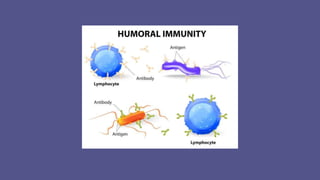
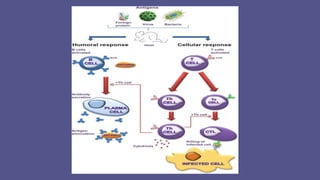
Immunity is the body's ability to defend against foreign pathogens, categorized into innate and acquired immunity. Innate immunity is the natural, first line of defense activated immediately upon infection, while acquired immunity develops post-birth through exposure to antigens. Acquired immunity includes humoral immunity, mediated by antibodies from B cells, and cellular immunity, involving T-helper cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes.