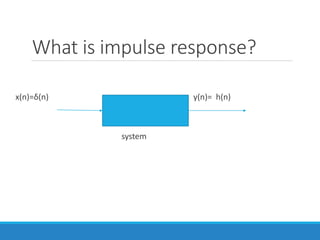
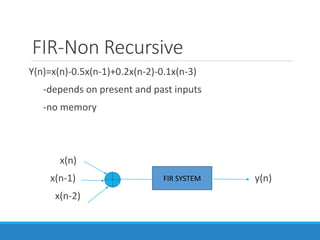
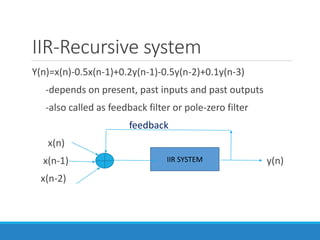
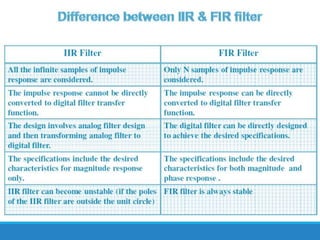
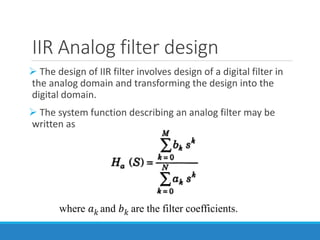
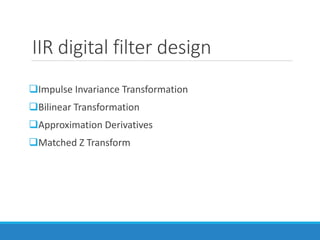
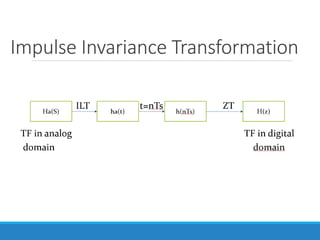
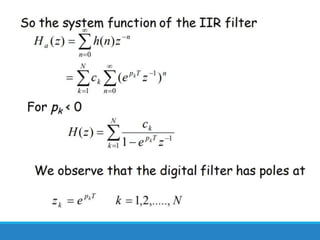
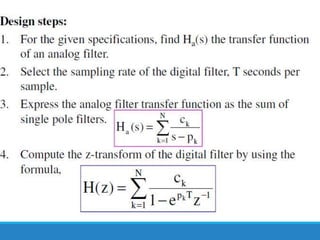
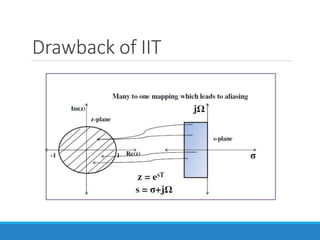
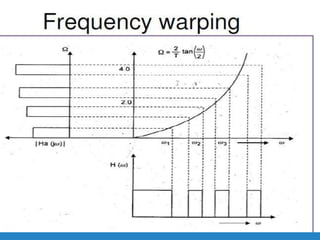
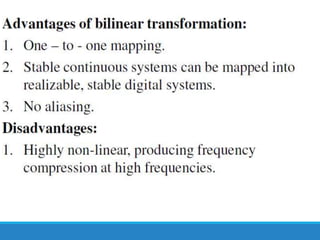
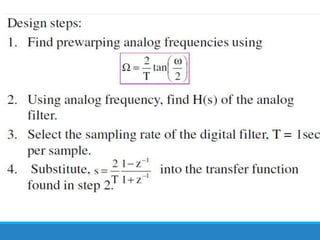
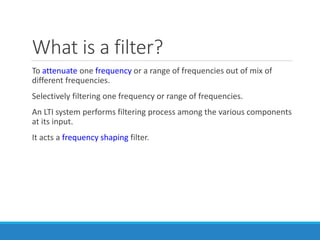
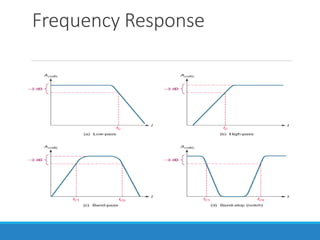
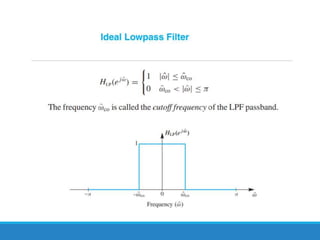
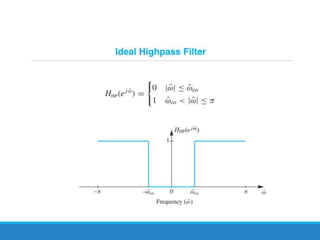
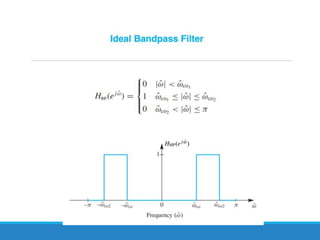
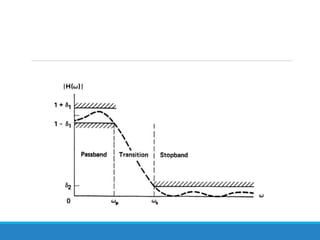
Filters selectively attenuate certain frequency ranges in a signal. They are used widely in electronics, telecommunications, audio/video, and other applications. Filters are classified as analog or digital depending on the signal type. Ideal filters have constant gain in the passband and zero gain in the stopband with linear phase, but practical filters have variable gain and non-zero/non-linear characteristics. Digital filters are further divided into finite impulse response (FIR) filters, which depend only on past inputs, and infinite impulse response (IIR) filters, which are recursive and depend on both past inputs and outputs. IIR filters are designed by first designing an analog filter prototype and transforming it to the digital domain using techniques like impulse invari






![Classification of Digital Filters
FIR-Finite Impulse Response
-impulse response h(n) is of finite duration
Eg: h(n)={1,2,3,4}
IIR-Infinite Impulse Response
-impulse response h(n) is of infinite duration
Eg: h(n)=[(1/2)^n -(0.1)^n]u(n)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unitiiintroduction-220106101519/85/IIR-filter-14-320.jpg)