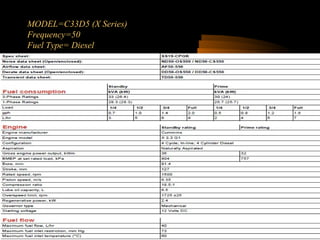
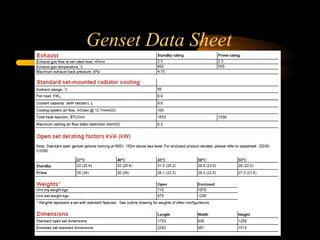
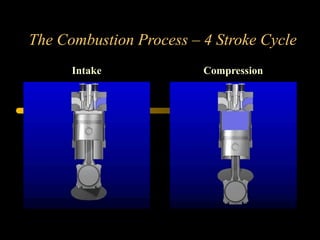
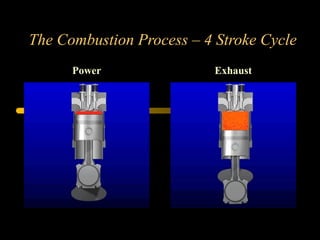
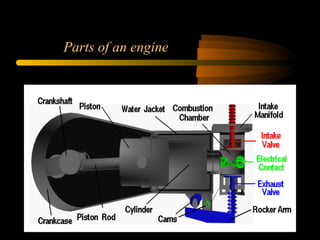
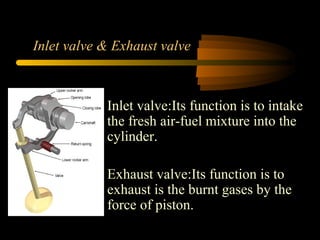
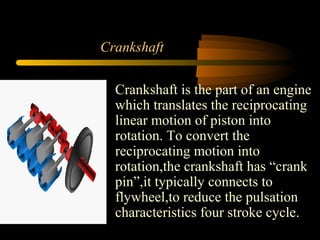
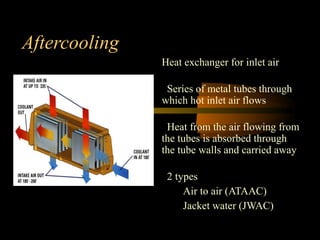
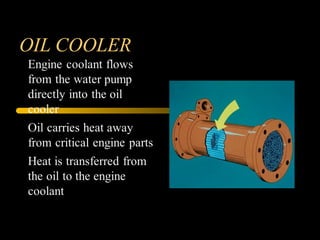
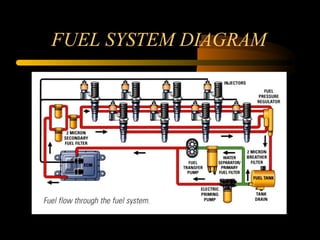
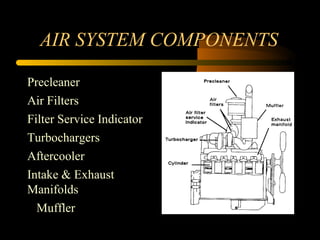
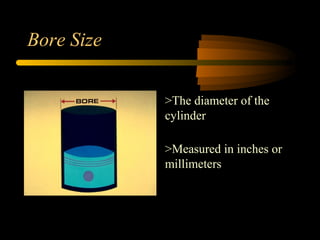
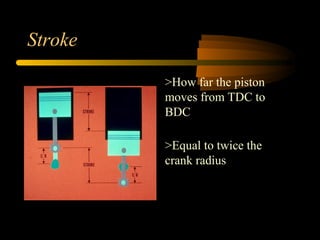
Bilal Ahmad is a service engineer for Orient energy system pvt. He describes the C33D5 diesel engine used in their gensets. The 4-cylinder inline engine has a compression ratio of 18.5:1 and uses a direct injection fuel system. Bilal explains the basic 4-stroke combustion process and lists key internal engine components like the cylinder block, head, valves, piston, rings, and crankshaft. He also describes several external components critical to engine operation, including the cooling system, fuel system, air intake system, and turbocharger.