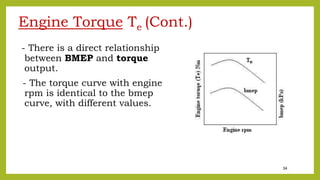
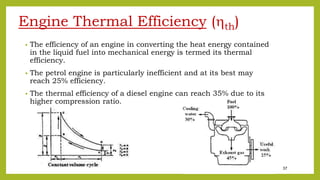
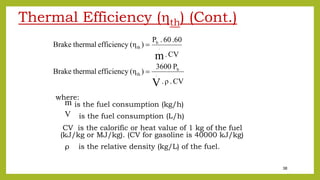
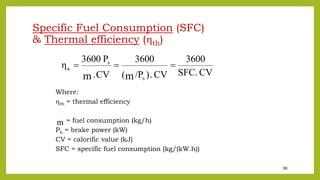
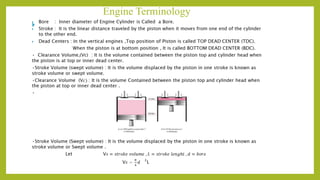
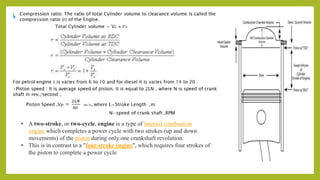
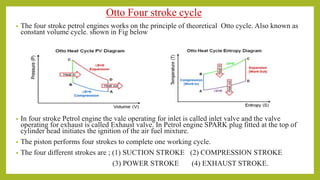
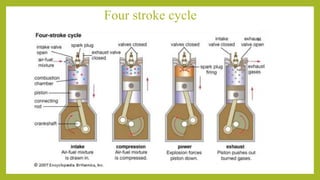
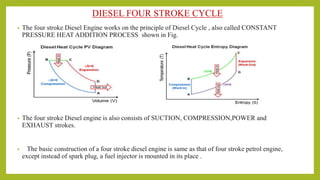
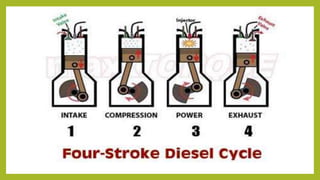
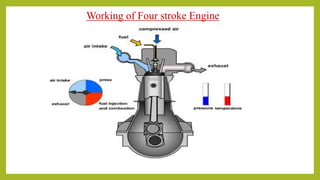
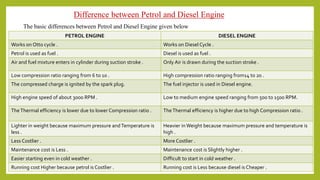
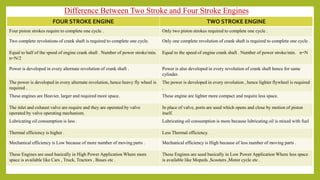
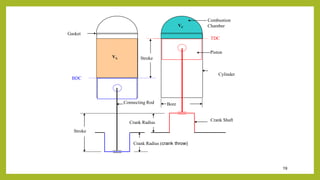
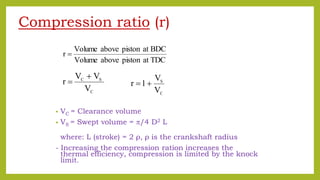
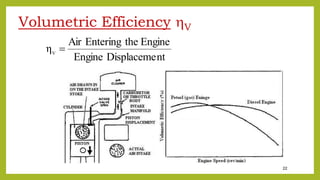
The document provides a comprehensive overview of internal combustion engines, detailing the development and classification of various engine types, including Otto and Diesel cycles, and outlining their operating principles. It contrasts two-stroke and four-stroke engines, highlighting key differences in their operational mechanisms, thermal efficiency, and applications. Additionally, it discusses engine performance factors such as power, fuel consumption, and thermal efficiency with technical insights into calculations and efficiency metrics.





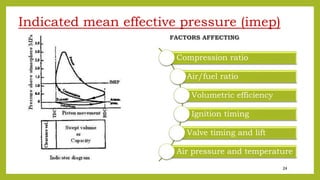
![25
Pressure, Force, Work & Power
p = imep (N/m2)
A (m2)
F= P.A (N)
L (m)
F (N)
Work (W) = F.L (N m)
Time (t) = 60 / (Ne /k) (s)
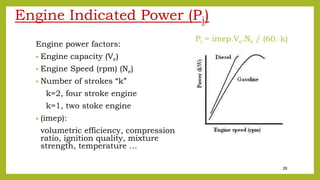
Indicated power (Pi) cylinder = W/t = F.L .Ne/(k*60) (W)
(Pi) cylinder = (imep.A.L.Ne) / (k . 60)
(Pi) engine = imep. (A.L.n) Ne / (k . 60)
(Pi) engine = [imep. Ve . Ne/ (k . 60)] (W)
a
b
c
k = 2 (four stroke)
k = 1 (two stoke)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presention-150806044916-lva1-app6891/85/Basic-of-engine-25-320.jpg)