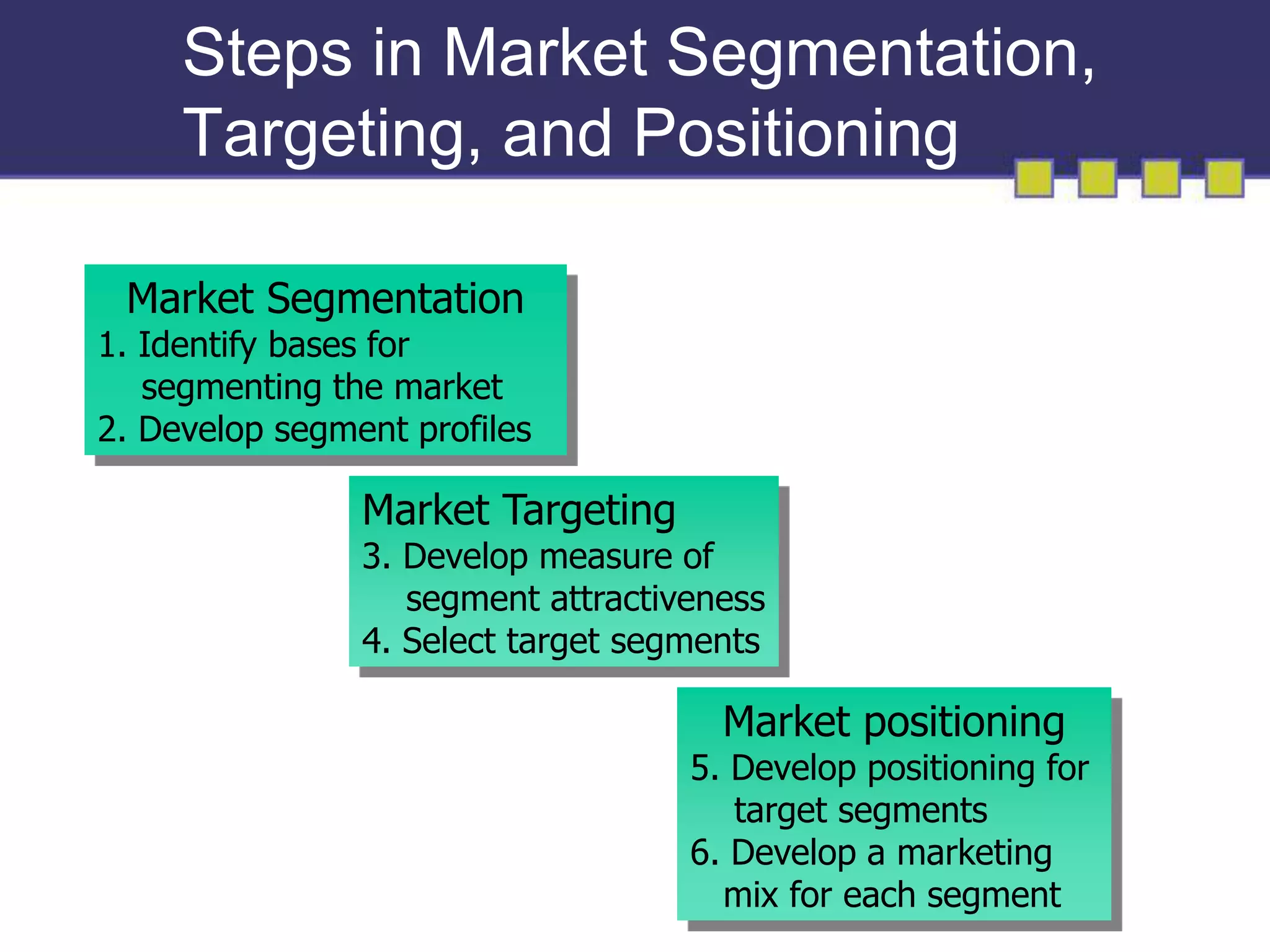
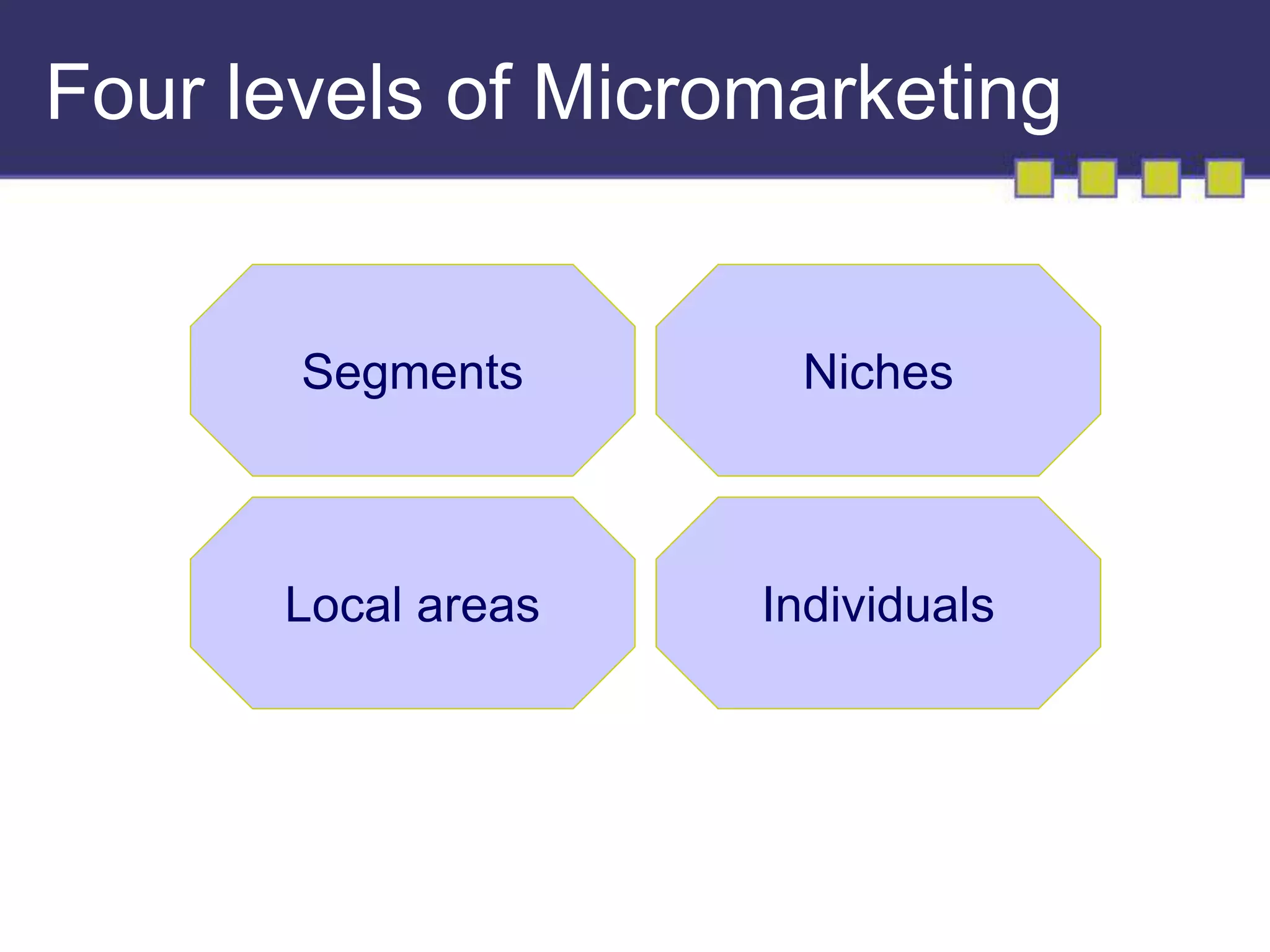
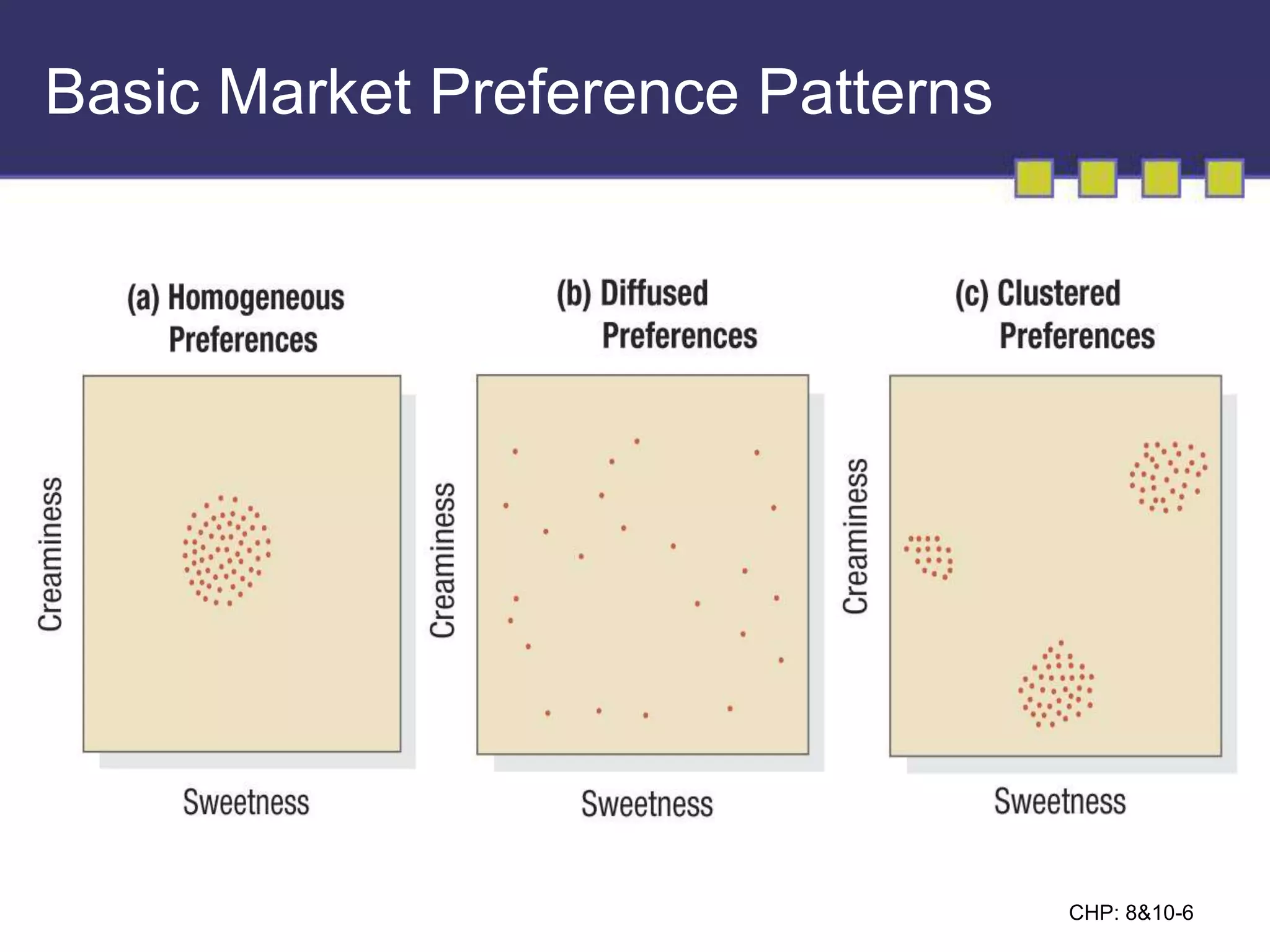
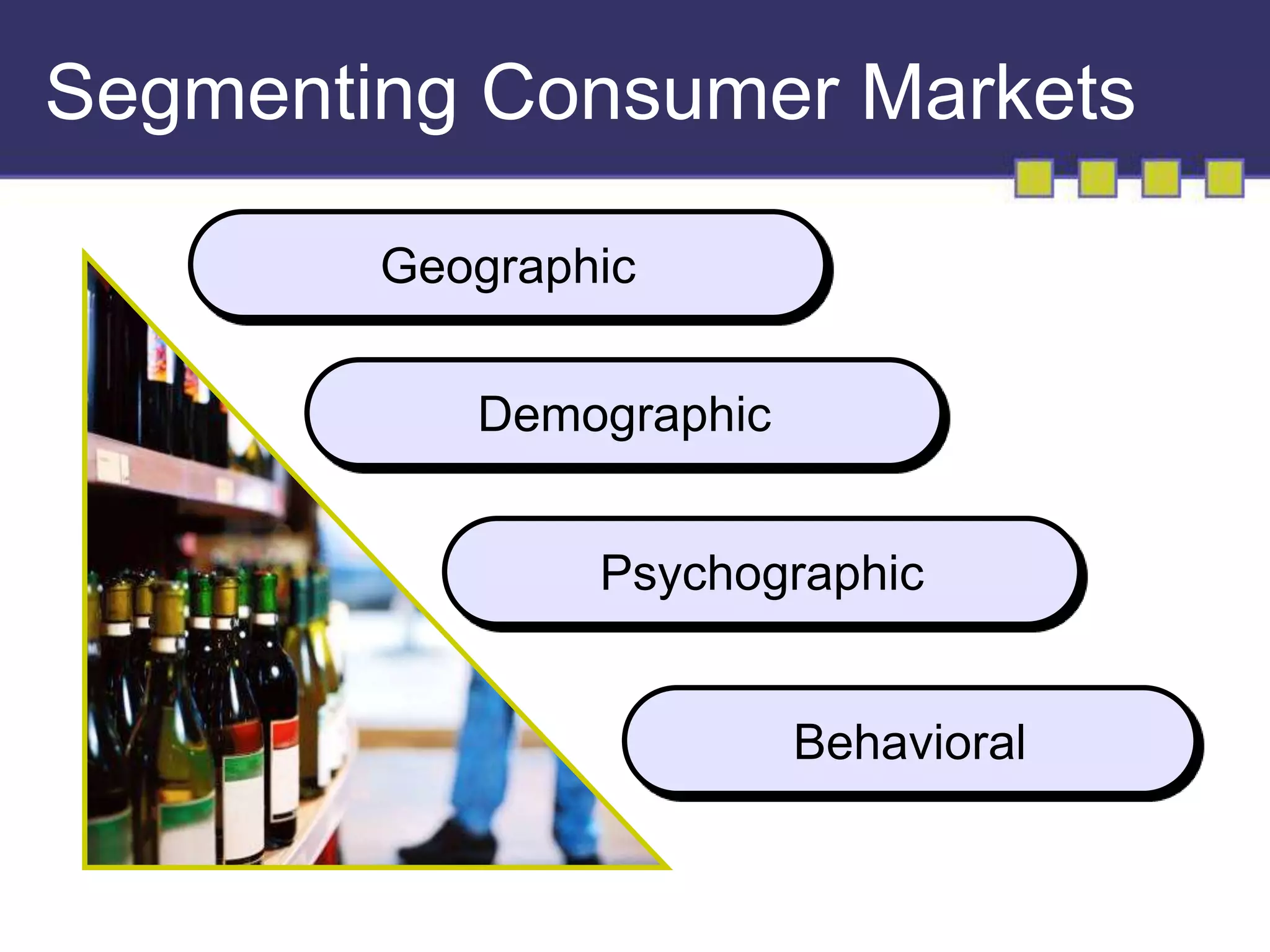
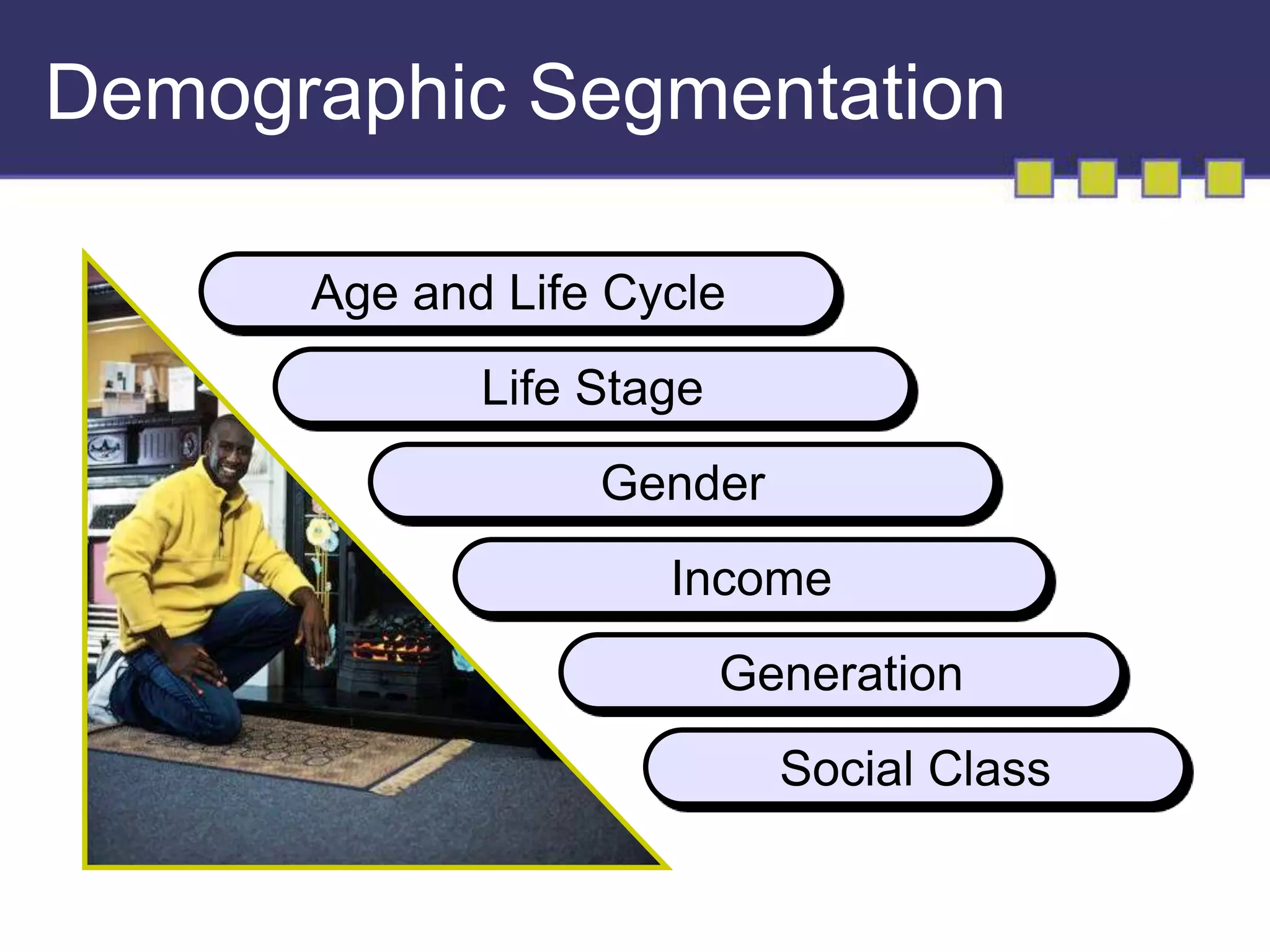
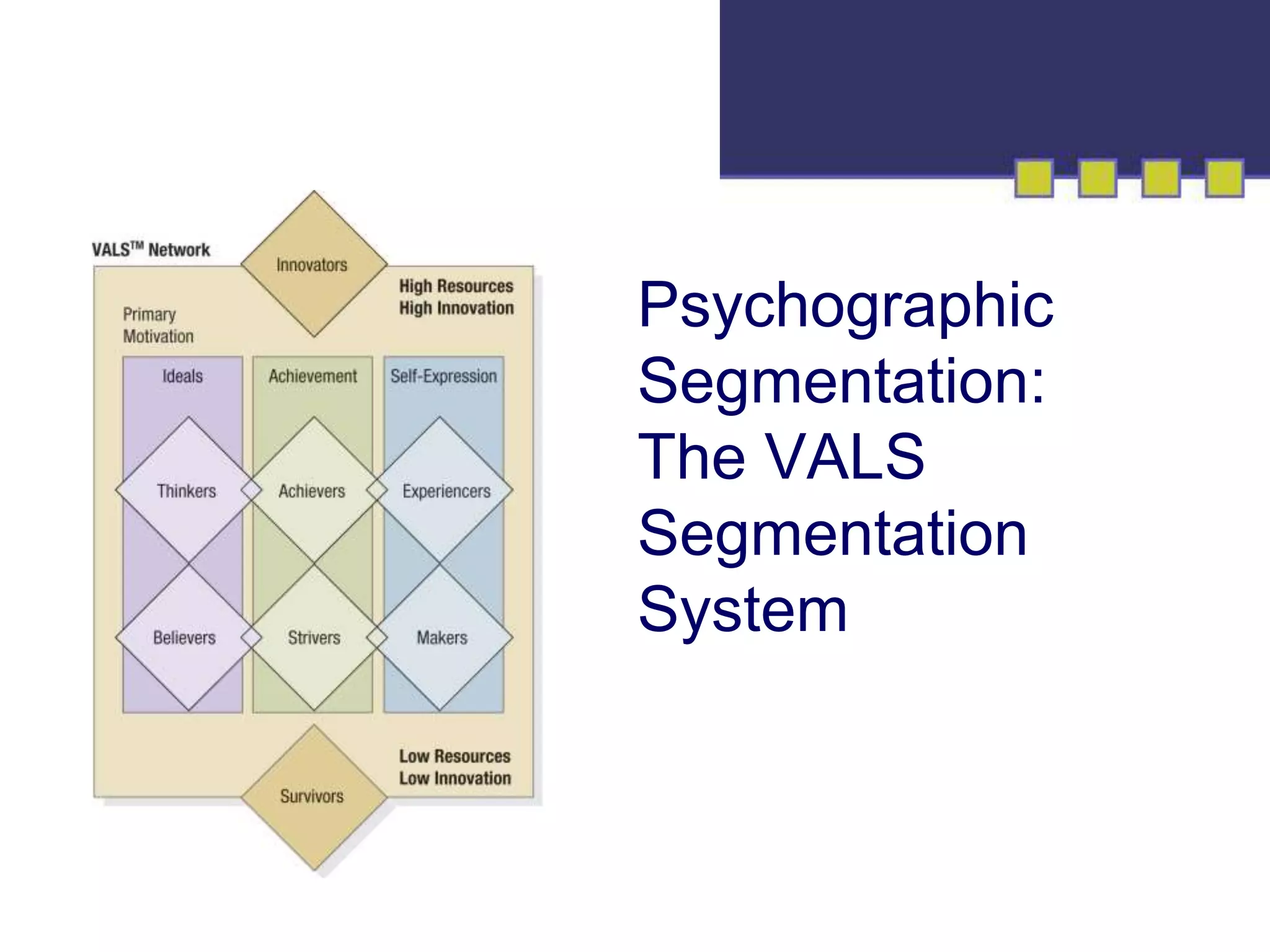
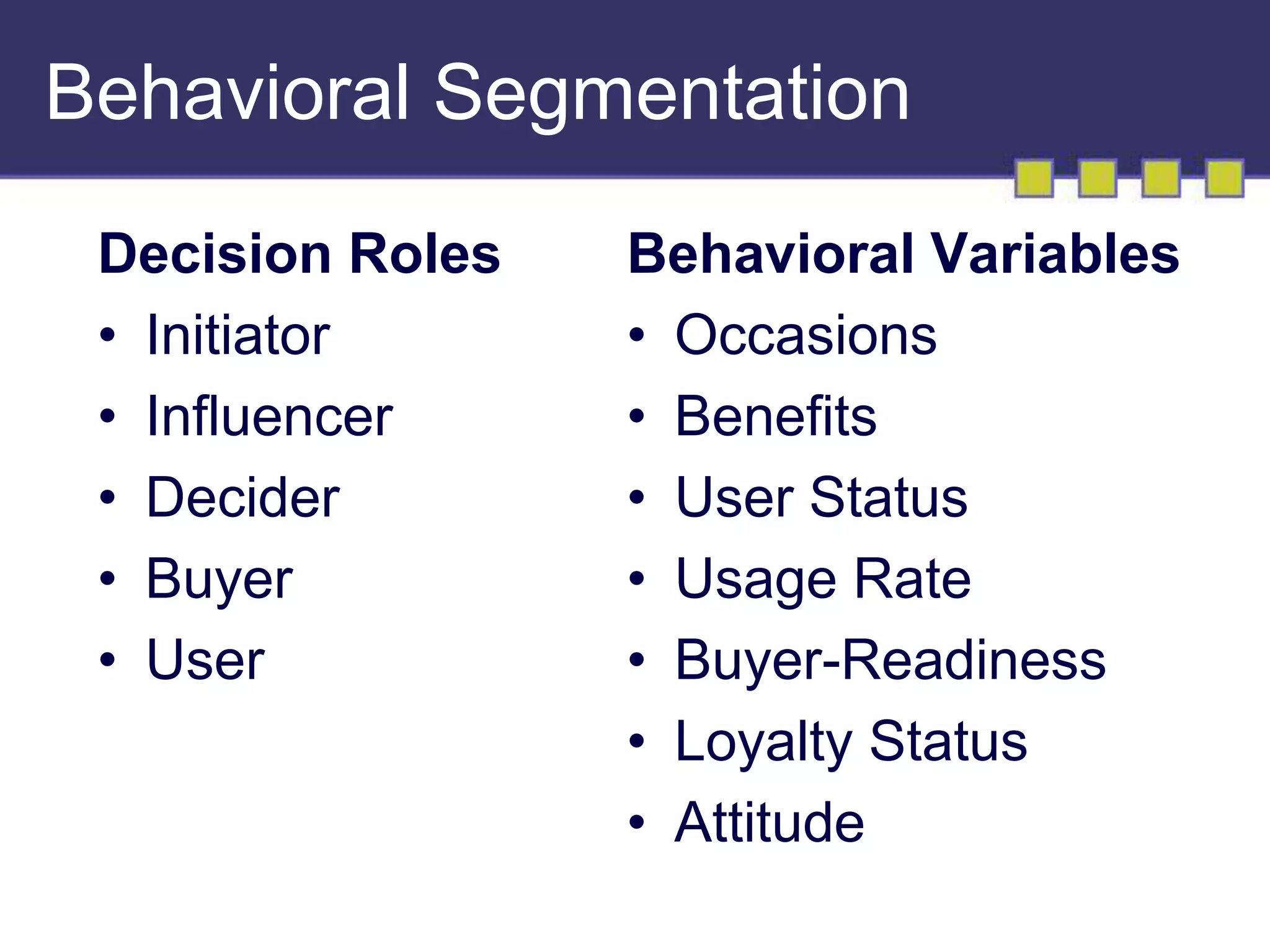
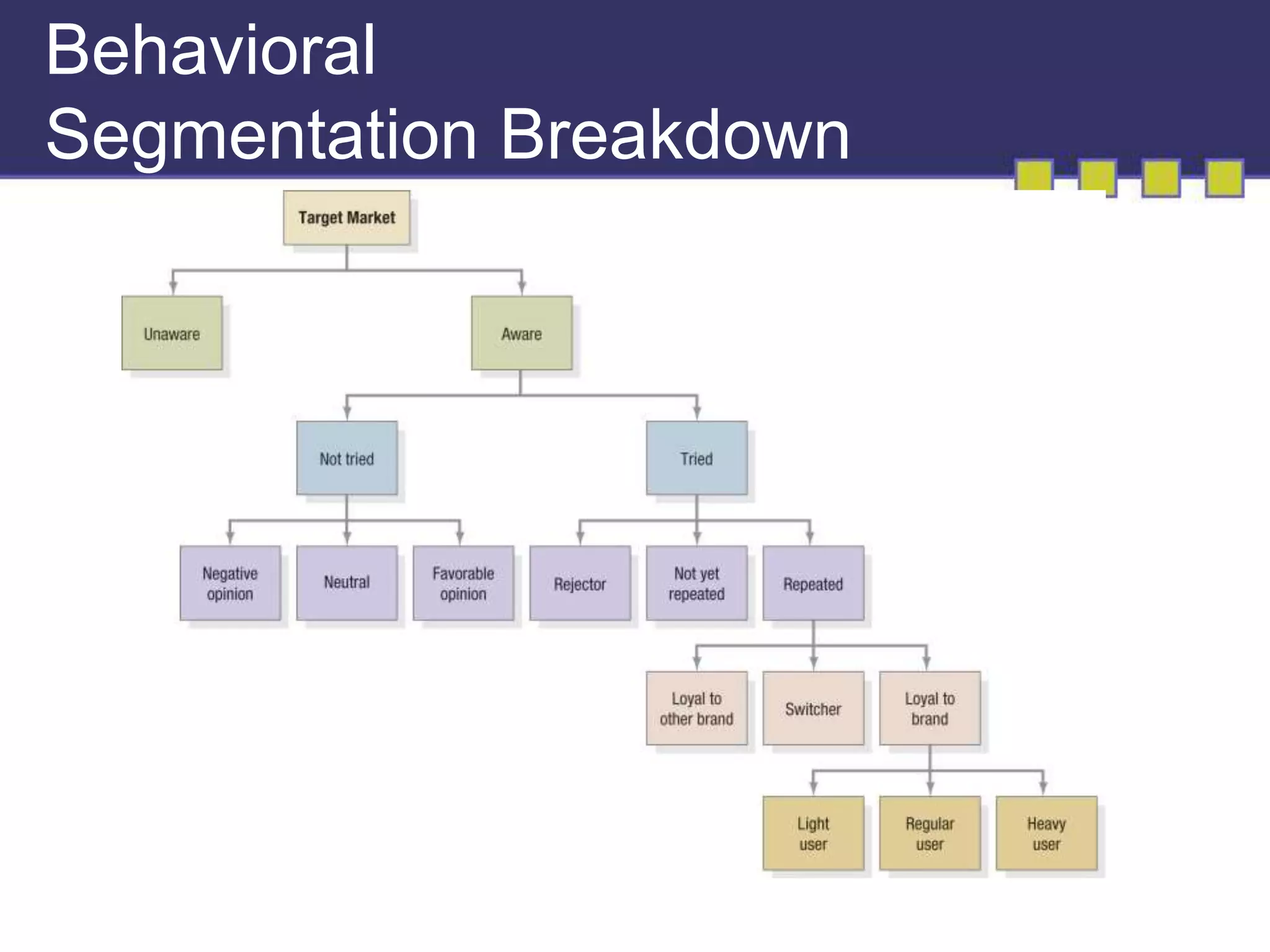
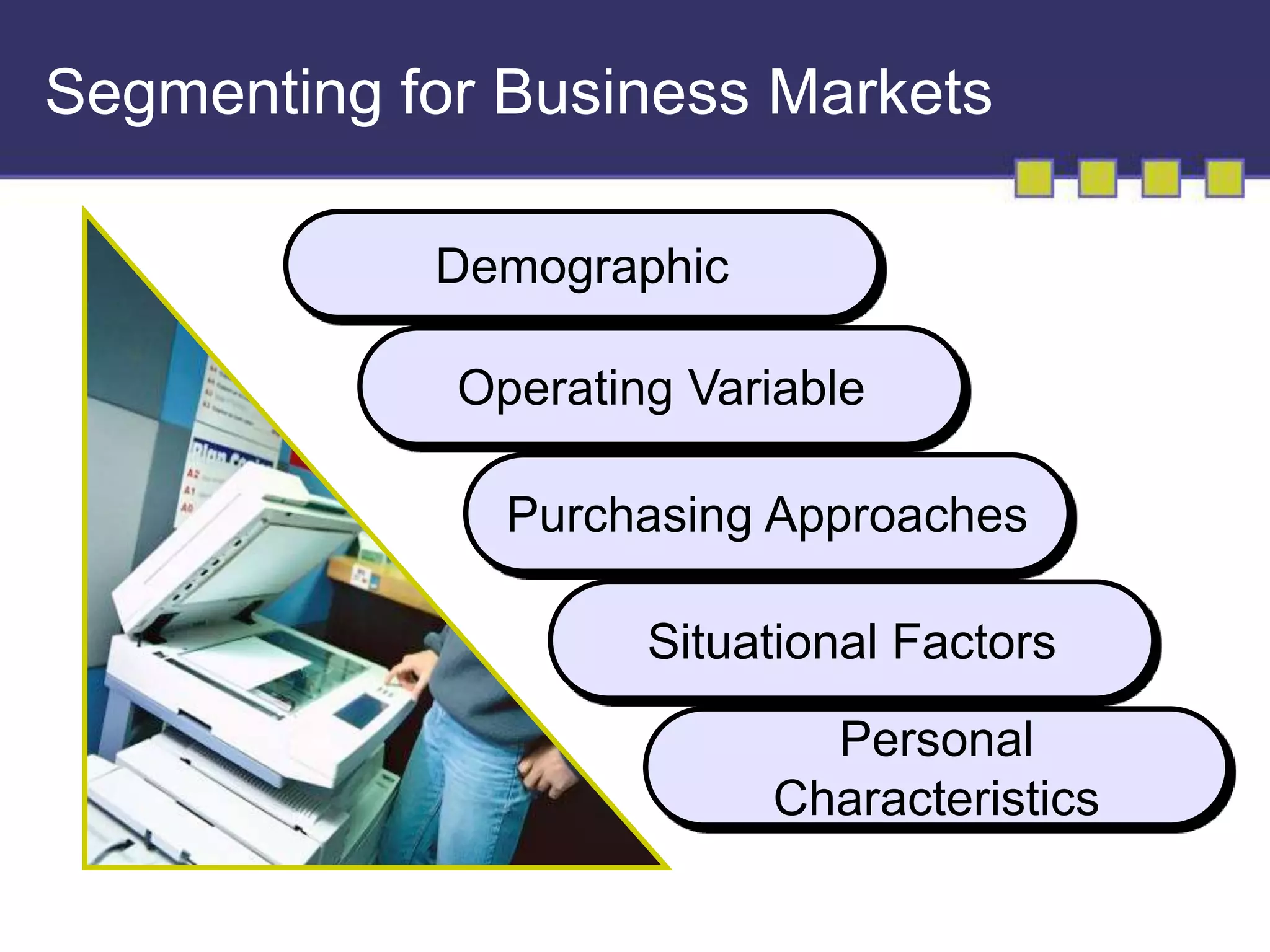
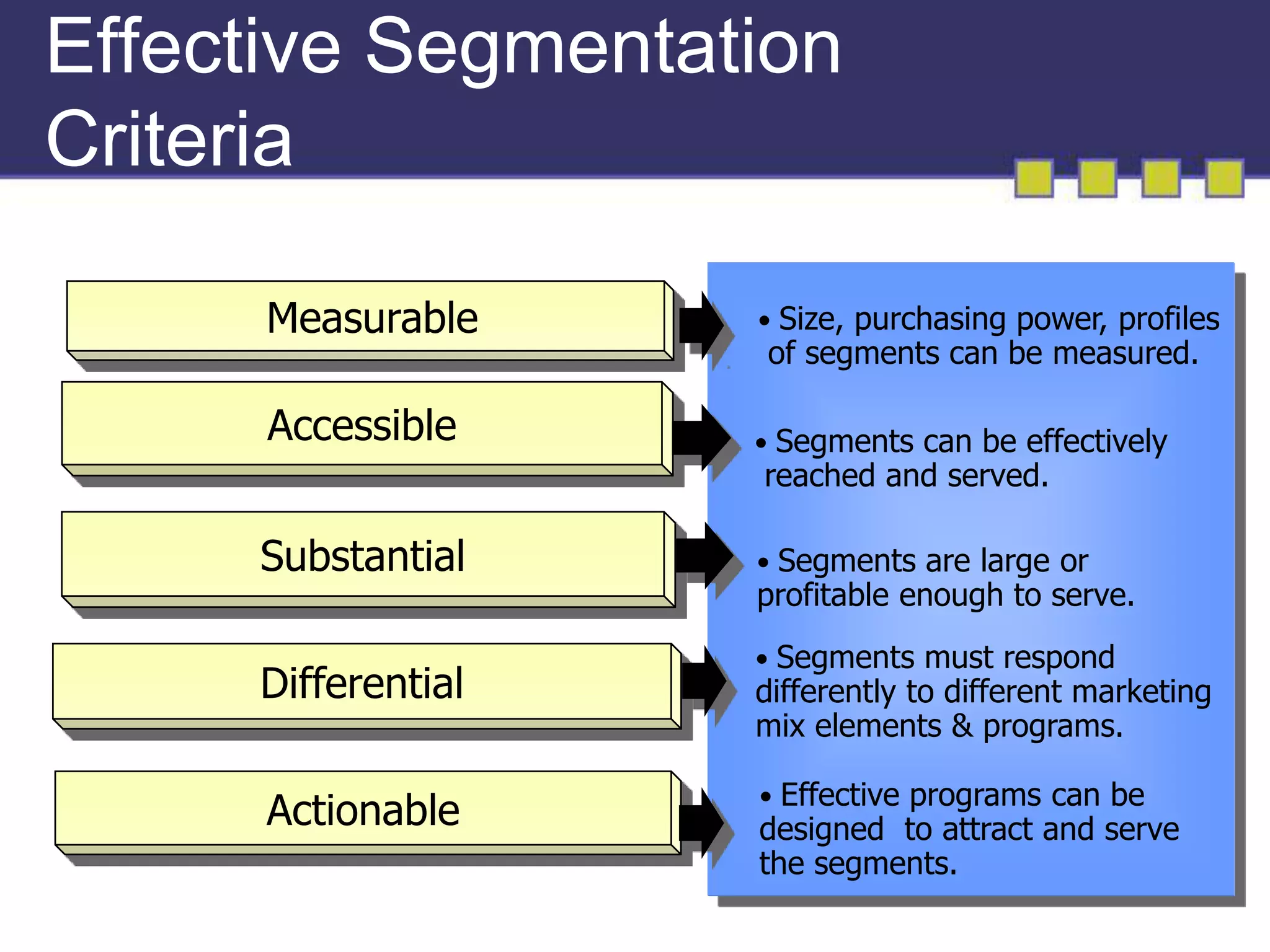
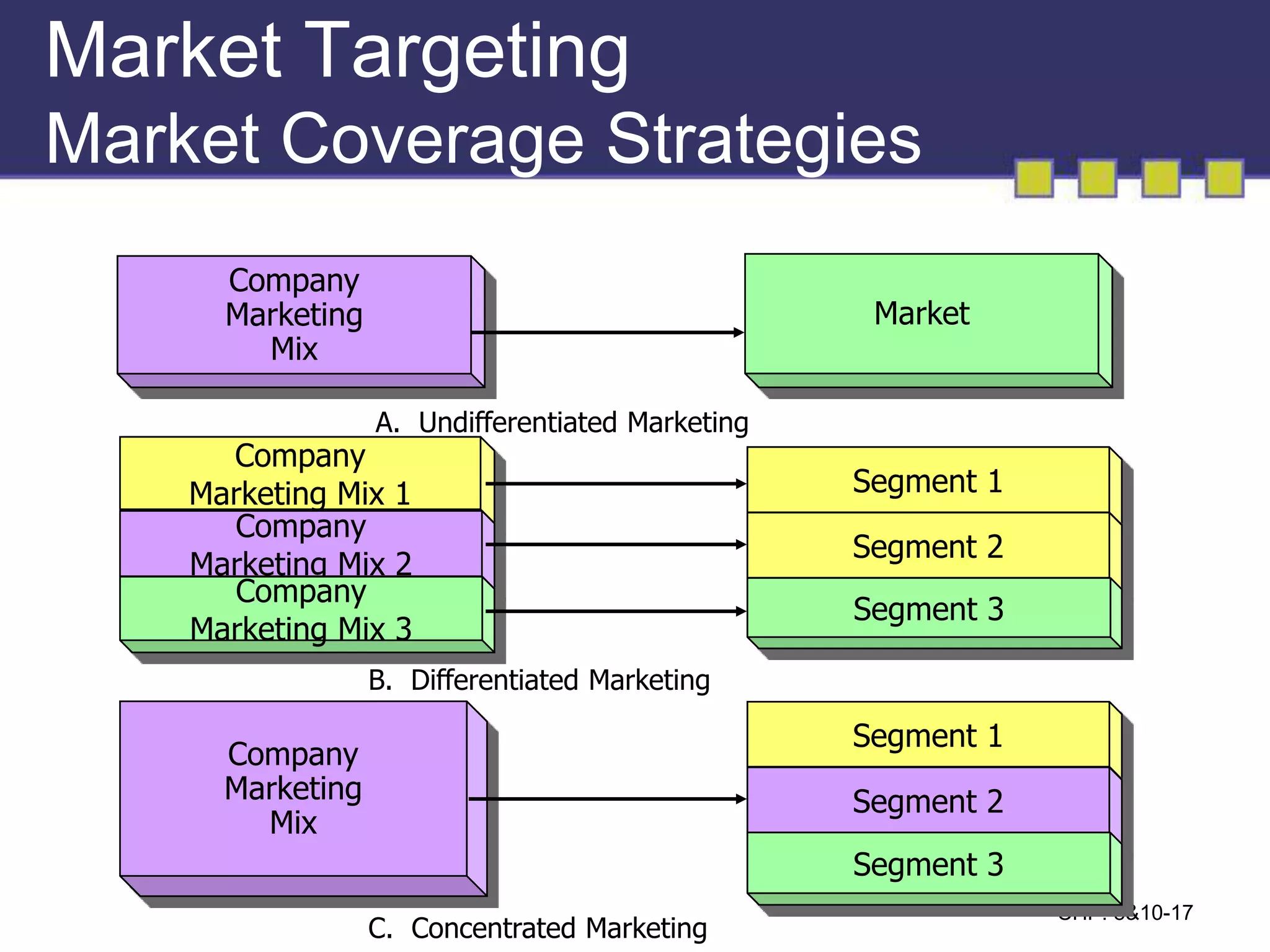
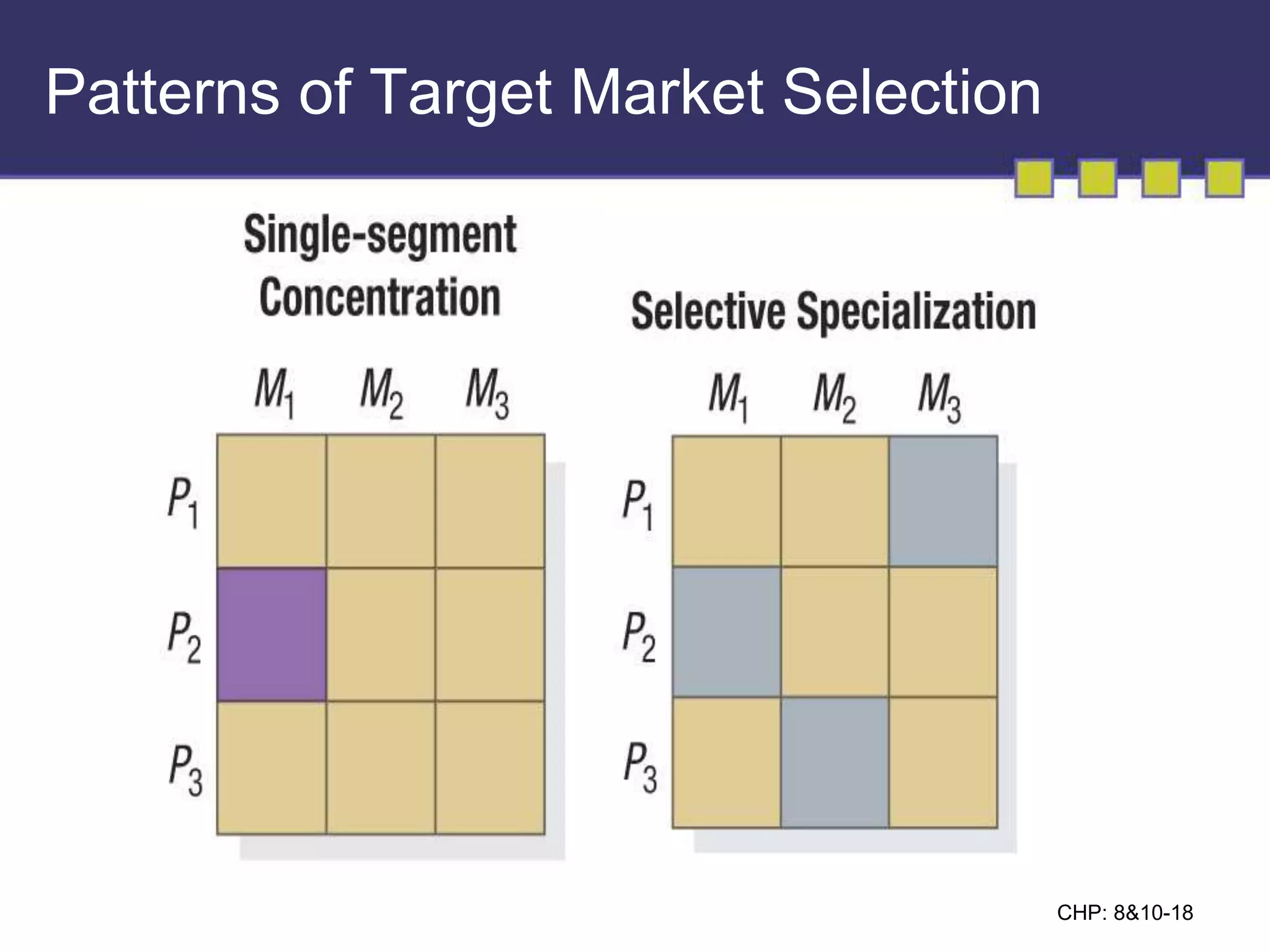
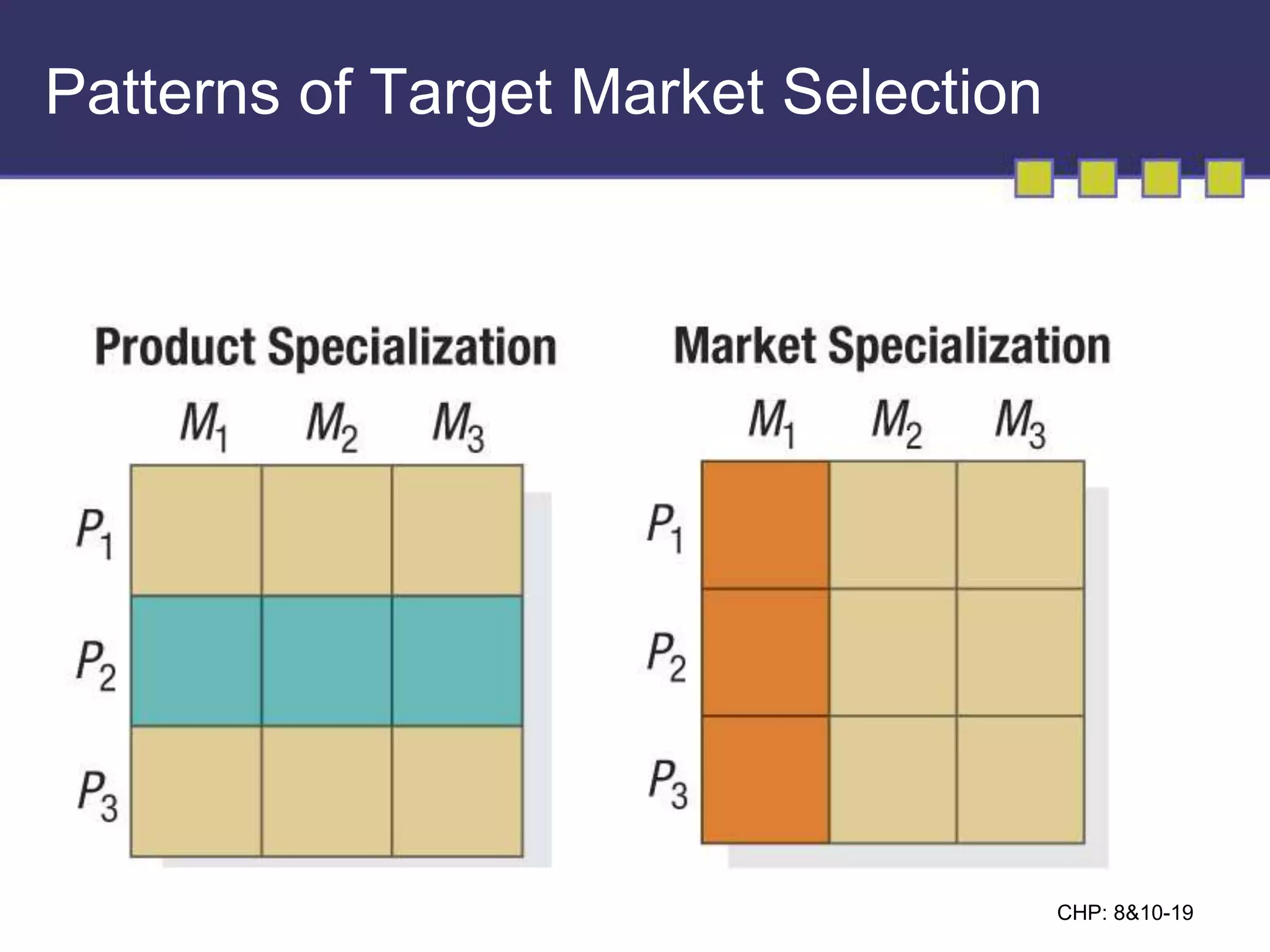
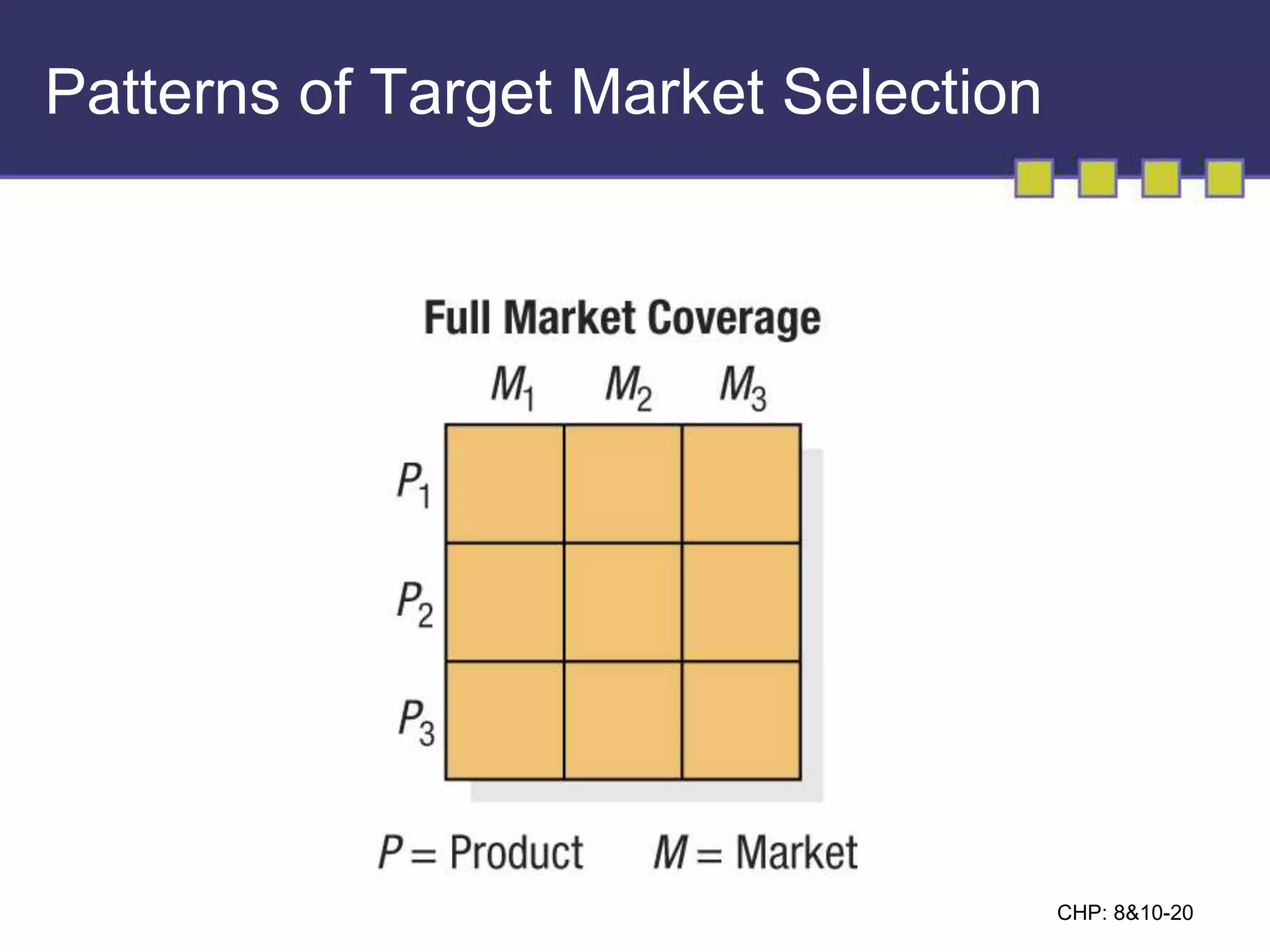
The document discusses market segmentation, targeting, and positioning. It describes identifying distinct customer groups based on needs and selecting target segments. There are several bases for segmenting consumer and business markets such as demographics, behaviors, and firmographics. Effective segmentation results in segments that are measurable, accessible, substantial, and responsive to different marketing strategies. Companies evaluate segment attractiveness based on size, growth, industry forces, and their objectives and resources to determine which target segments to enter.