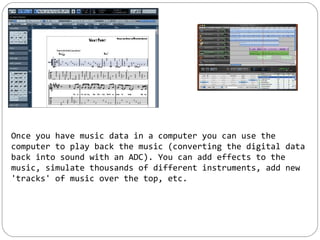
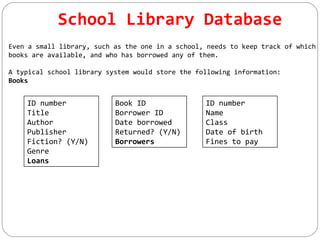
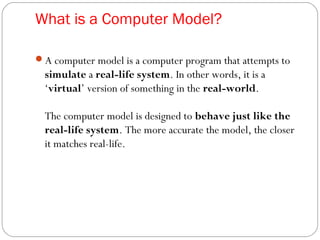
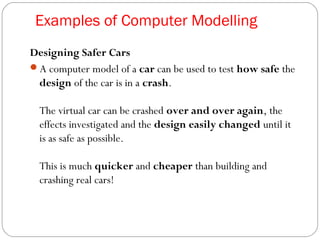
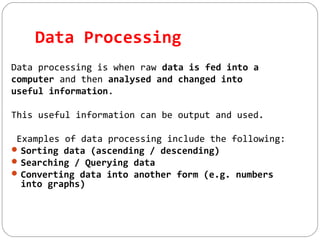
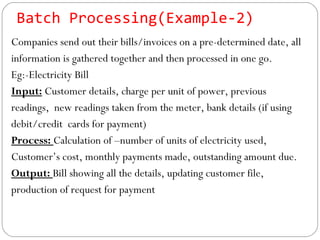
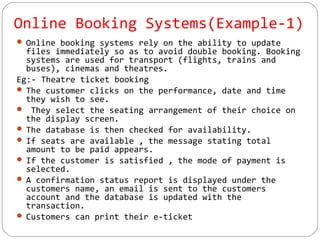
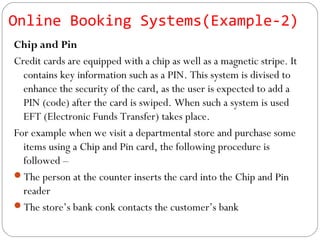
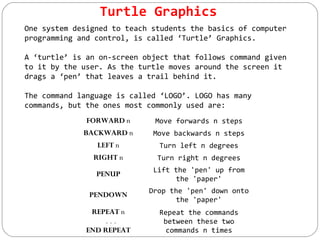
This document discusses various ways that ICT is used, including communicating ideas through websites and multimedia, producing and editing pictures, desktop publishing, website design, and interactive communication. It also covers using computers to keep records like address books, club memberships, surveys, and school reports. Other uses of ICT discussed are computer modeling, data logging, electronic fund transfers, using ATMs, electronic payments, and internet banking.


































![Chapter 7 the ways-in_which_is_ict_is_used[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-thewaysinwhichisictisused1-140526103116-phpapp02/85/Chapter-7-the-ways-in_which_is_ict_is_used-1-47-320.jpg)
![Chapter 7 the ways-in_which_is_ict_is_used[1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter7-thewaysinwhichisictisused1-140526103116-phpapp02/85/Chapter-7-the-ways-in_which_is_ict_is_used-1-48-320.jpg)