Embed presentation
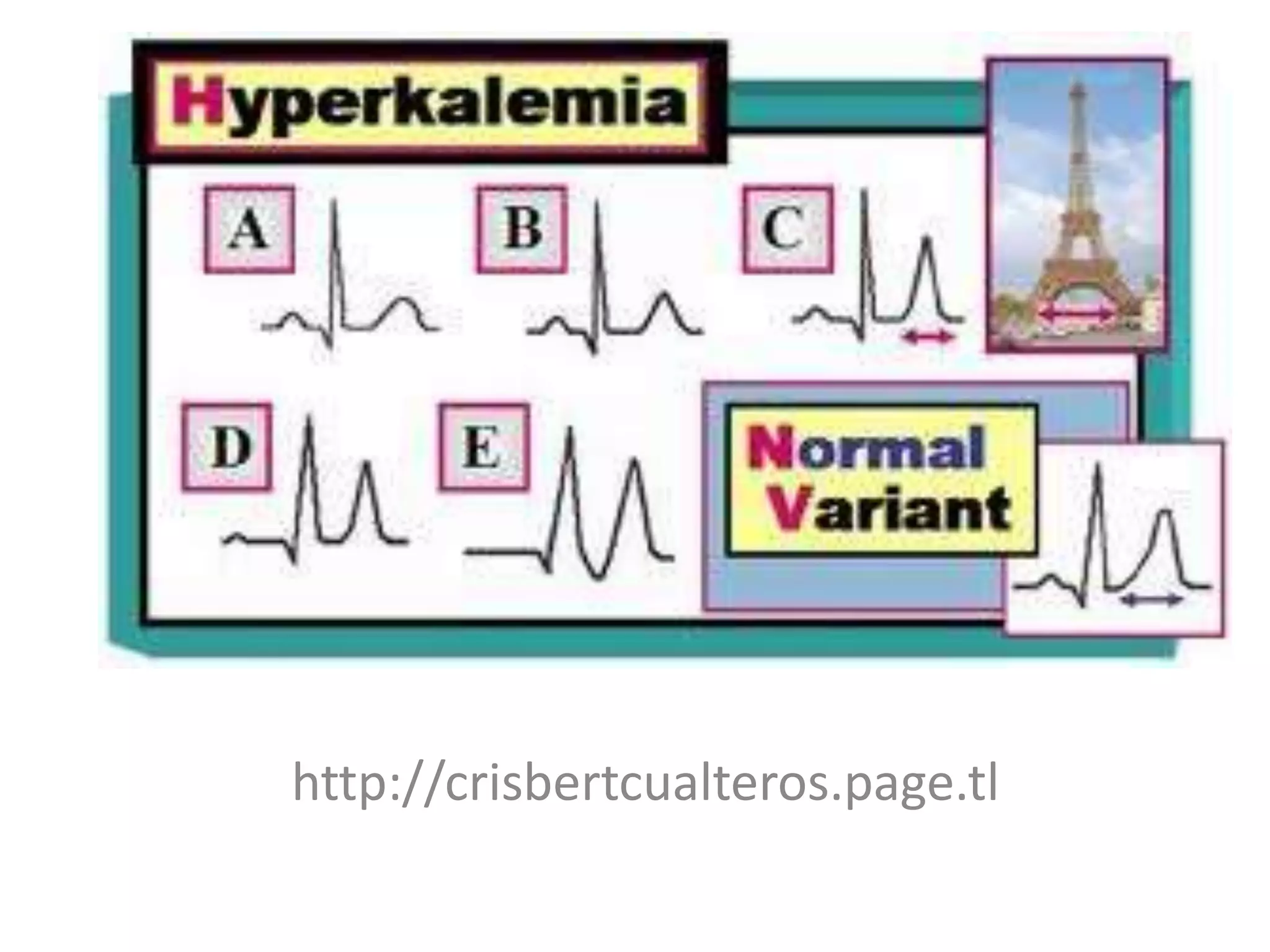
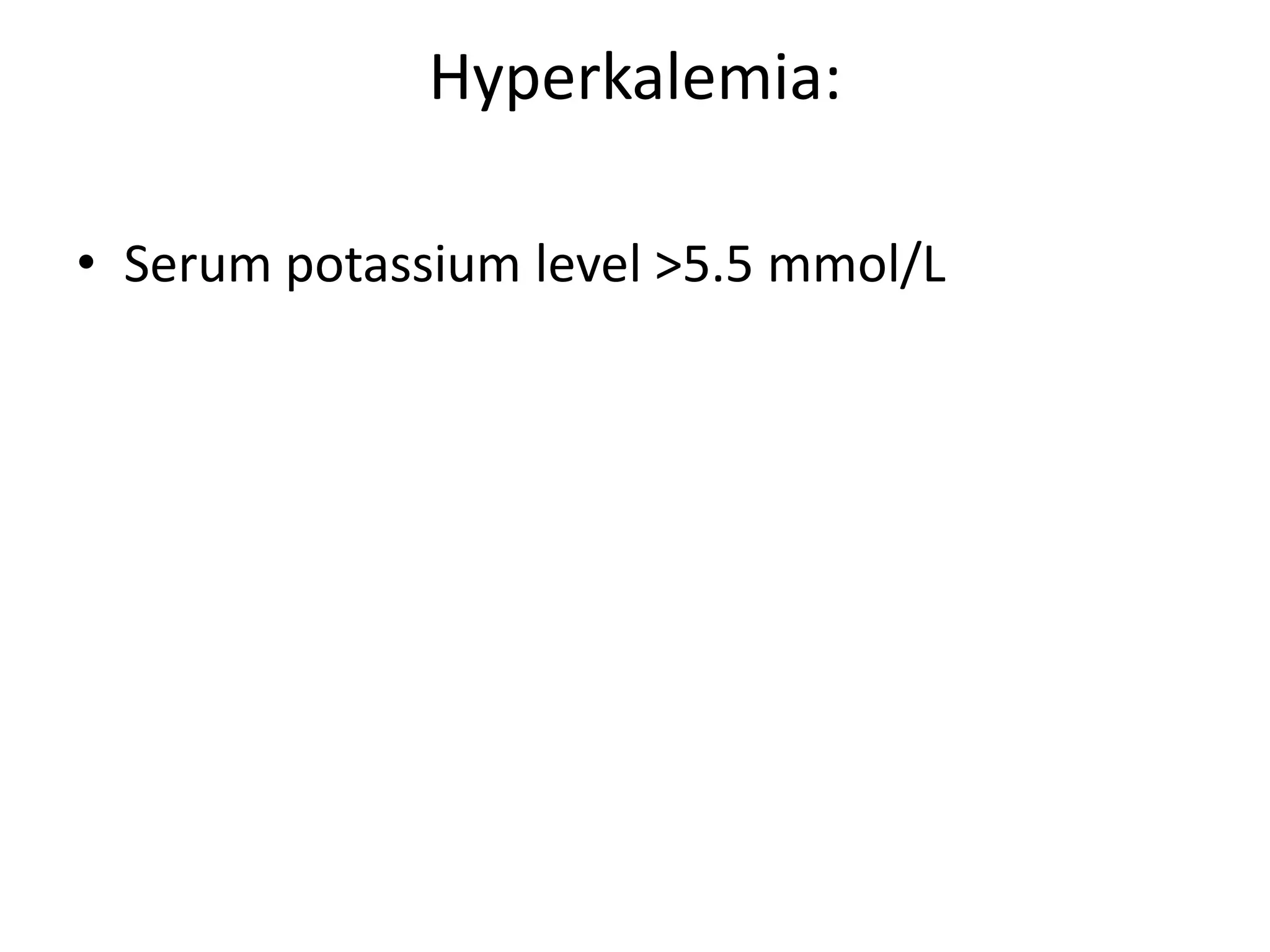
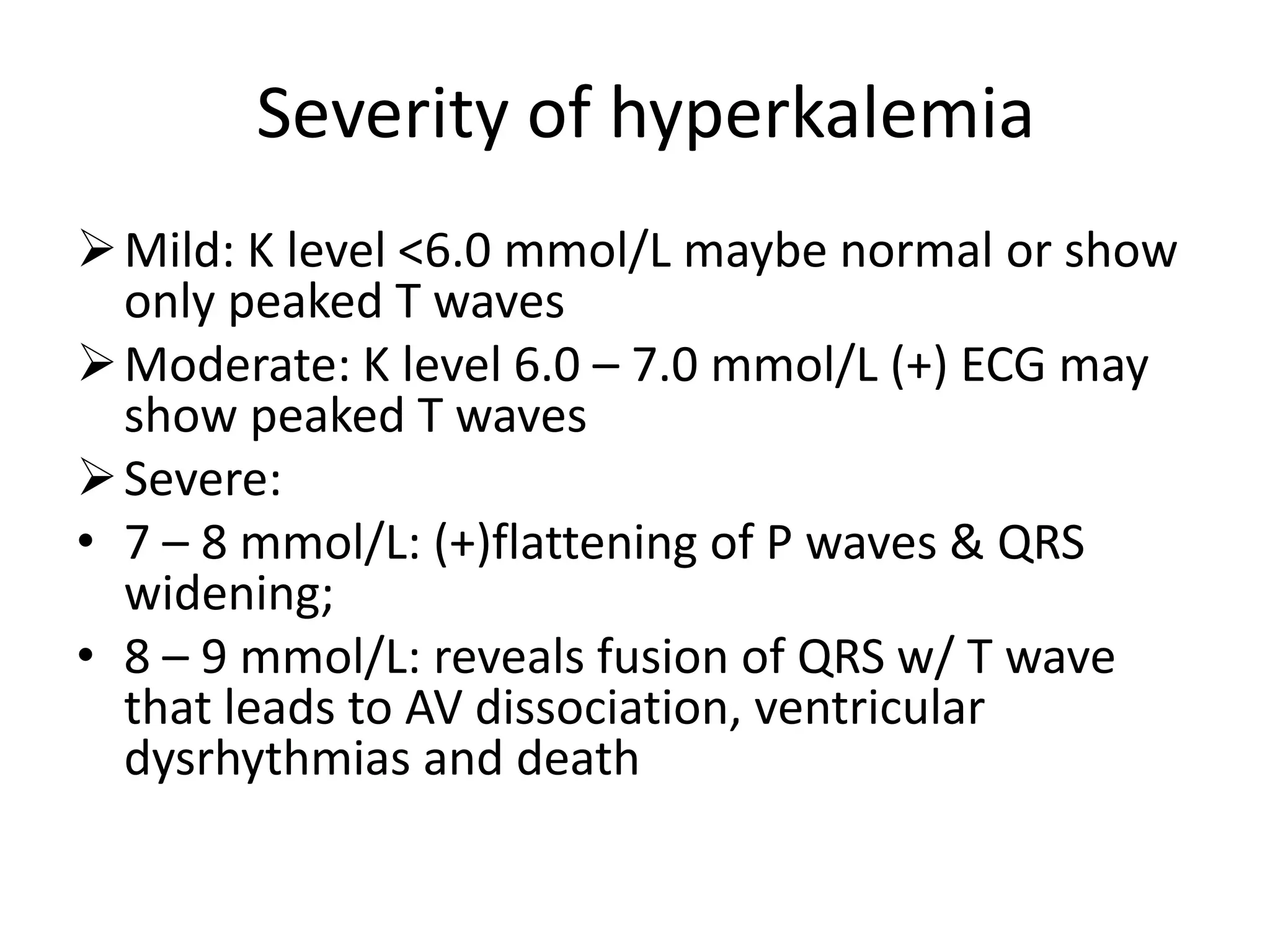
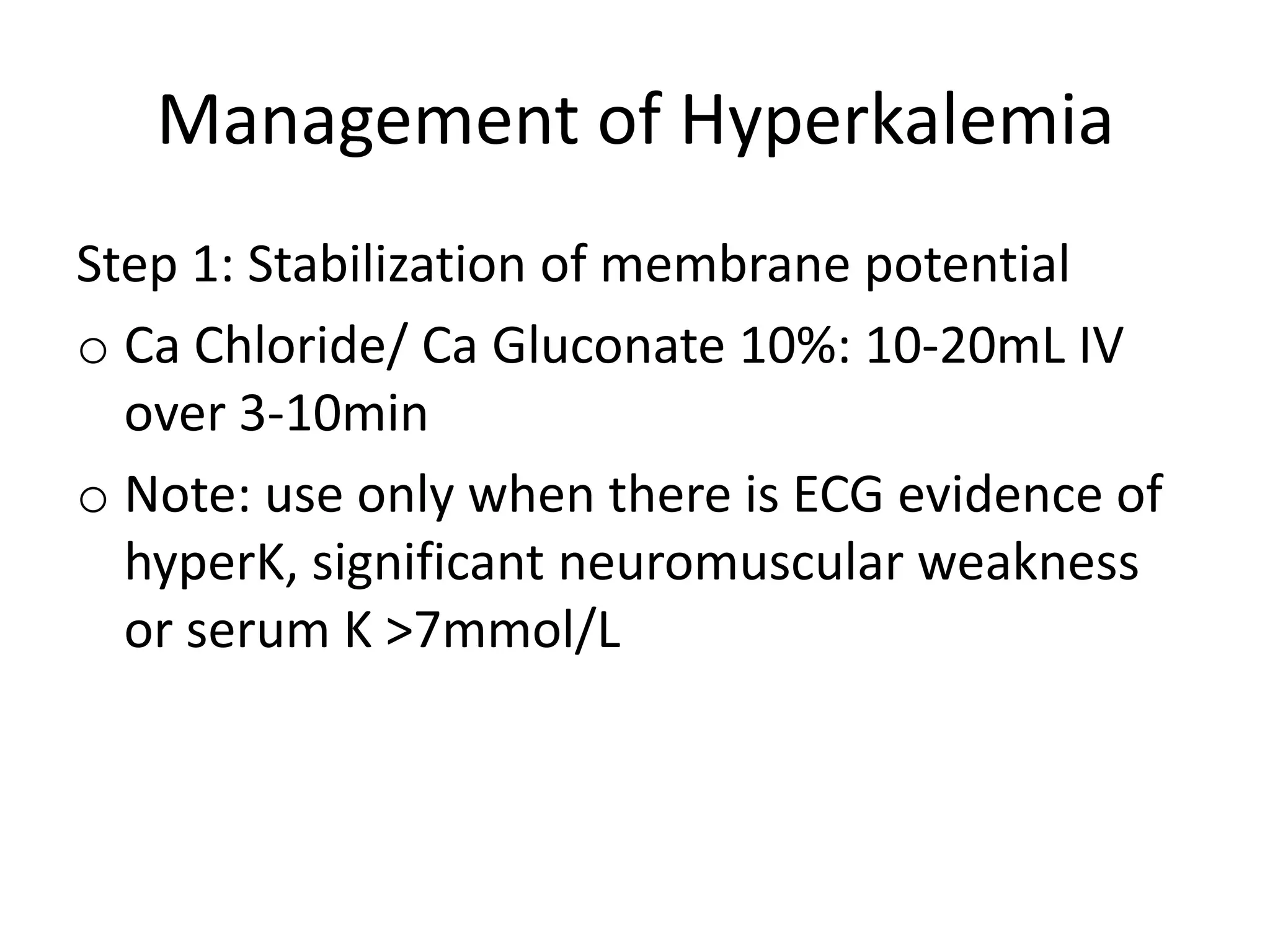




Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium level greater than 5.5 mmol/L. The severity can range from mild (<6.0 mmol/L) to moderate (6.0-7.0 mmol/L) to severe (7.0-8.0 mmol/L potentially causing ECG changes and above 8.0 mmol/L potentially causing cardiac arrest). Management involves stabilizing the membrane potential with calcium salts for ECG changes, shifting potassium into cells with insulin and glucose, removing potassium from the body with resins or dialysis, and preventing further increases by reviewing medications and diet.






