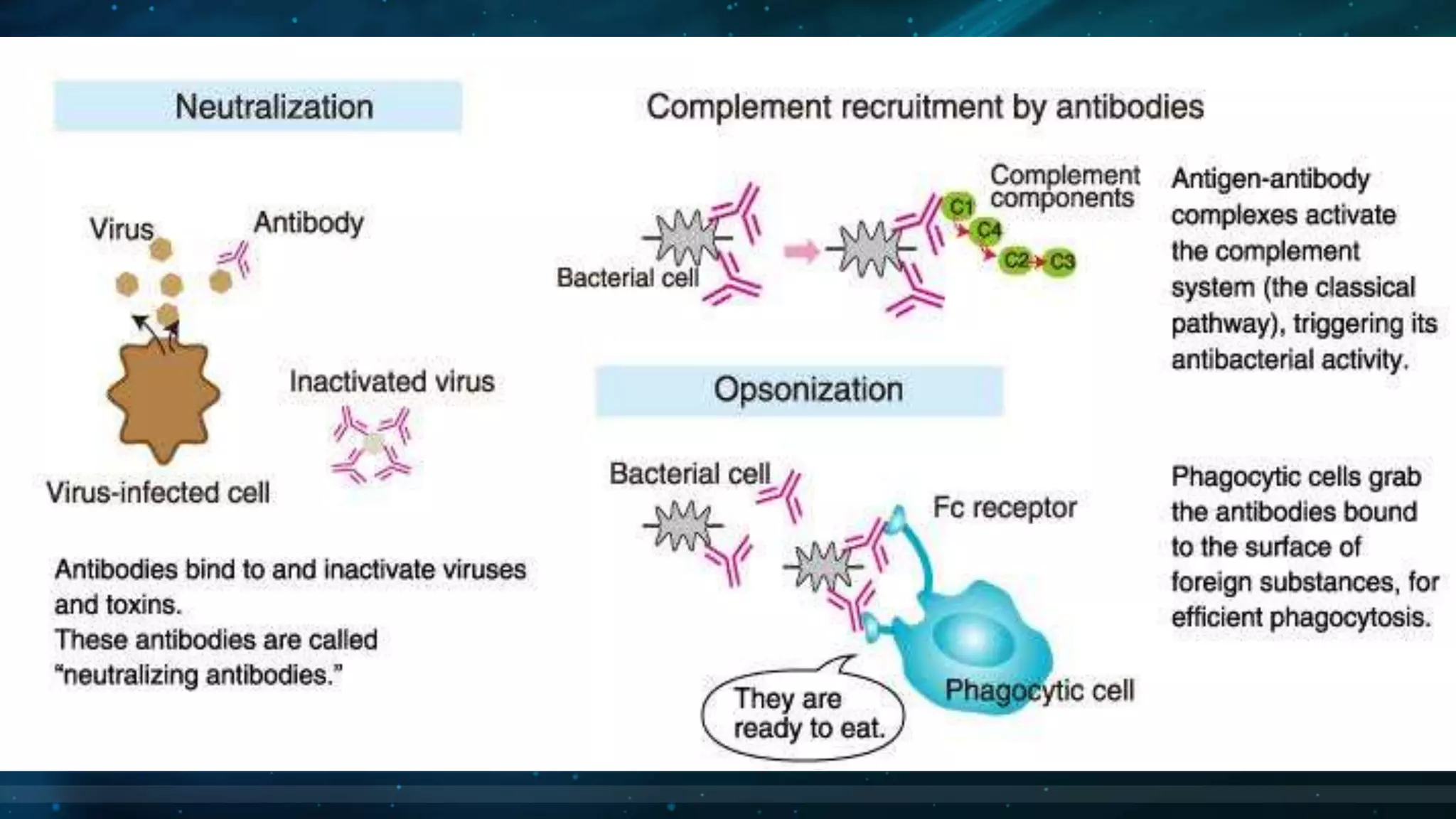
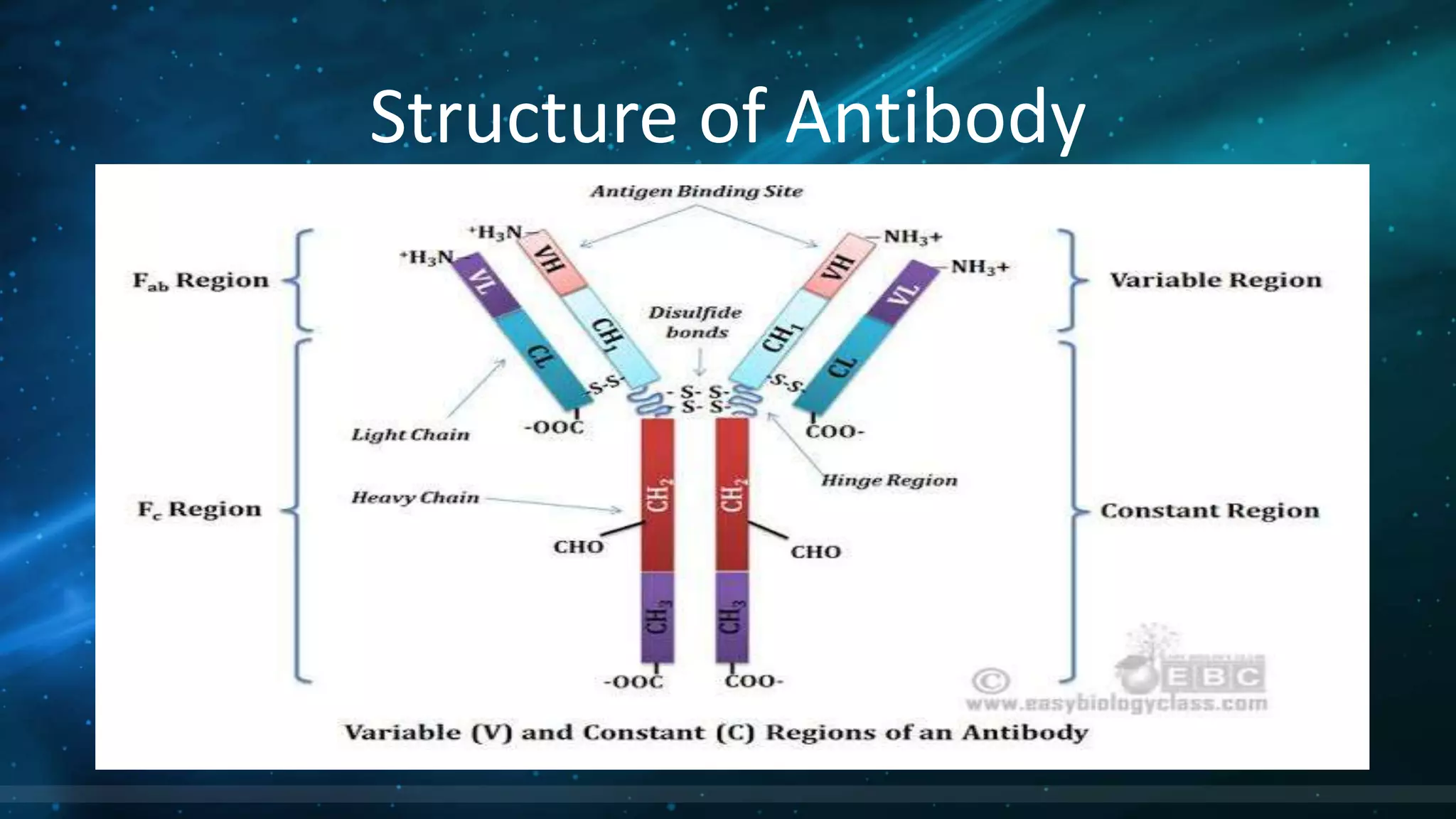
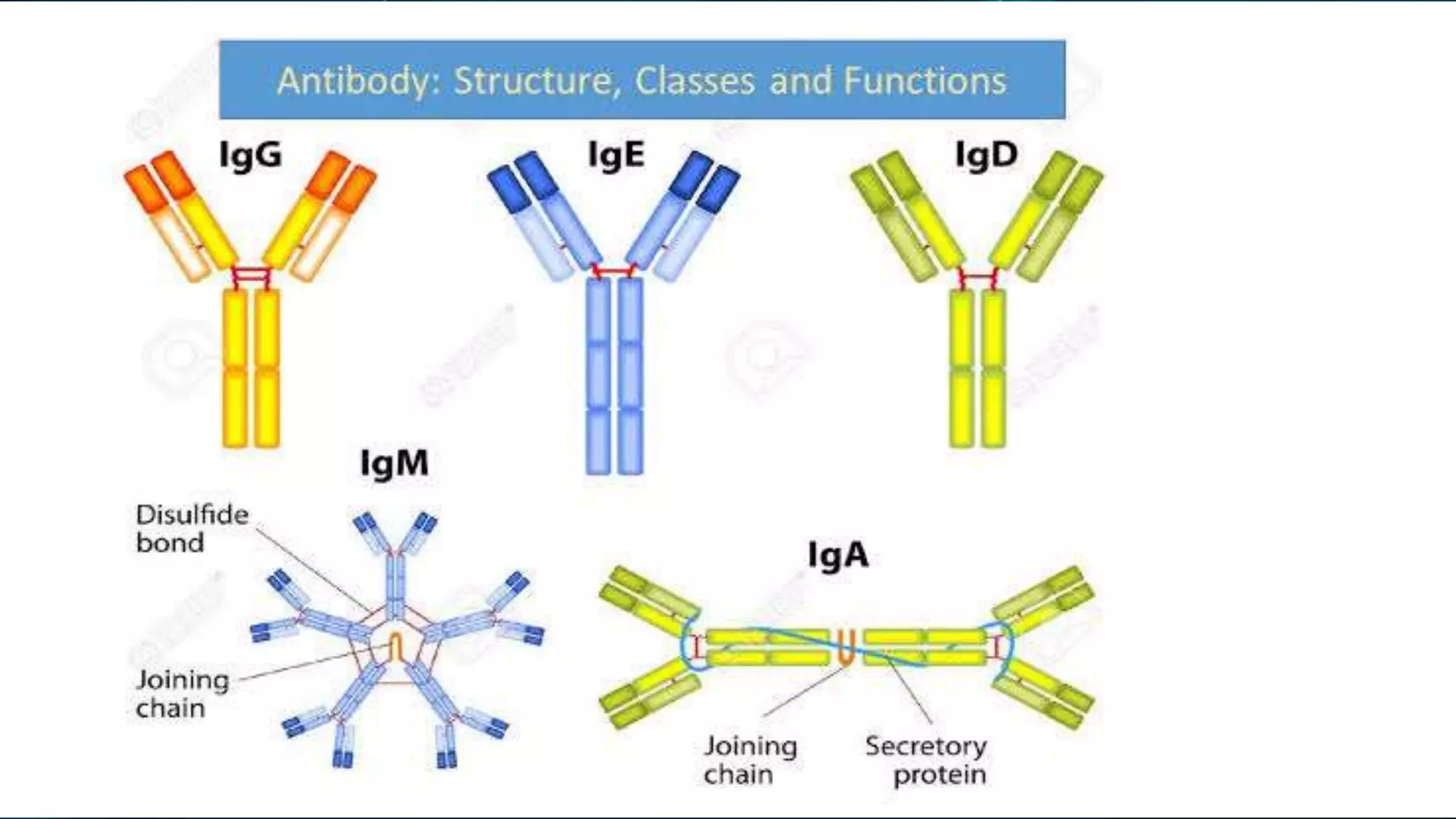
This document summarizes the main types of antibodies (immunoglobulins). It discusses the structure of antibodies, which consist of two heavy chains and two light chains arranged in a Y-shape. Antibodies are classified based on their heavy chain type, with the main types being IgG, IgA, IgM, IgE, and IgD. Each antibody type serves a different function, such as IgG being the most common antibody in serum and IgA providing defense in external secretions like breast milk. In summary, the document outlines the structure of antibodies and classifies the main antibody types while briefly describing their functions in the immune system.