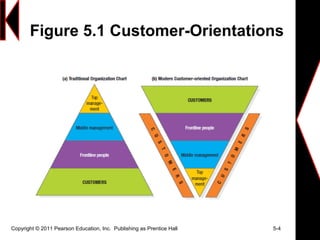
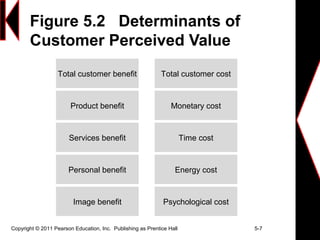
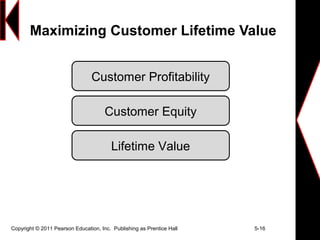
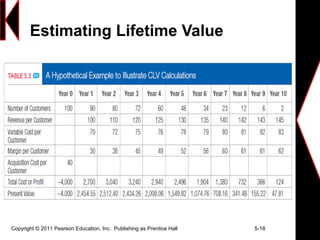
This document discusses creating long-term loyalty relationships with customers. It defines key concepts like customer value, satisfaction and loyalty. It also discusses how companies can maximize customer lifetime value and attract and retain customers through customer relationship management programs and databases. Specific strategies highlighted include identifying customer needs, customizing interactions, reducing defection rates and focusing efforts on high-value customers.