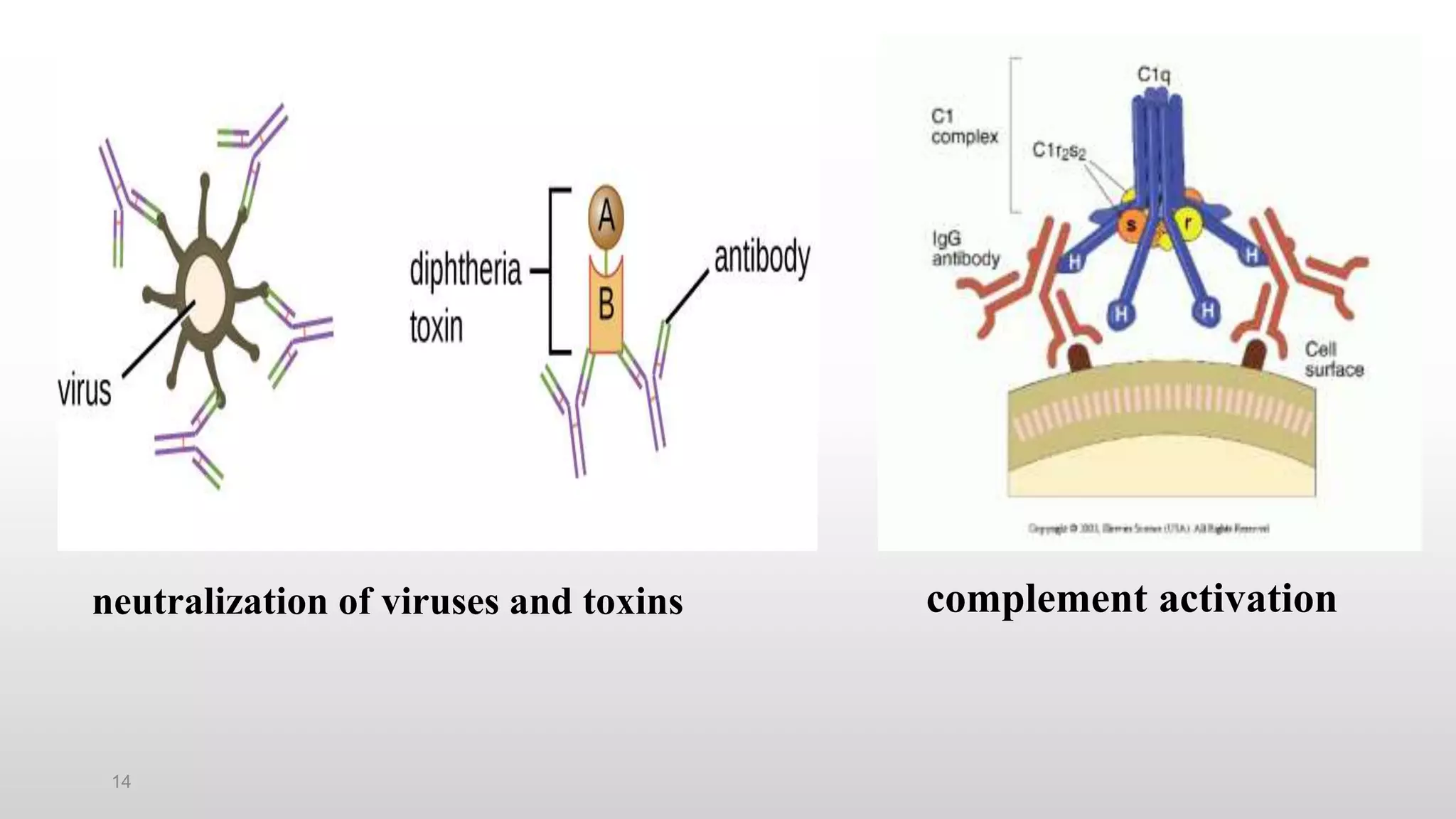
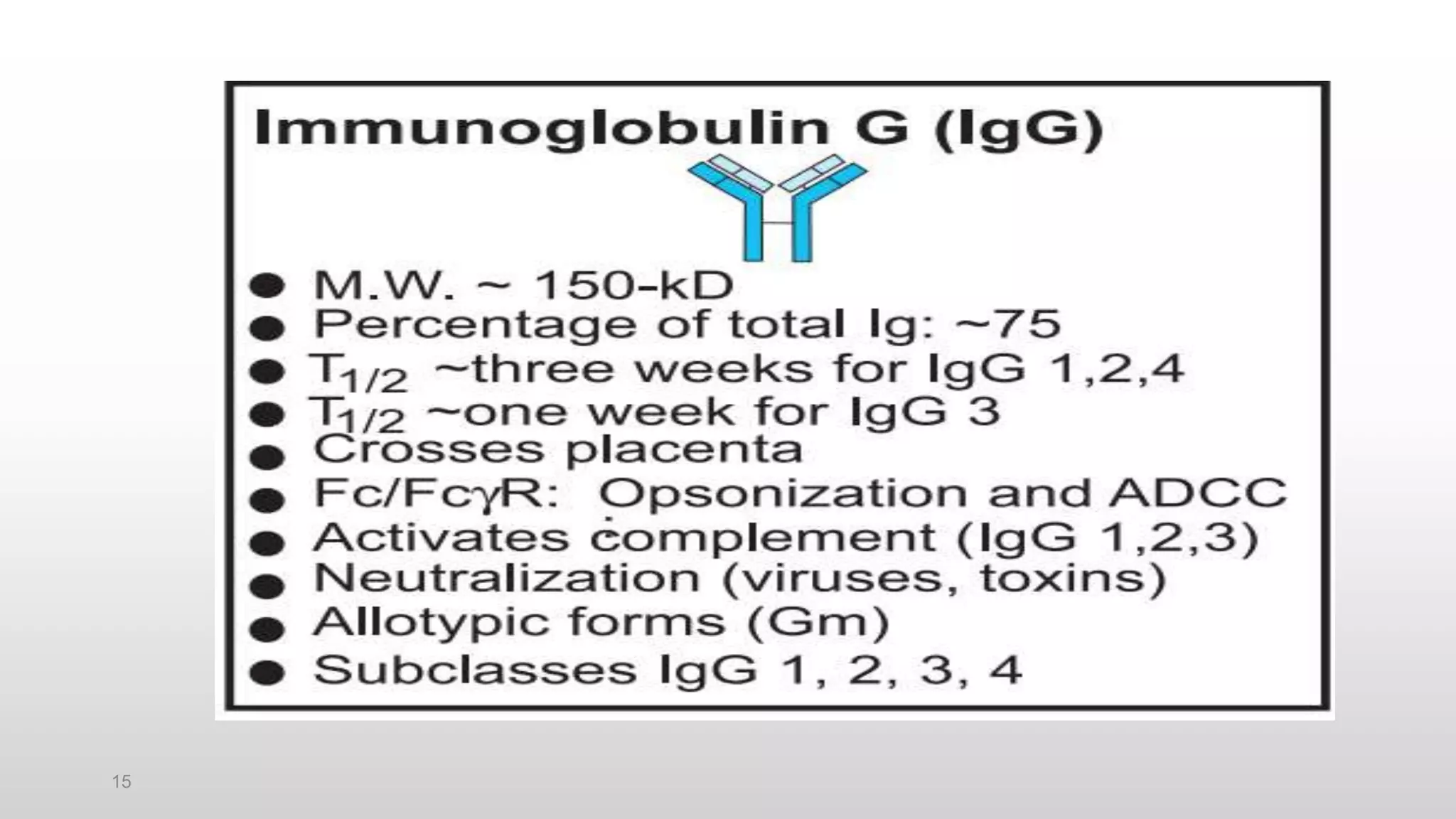
3) The major classes of antibodies in mammals are IgG, IgM, IgA, IgD, and IgE, which differ in their heavy chain constant regions. IgG is the most abundant in serum and provides a major defense against bacteria, viruses, and parasites through mechanisms like