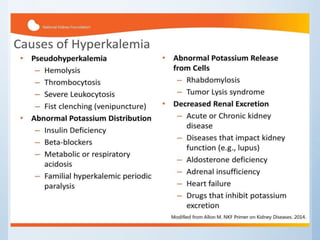
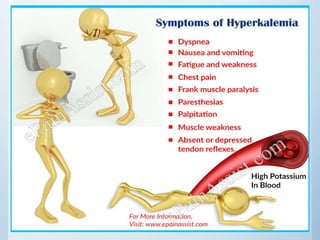
Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of potassium in the blood above 5.5 mmol/L. Initial treatments include calcium gluconate to protect the heart, insulin with glucose to shift potassium into cells, salbutamol to also shift potassium into cells, sodium bicarbonate to treat acidosis, and sodium polystyrene sulphonate to bind potassium in the gut. Definitive treatment is hemodialysis to remove excess potassium from the blood. The emergency management involves determining the cause and using temporary treatments to stabilize the heart and lower potassium through redistribution while arranging hemodialysis if needed for severe cases.

![• Hyperkalemia is an elevated level of
potassium (K+) in the blood serum.[1] Normal
potassium levels are between 3.5 and 5.0
mmol/L
• Levels above 5.5 mmol/L defined as
hyperkalemia](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperkalemeamanagement-190617201600/85/Hyperkalemea-management-2-320.jpg)