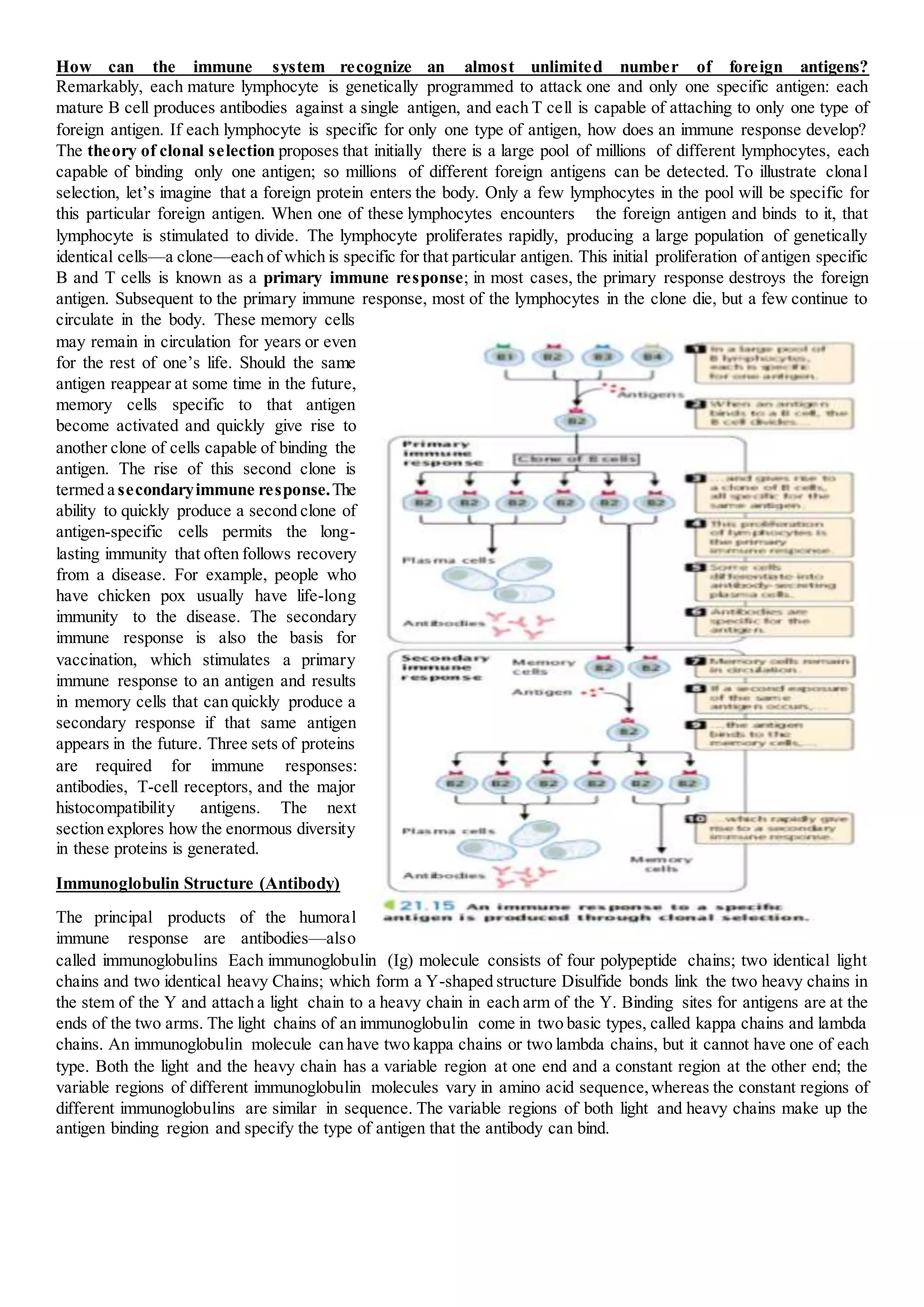
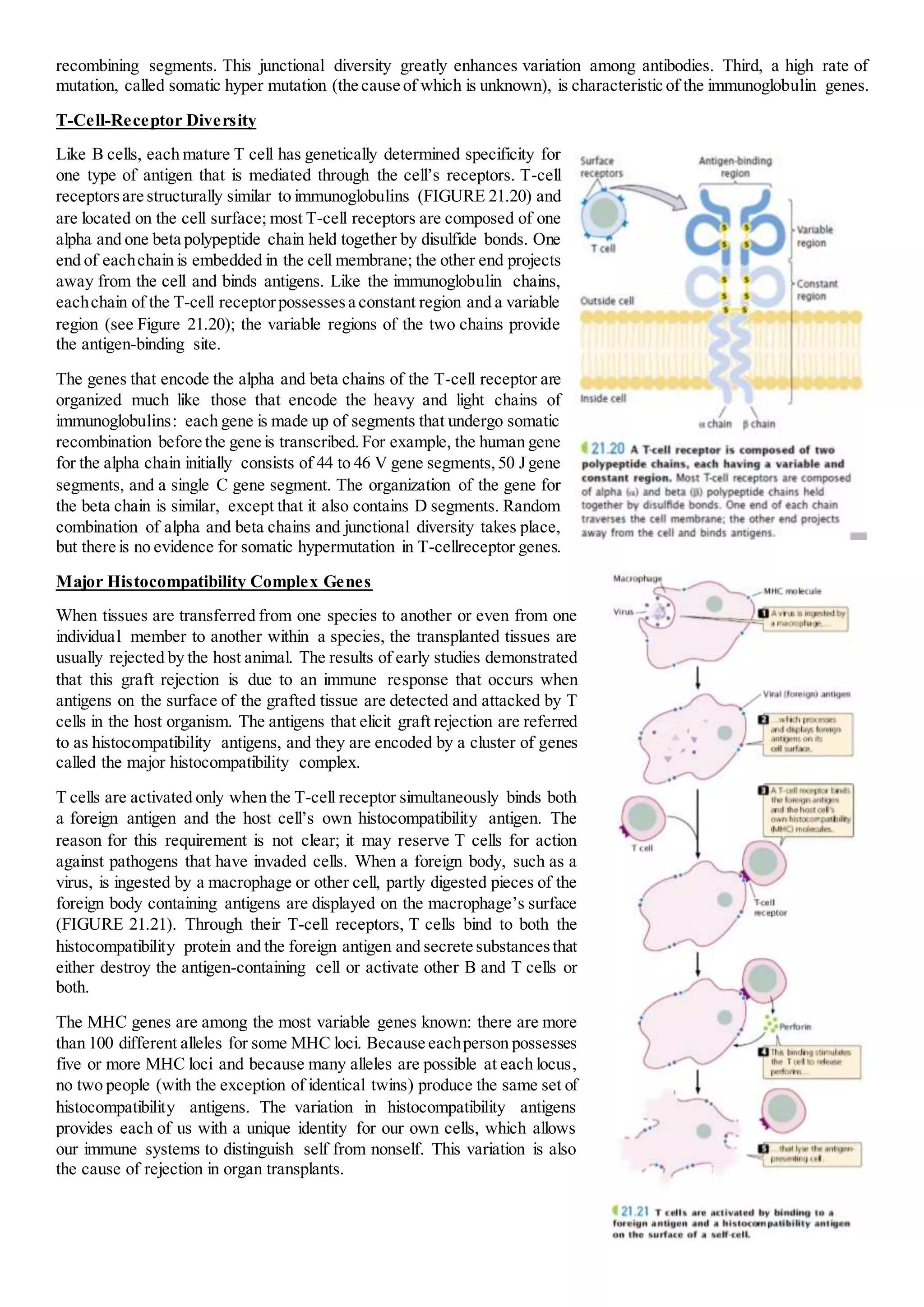
The immune system provides protection against infection through humoral and cellular immunity. Humoral immunity involves antibodies produced by B cells that bind to antigens. Cellular immunity is mediated by T cells that respond to antigens on host cells and mark infected cells for destruction. The immune system has the ability to recognize an almost unlimited number of antigens through clonal selection, where antigen exposure stimulates proliferation of antigen-specific lymphocytes. Memory cells generated during primary responses allow for rapid secondary responses against the same antigen. Antibody diversity is generated through somatic recombination of gene segments during B cell development.