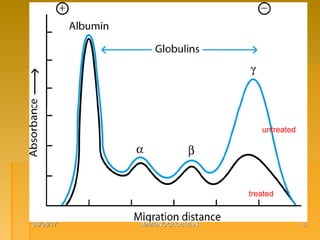
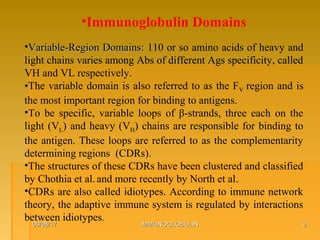
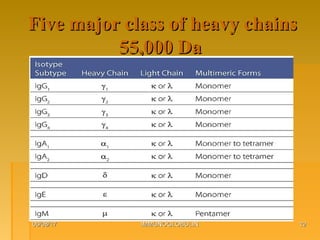
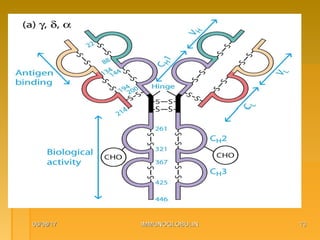
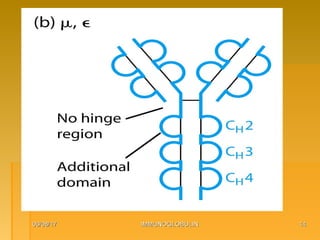
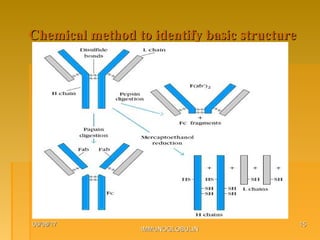
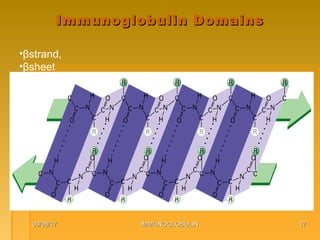
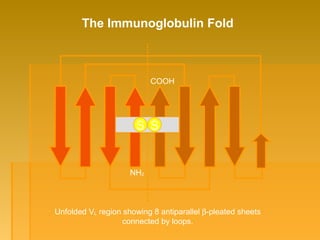
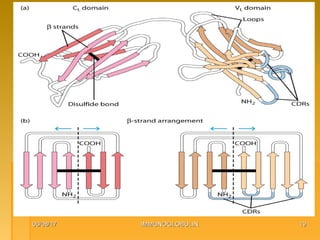
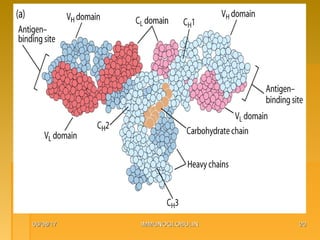
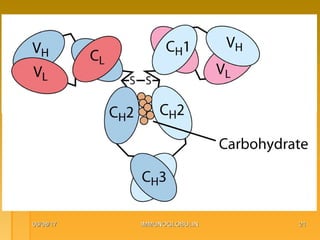
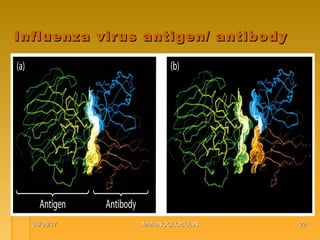
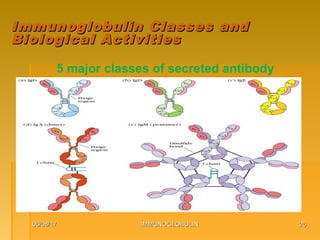
This document focuses on the structure and function of immunoglobulins (antibodies), detailing their glycoprotein composition, chain structure, and regions responsible for antigen binding. It explains the classification of immunoglobulins, the significance of their constant and variable regions, and their effector functions. The presentation also highlights historical experiments that led to the identification of immunoglobulins and their role in the immune response.