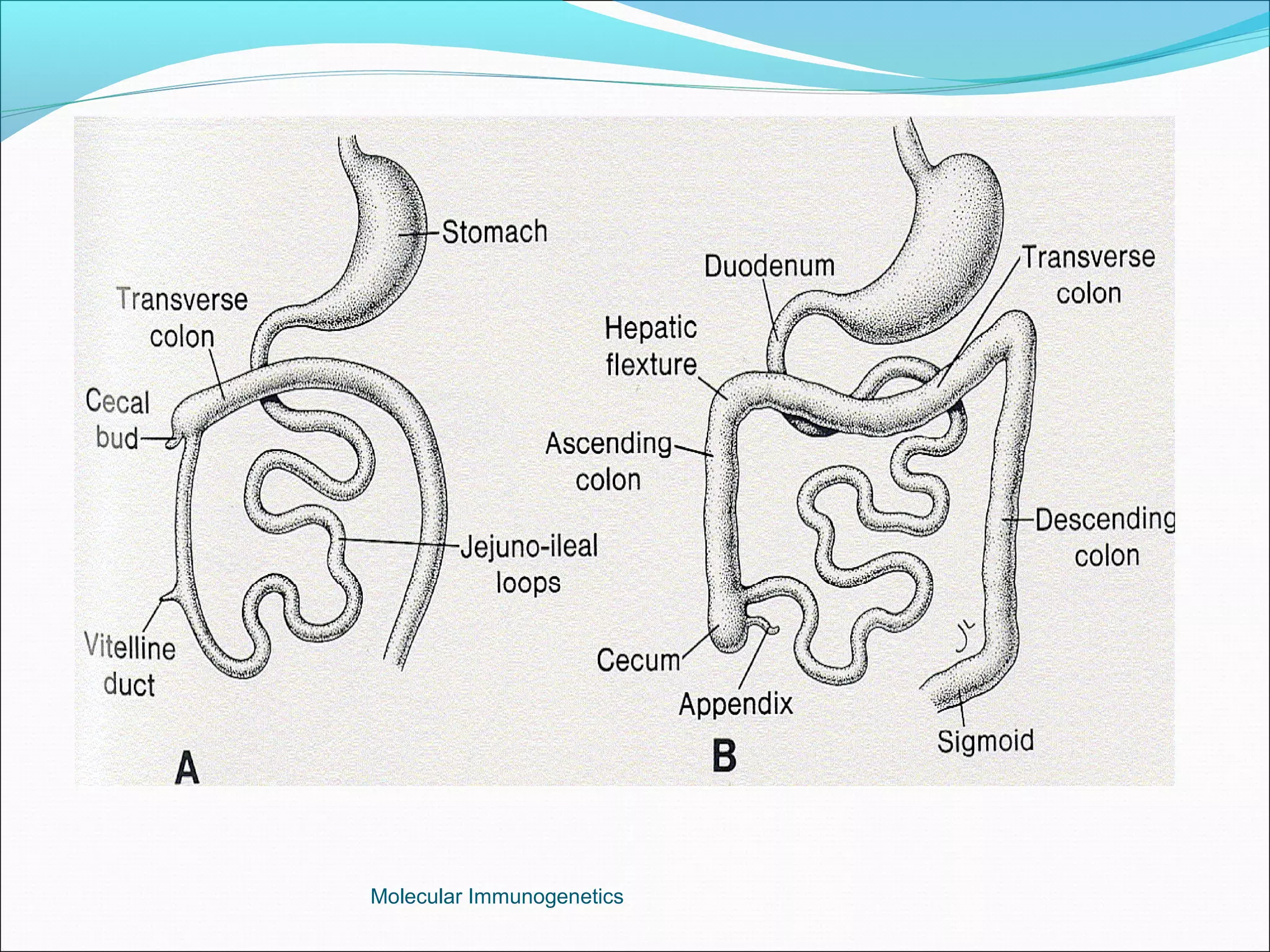
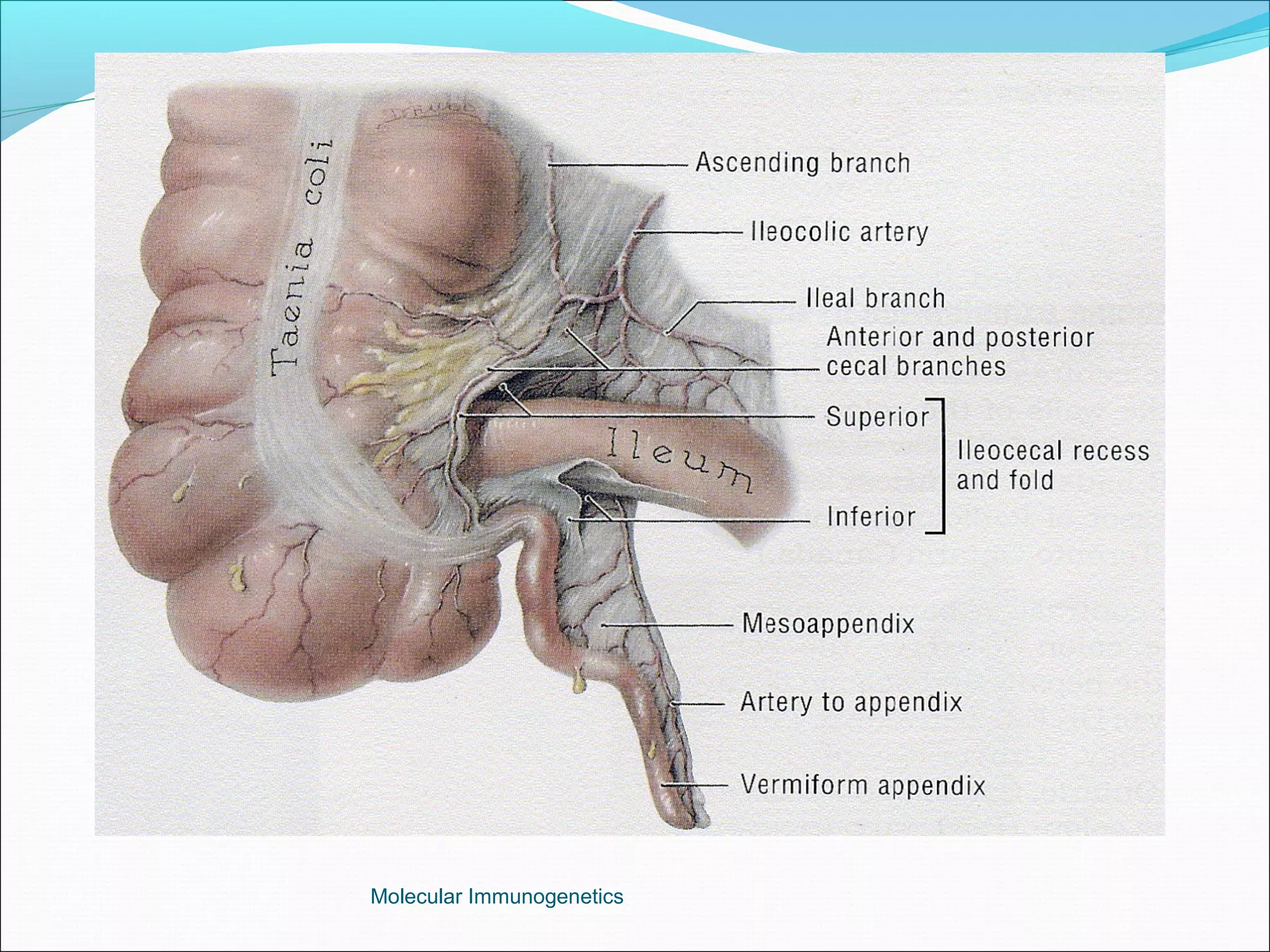
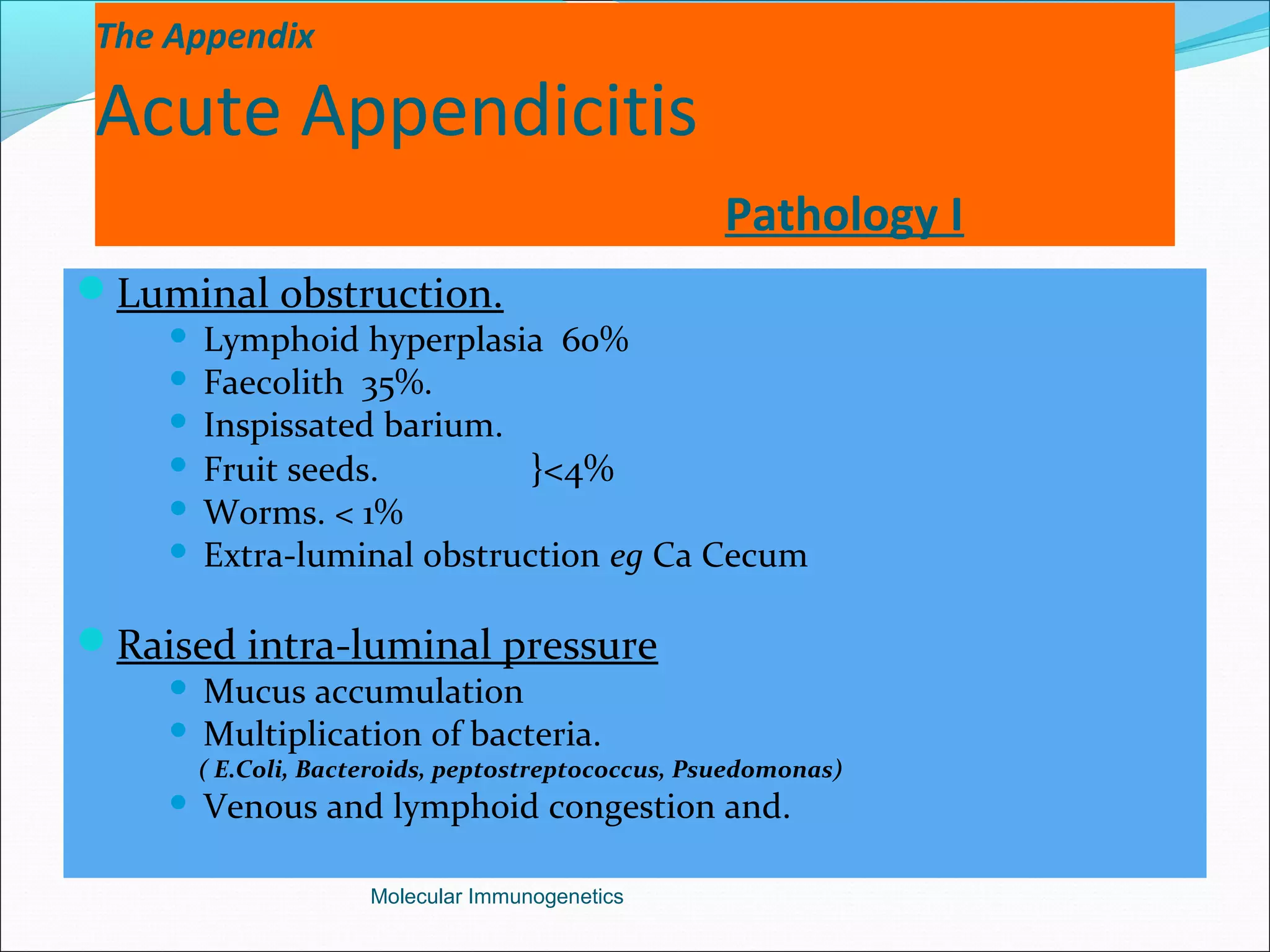
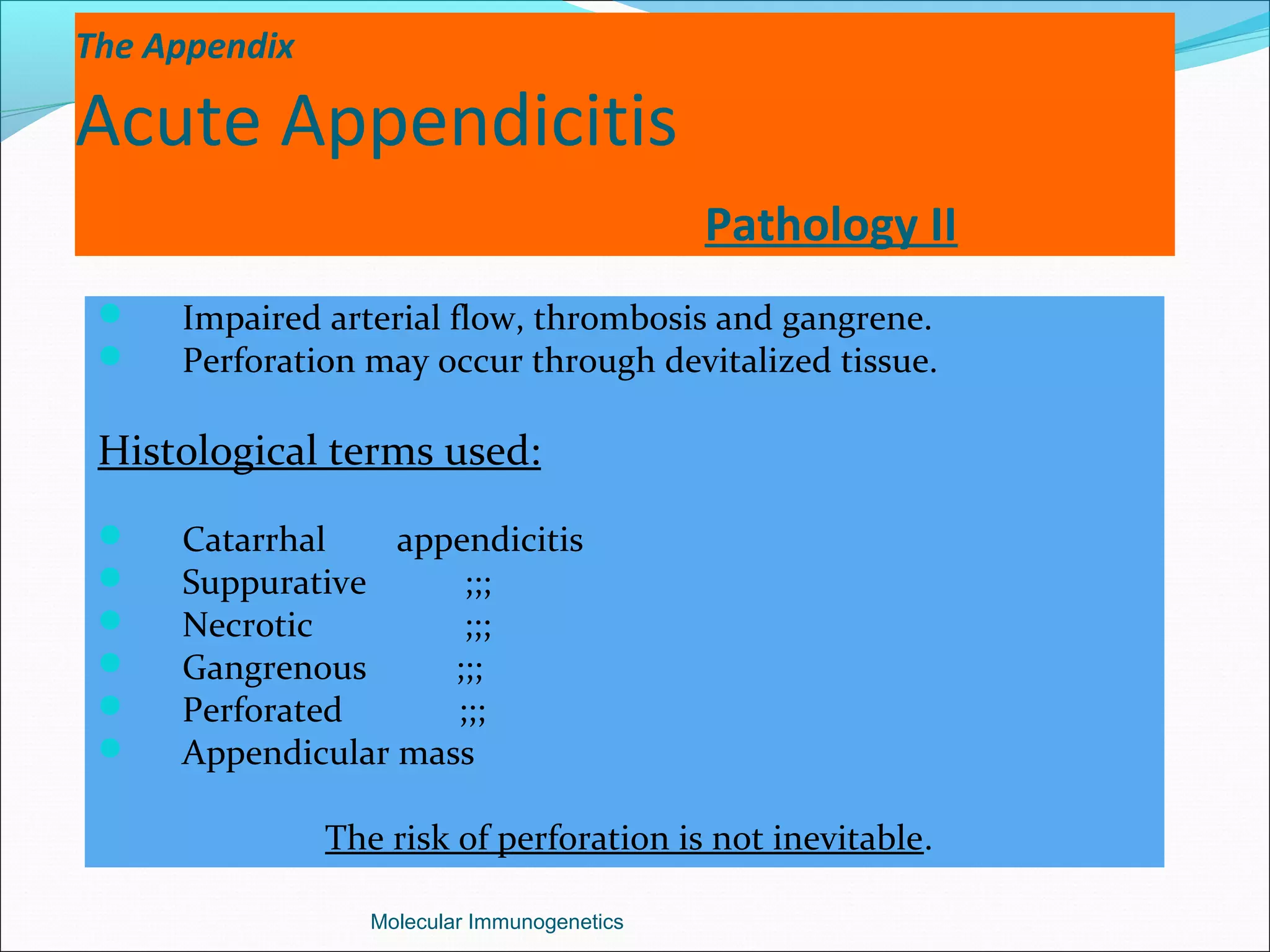
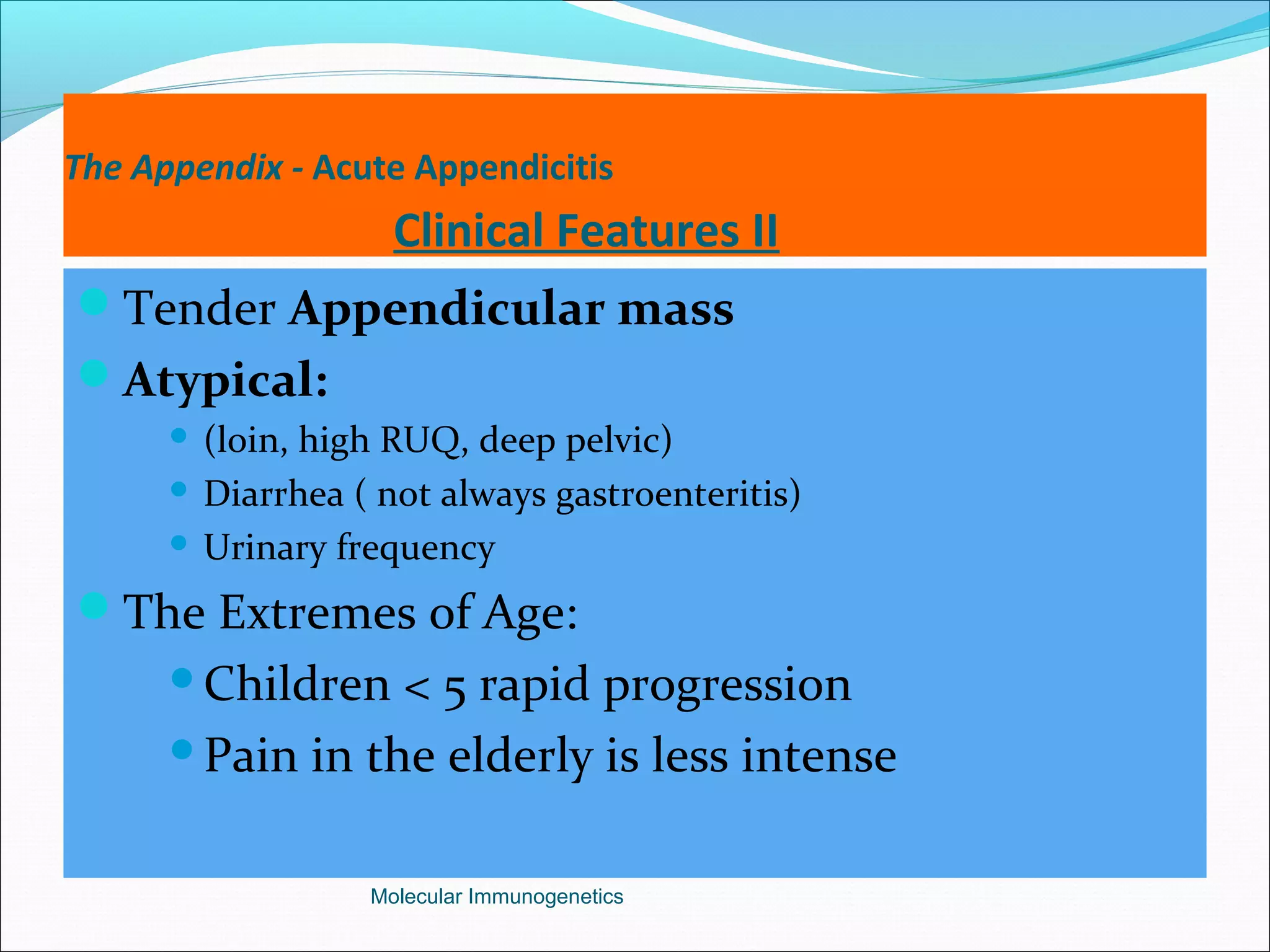
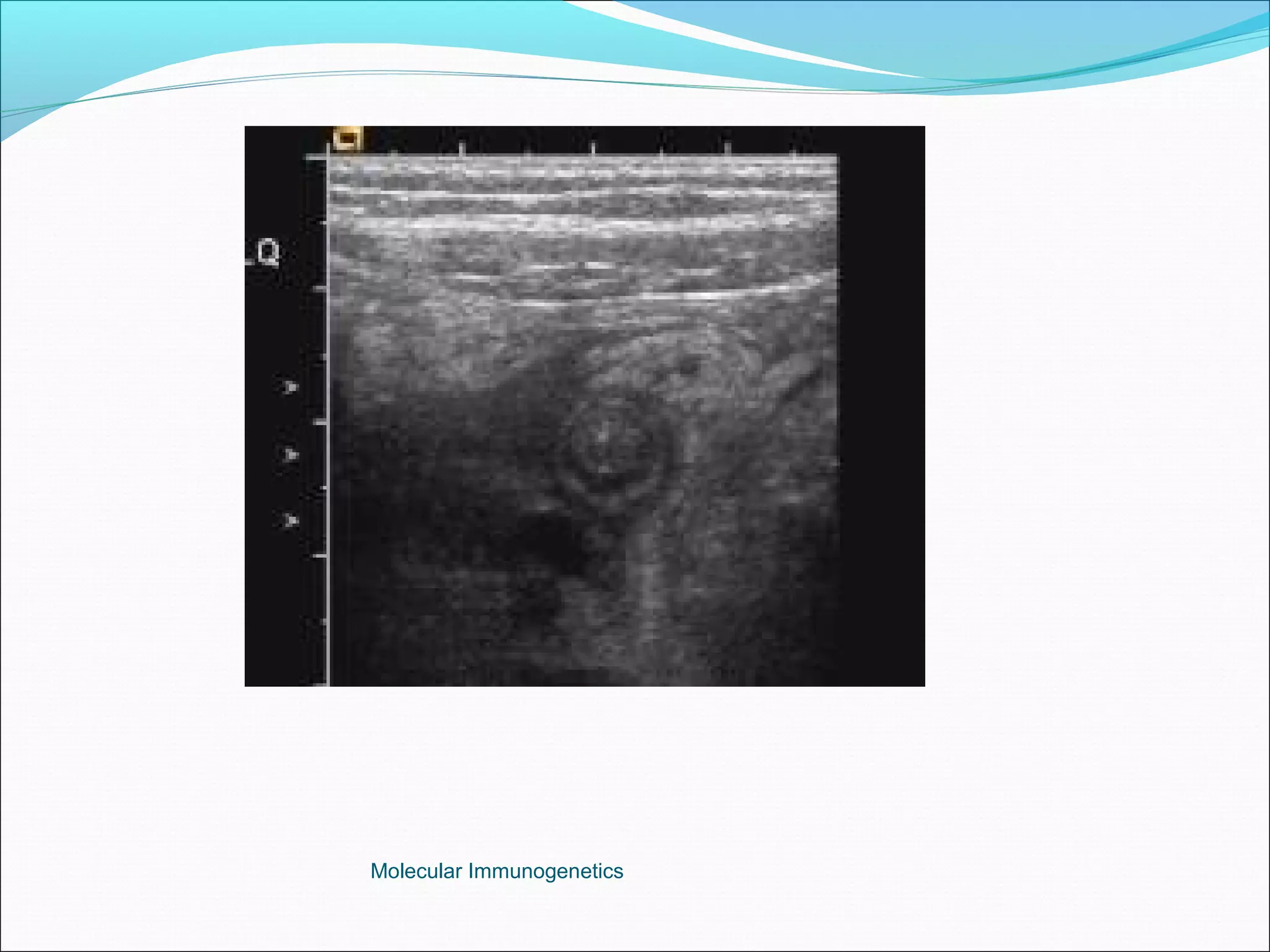
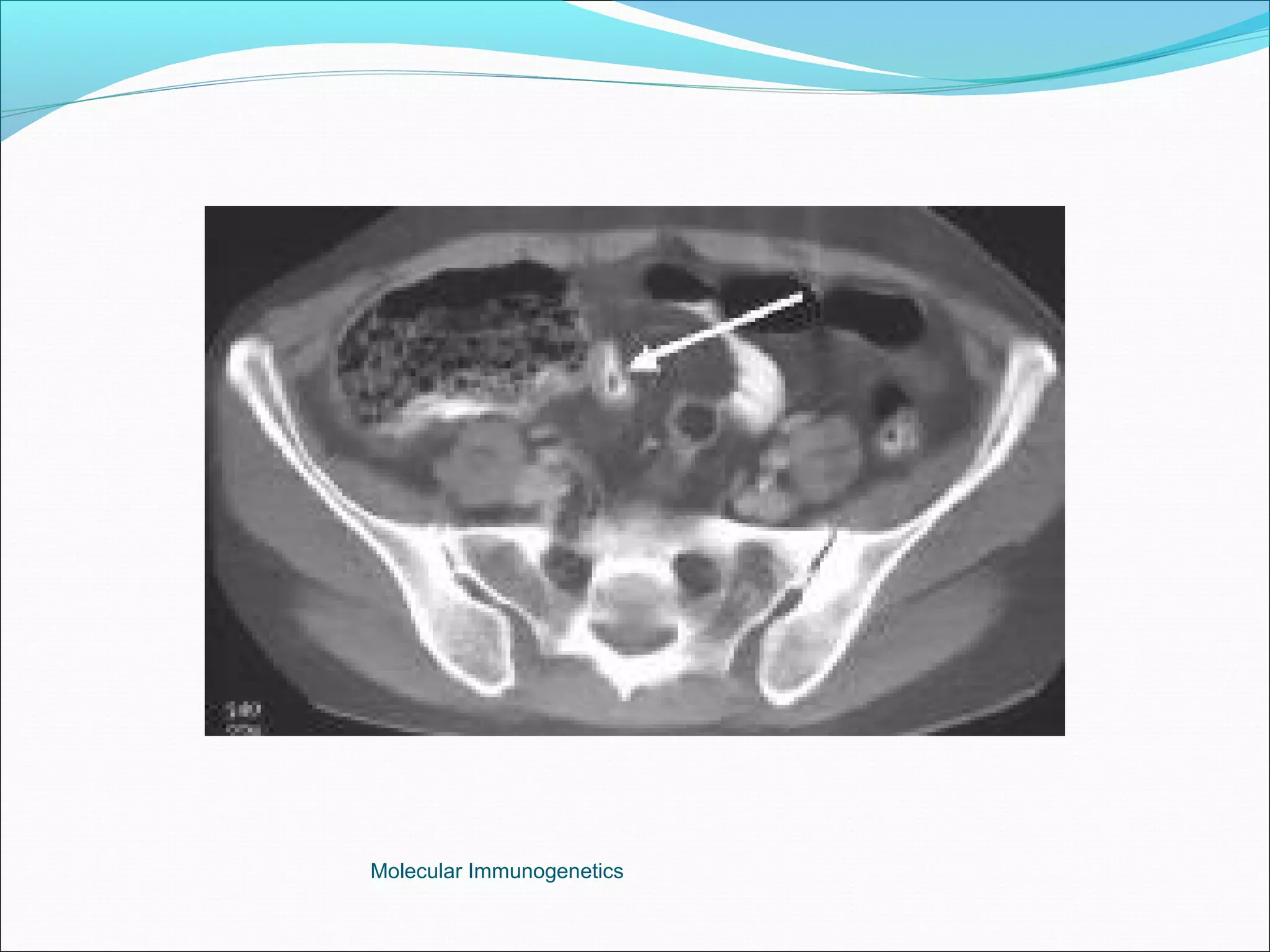
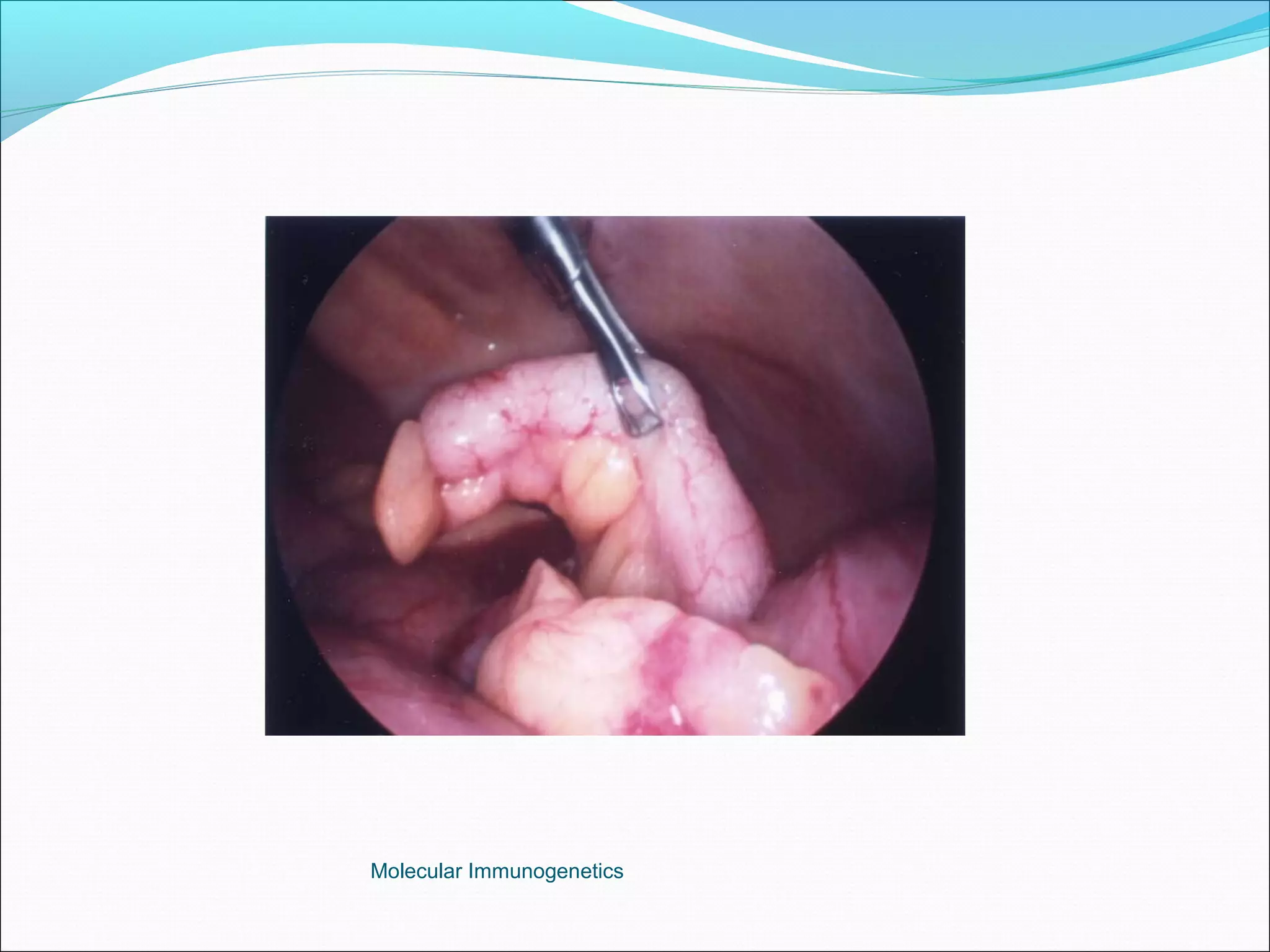
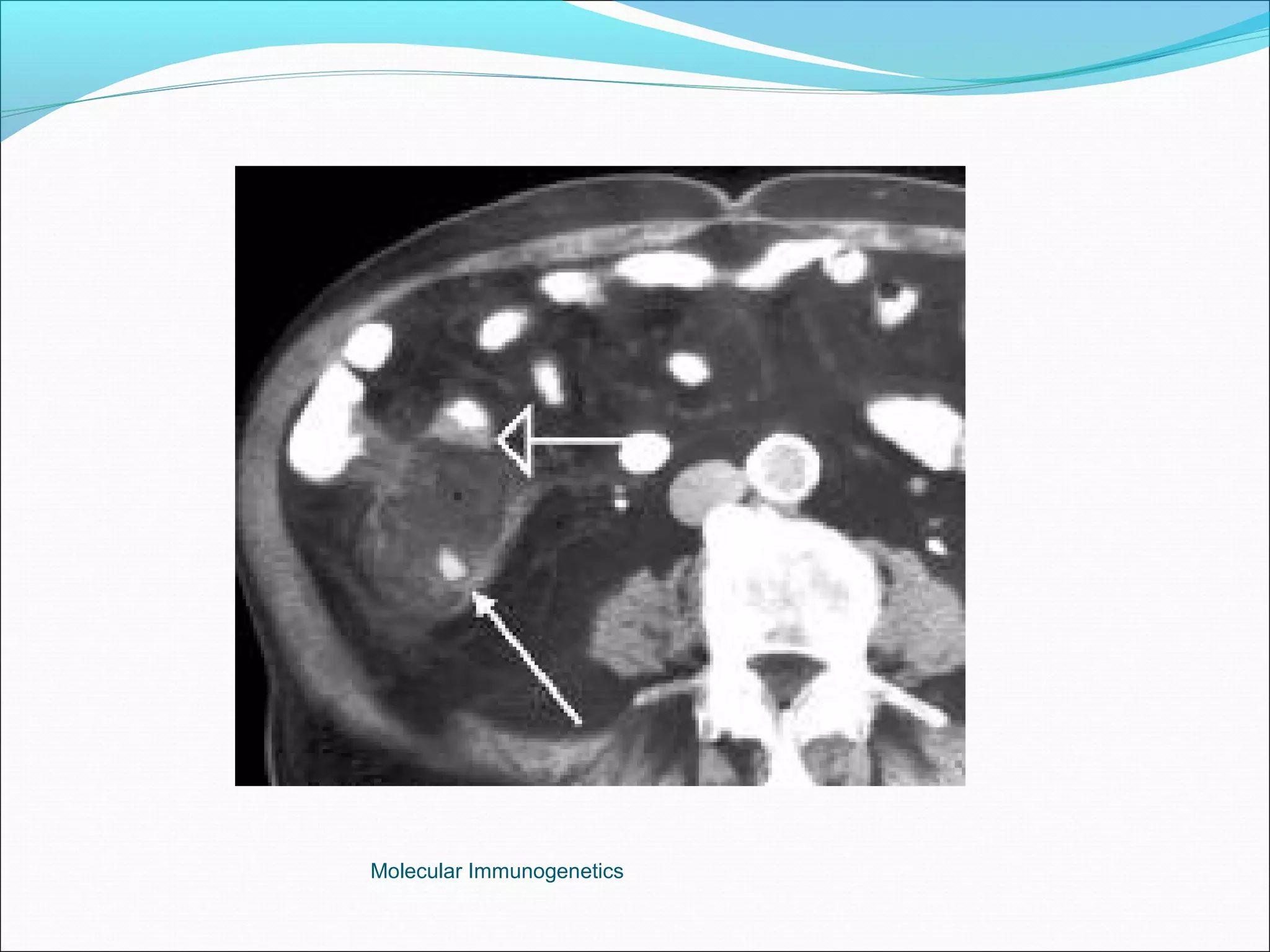
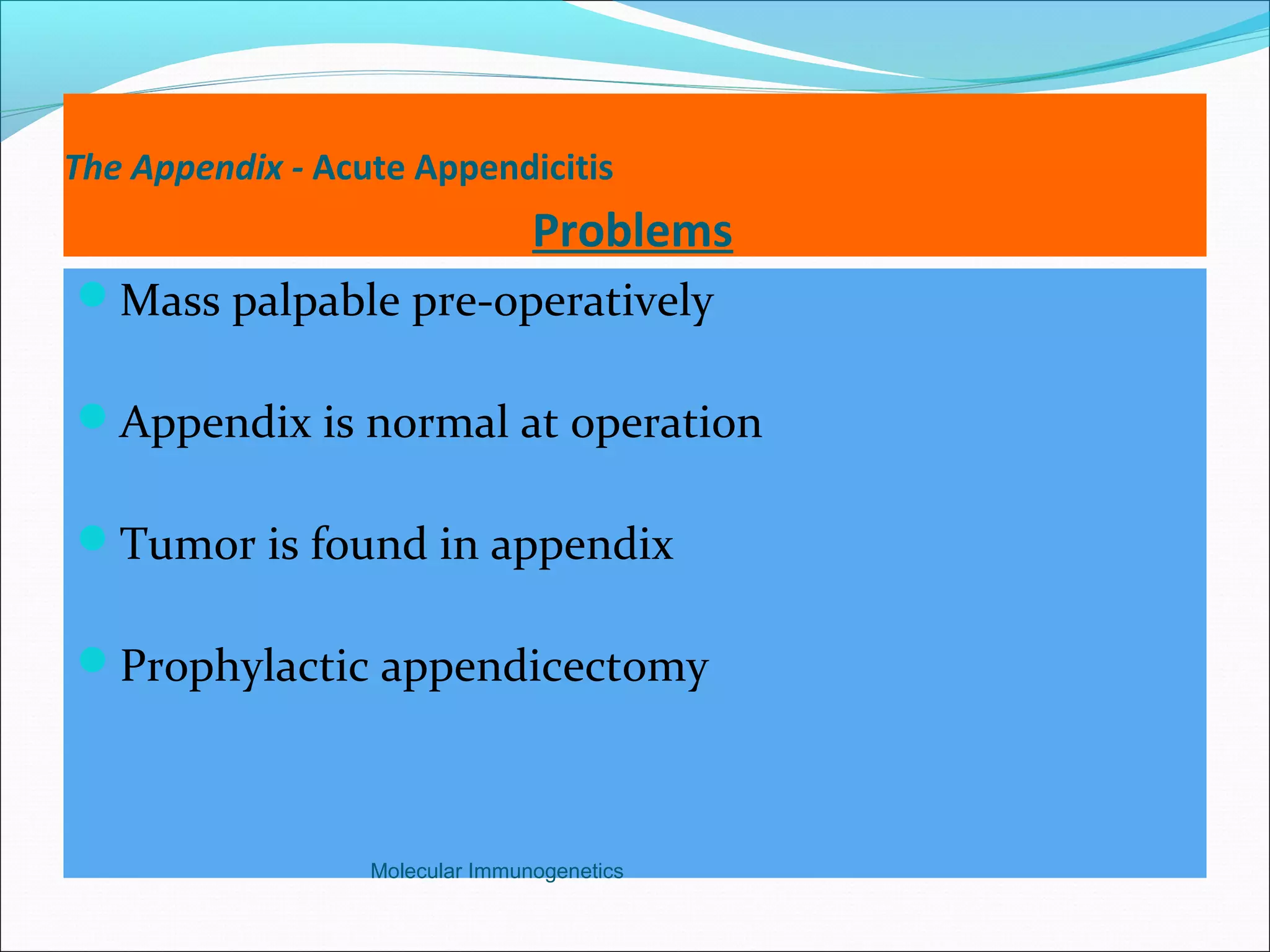
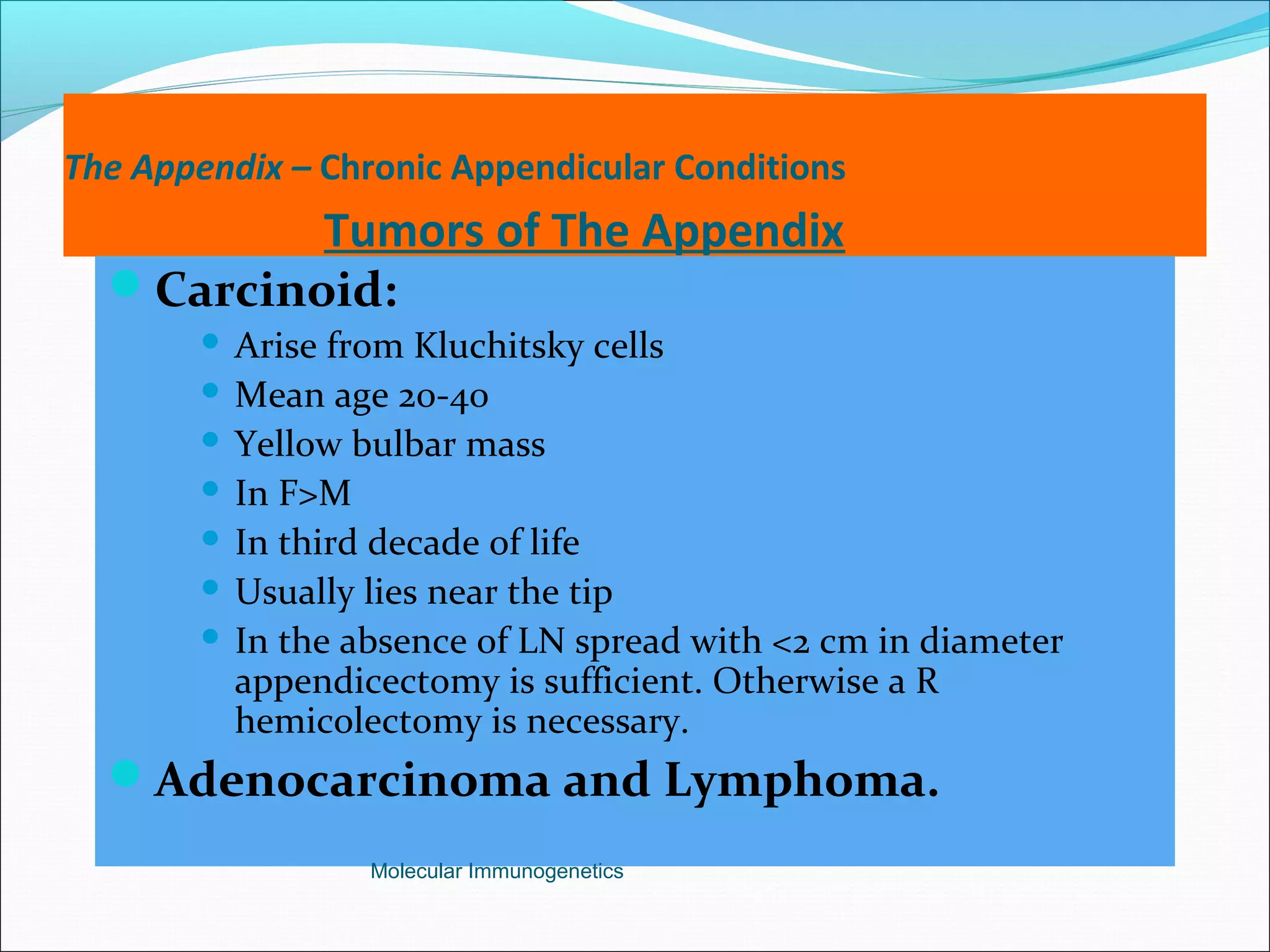
The document discusses the anatomy, development, function, and clinical presentation of appendicitis of the appendix. It describes the appendix as a thin tube located in the lower right abdomen that develops from the cecum and contains lymphoid tissue. While its function was originally unknown, it is now believed to play a role in immune function as lymphoid tissue accumulates after birth, exposing white blood cells to antigens from the gastrointestinal tract. Acute appendicitis occurs when the appendix becomes blocked and infected, most commonly from lymphoid hyperplasia or fecaliths. Clinical features include abdominal pain that localizes to the right lower quadrant along with nausea, vomiting, and fever. Diagnosis involves examination