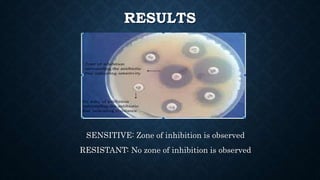
The document discusses the antibiotic sensitivity test, aiming to determine the efficacy of antibiotics against bacterial pathogens using methods like the Kirby-Bauer test. This test assesses the growth inhibition of bacteria through zones of inhibition after antibiotic disks are placed on agar plates. It highlights the advantages, such as low cost and ease of use, along with certain limitations regarding the testing of specific slow or fastidious organisms.