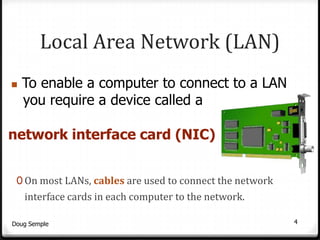
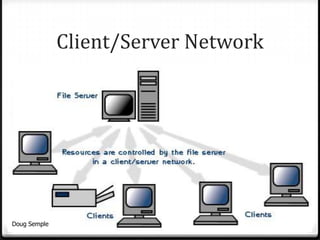
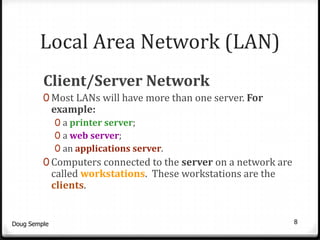
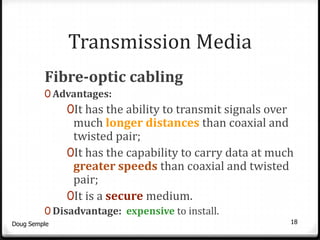
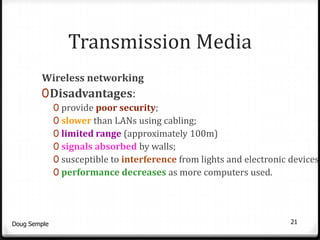
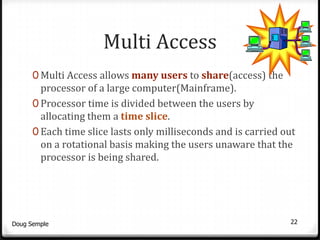
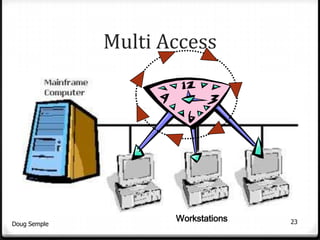
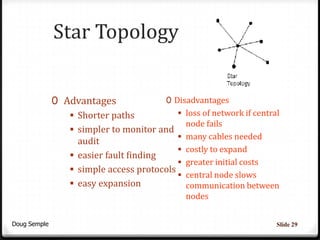
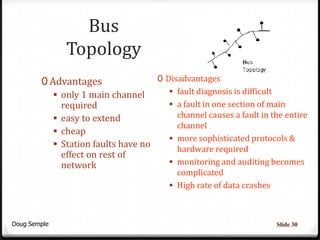
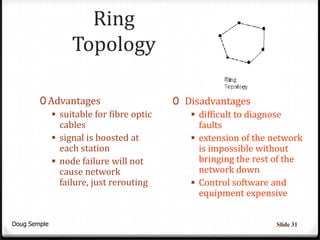
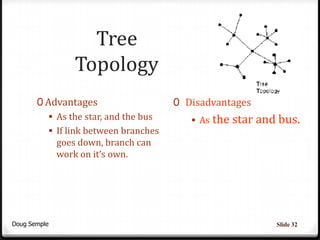
A network connects two or more computers together to share resources. Computers on a network can be connected through cables, phone lines, wireless connections or other methods. A local area network (LAN) connects computers within a small area like a building through cables or wireless connections. Each computer needs a network interface card to connect to the LAN. Most LANs use a powerful server computer that stores shared files and software and controls the network, while other computers that access these resources are called clients.