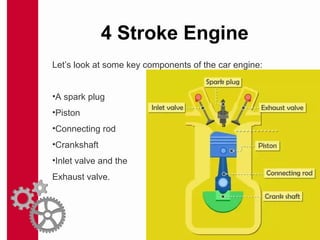
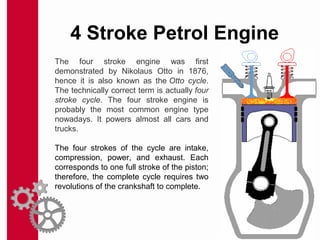
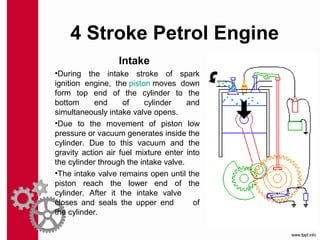
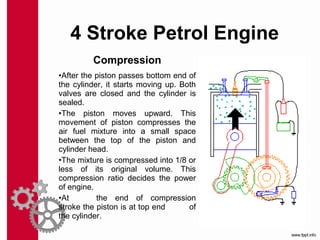
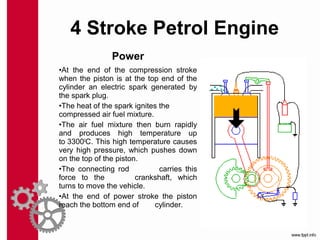
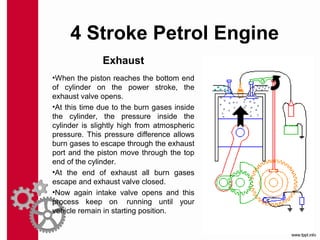
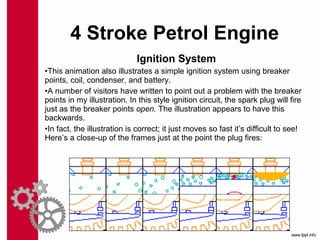
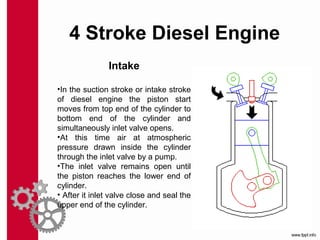
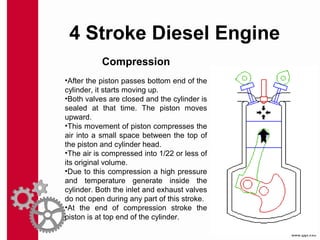
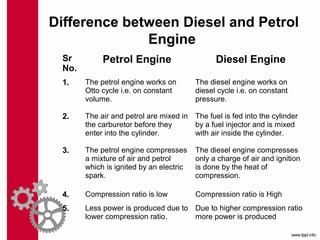
The document discusses the mechanics and differences between 4-stroke petrol and diesel engines, detailing their components, cycles of operation (intake, compression, power, and exhaust), and ignition processes. It explains that petrol engines operate on the Otto cycle and rely on a spark plug for ignition, while diesel engines use the diesel cycle, with fuel injected directly into compressed air for ignition. Key comparisons highlight their operational differences, power efficiency, fuel consumption, and maintenance costs.