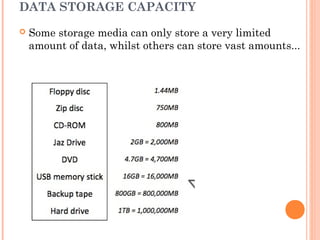
This document discusses various types of data storage media and devices. It begins by defining data storage as putting data in a known location that it can later be retrieved from. Main memory (RAM) is used for temporary storage while processing, while backing storage like hard drives is for long-term storage. Storage media physically holds the data, while storage devices read and write to the media. Access speeds and storage capacities vary greatly across devices. Examples discussed include hard drives, optical discs, magnetic tapes, flash memory cards, and solid state drives. The purpose of backups is to create copies of important data to protect against loss from hardware failure or human error.