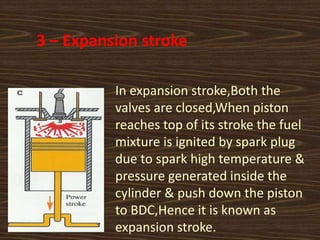
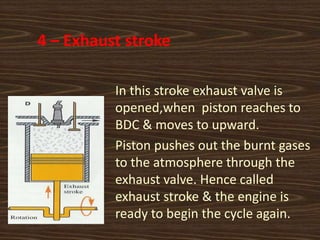
The document provides an overview of the key components and working principle of a four-stroke petrol engine. It discusses the history of the four-stroke engine invented by Nikolaus Otto in 1876. The four strokes include intake, compression, expansion, and exhaust. Key components are described such as the cylinder block, cylinder head, piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and spark plug. The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into rotational motion, while the camshaft operates the valves using cams.