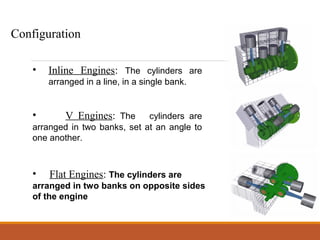
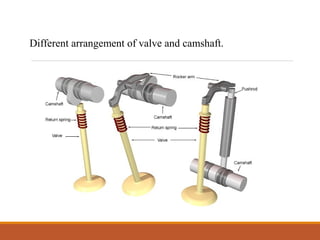
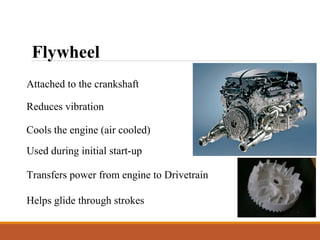
The document describes the main components of an internal combustion engine, including the cylinder head, engine block, pistons, valves, camshaft, crankshaft, connecting rods, and flywheel. It discusses the different types of engines like four-stroke gasoline, two-stroke gasoline, and diesel engines. It also explains the basic functions of engine components like the camshaft converting rotary motion to reciprocating motion and the flywheel reducing vibration and transferring power from the engine.