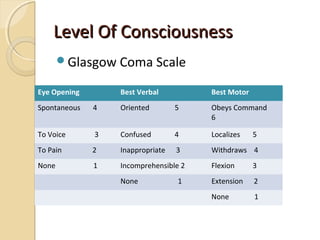
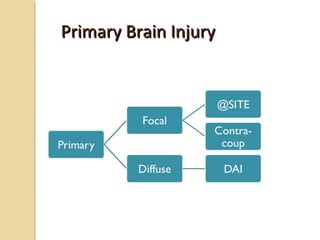
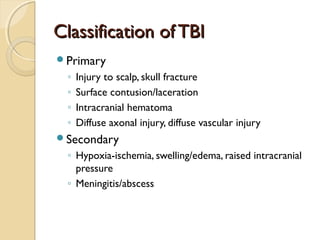
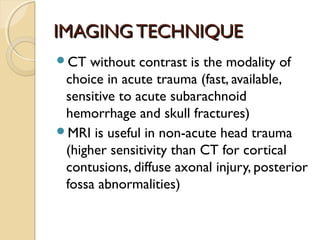
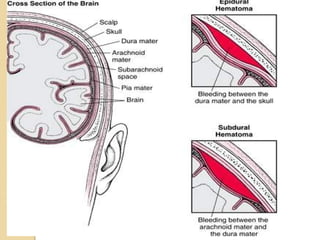
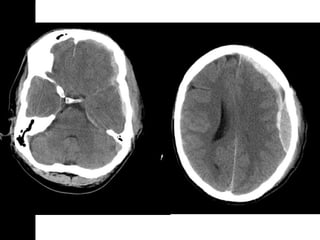
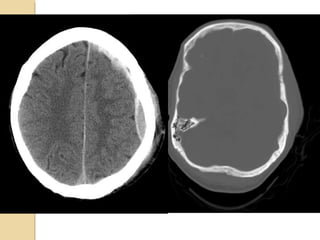
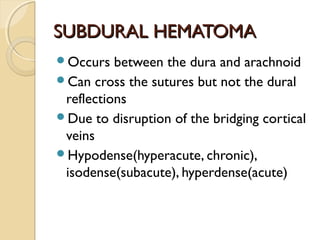
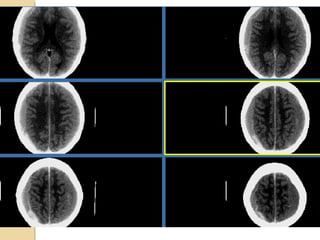
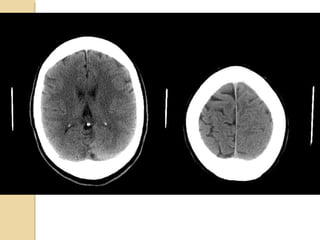
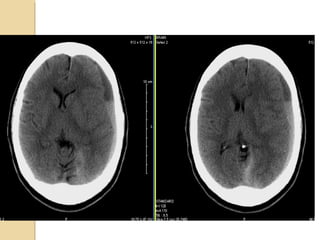
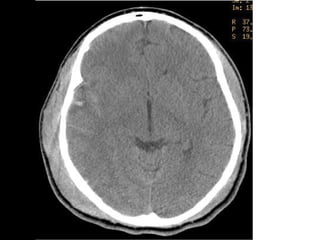
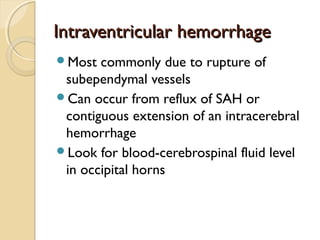
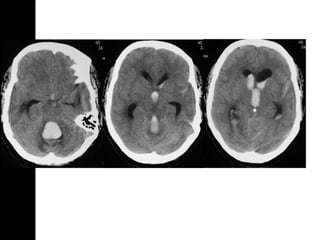
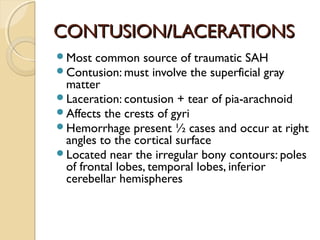
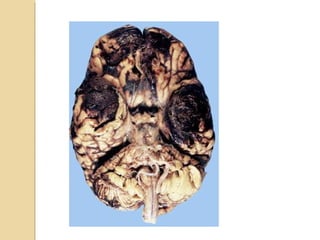
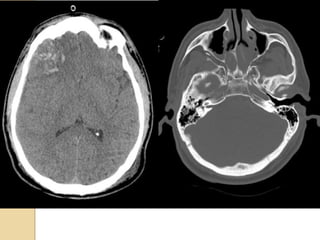
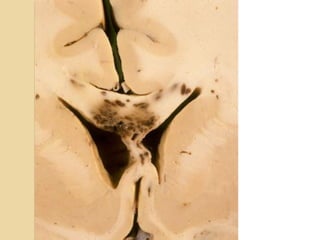
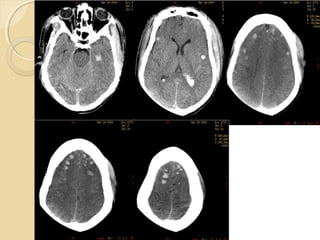
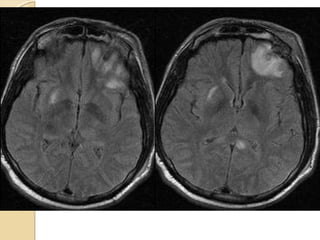
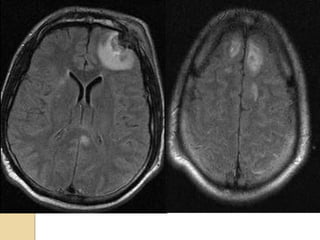
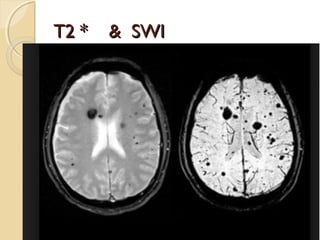
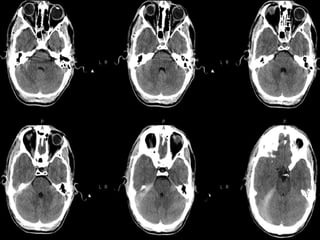
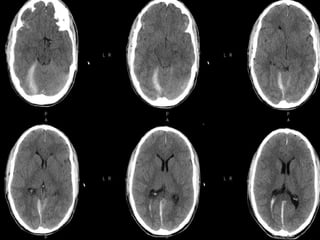
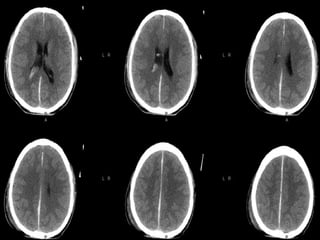
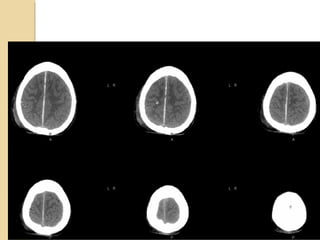
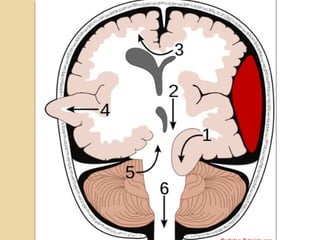
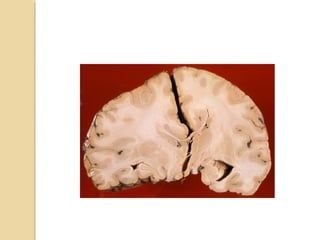
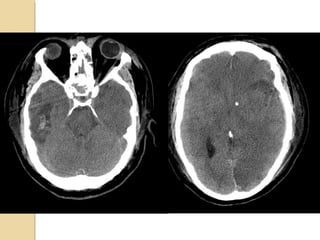
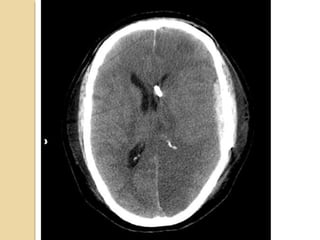
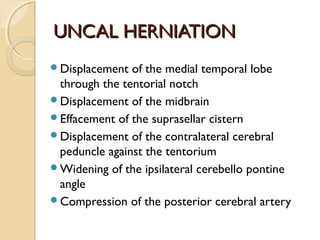
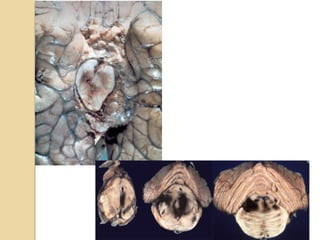
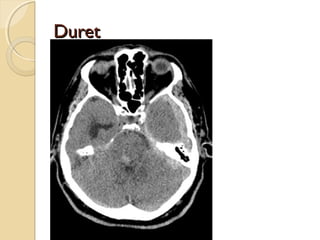
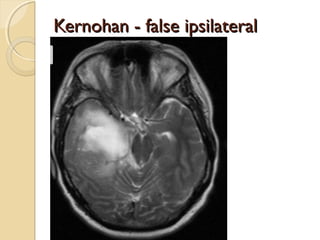
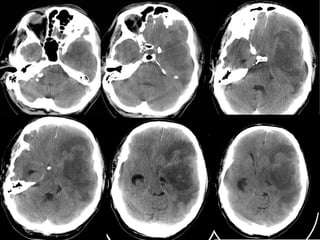
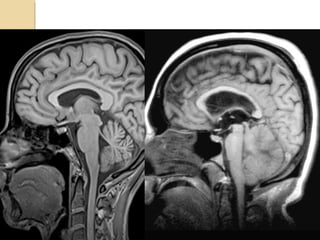
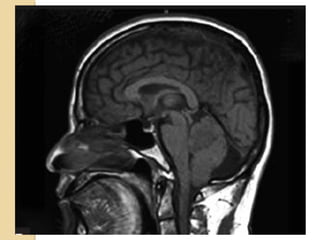
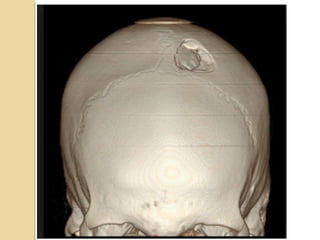
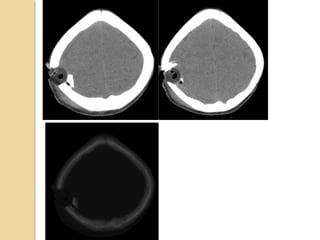
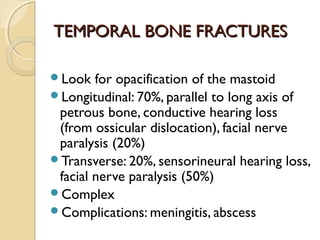
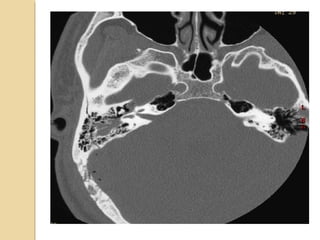
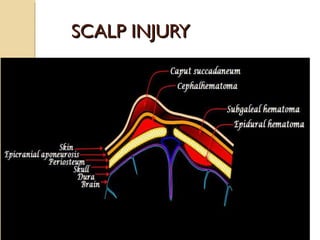
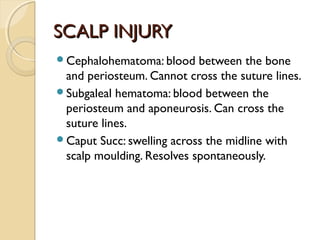
Brain imaging is important in trauma to identify injuries from primary impact and secondary complications. CT is best for acute trauma to detect fractures and hemorrhages while MRI is more sensitive for diffuse injuries. Common primary injuries seen include fractures, contusions, hematomas, shearing injuries and hemorrhages in various locations. Secondary complications can include swelling, infection and herniations putting pressure on vessels.