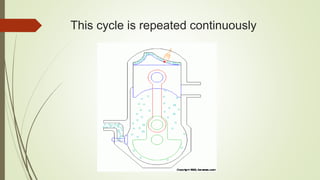
This document discusses a presentation on two-stroke petrol engines given by three students - Shahzaib Akhtar, Hassan Abbas Niazi, and Abdullah Saddiq. It defines the basic components of a two-stroke engine like the piston, connecting rod, crankshaft, and spark plug. It explains that in a two-stroke engine, the intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes are completed in two strokes of the piston rather than four. The intake and exhaust ports are opened and closed by the piston's motion rather than valves. The document outlines the working principle, advantages like lighter weight and lower cost, disadvantages like lower efficiency, and common applications of two-stroke engines.