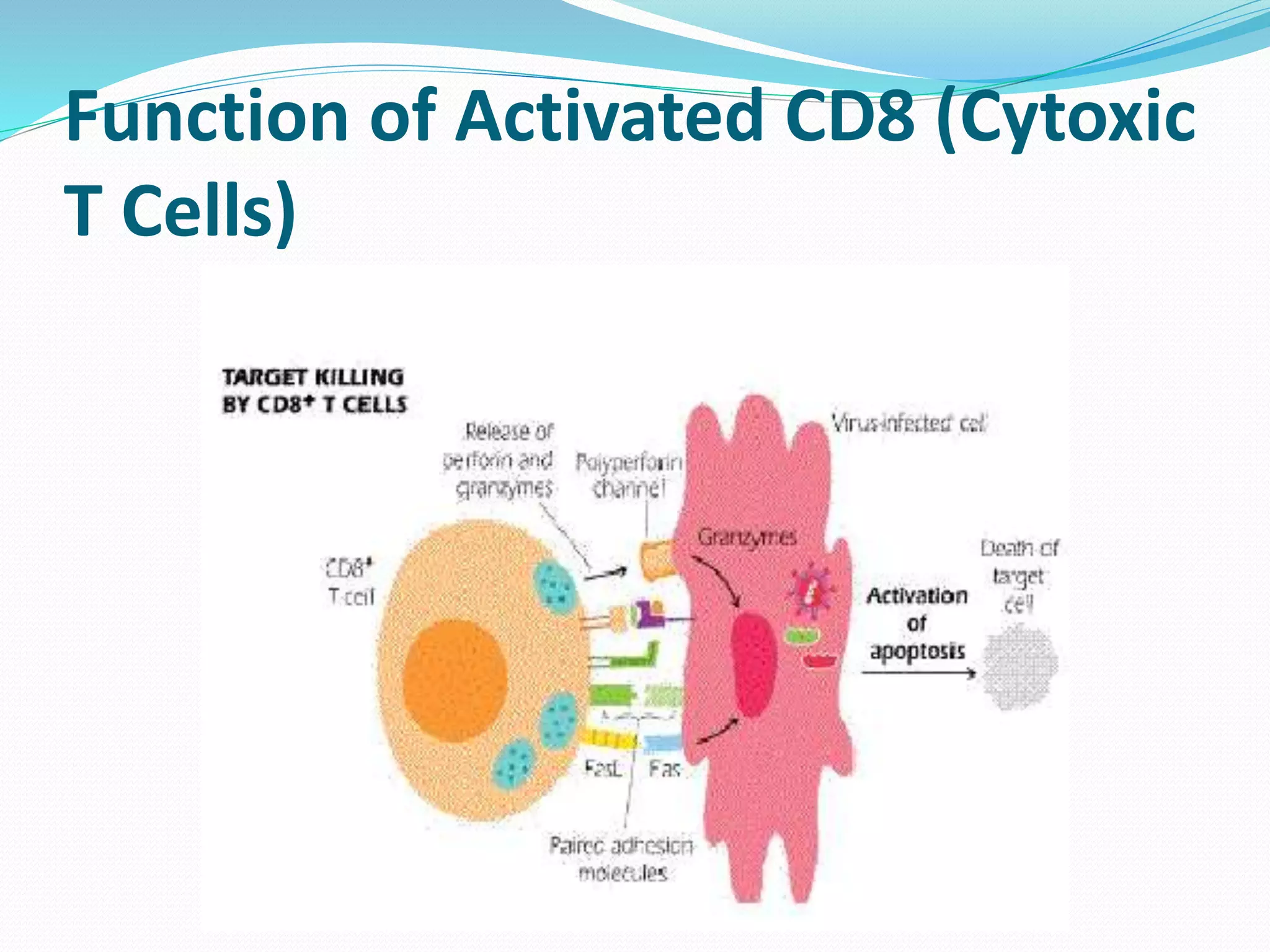
Hypersensitivity Type IV is a delayed type hypersensitivity that involves cell-mediated responses without antigen-antibody interactions. T lymphocytes recognize antigens that have been processed and presented by antigen-presenting cells via MHC molecules. Activated CD4+ T cells secrete cytokines that regulate the immune response, while activated CD8+ T cells kill cells displaying endogenous antigens on their MHC Class I molecules through the release of perforins and granzymes. This leads to loss of cell content and cell death.