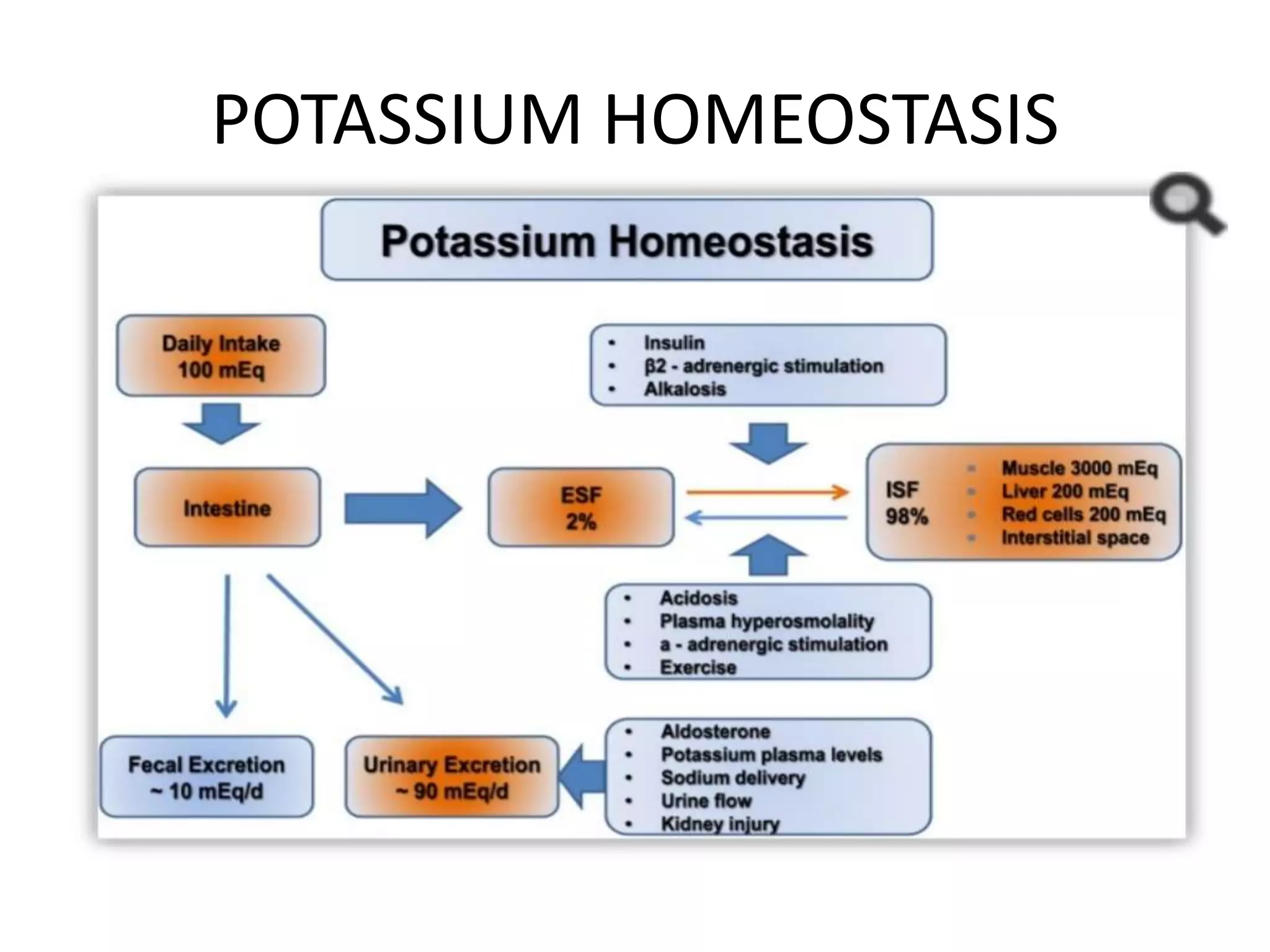
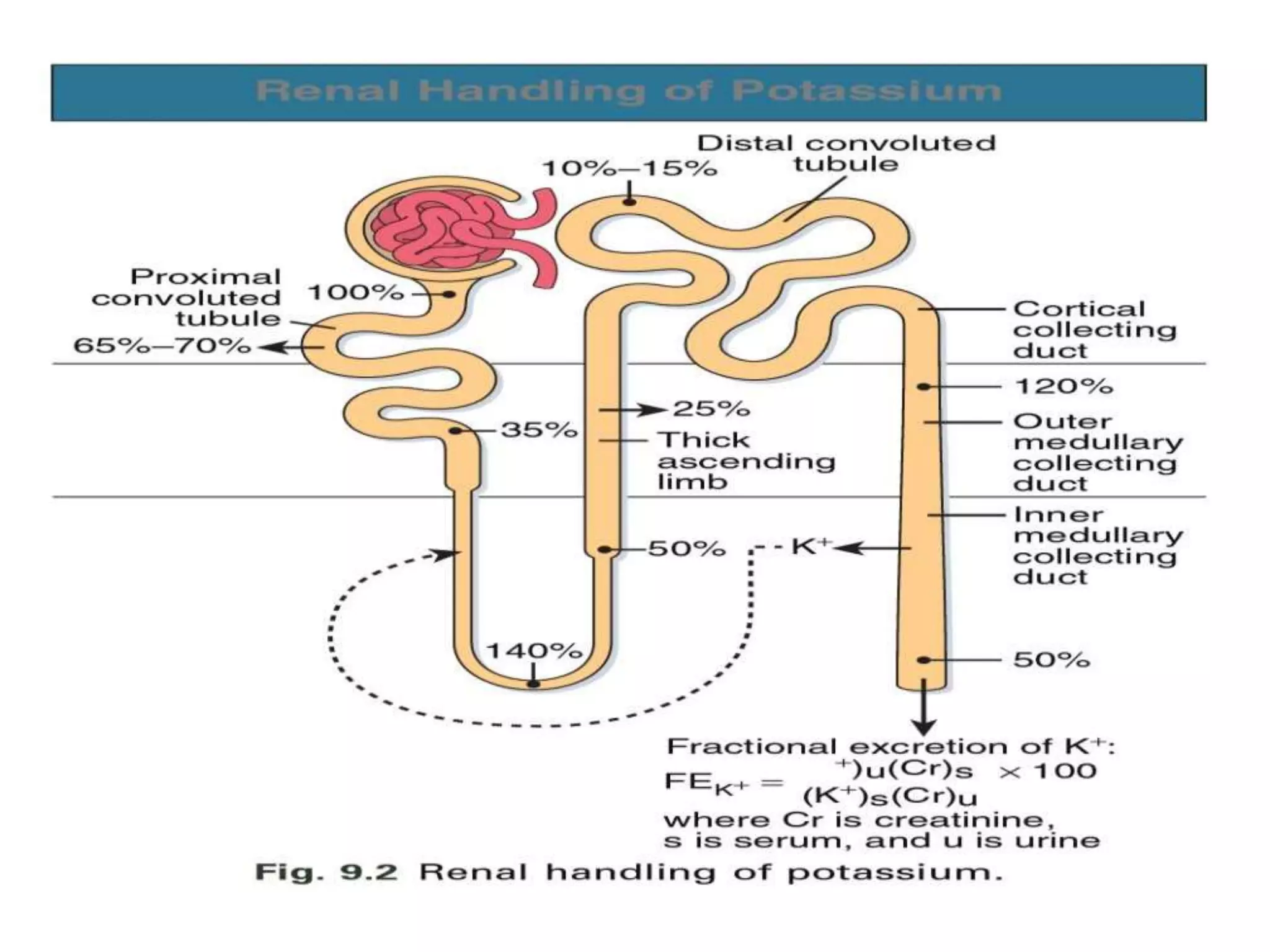
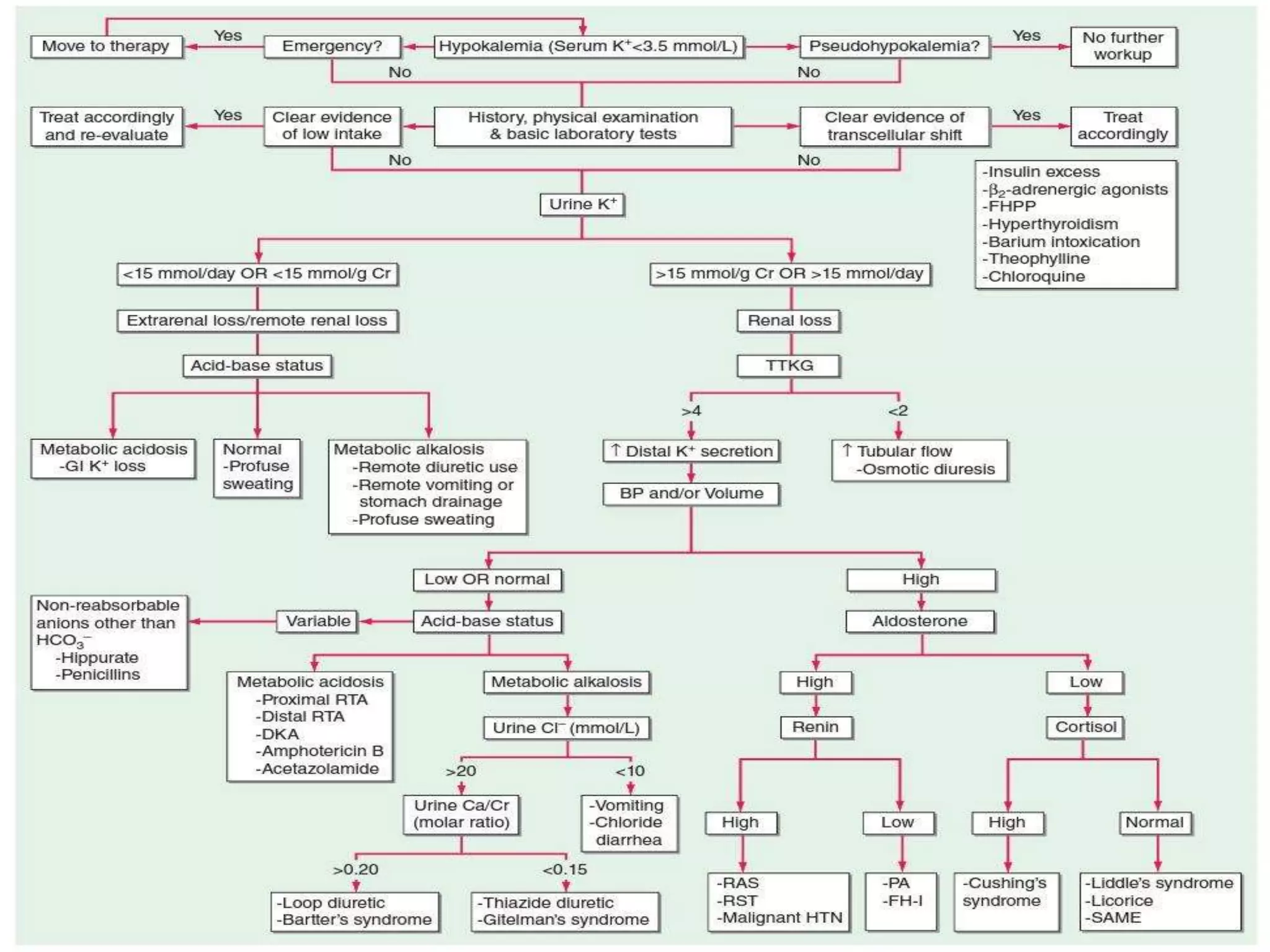
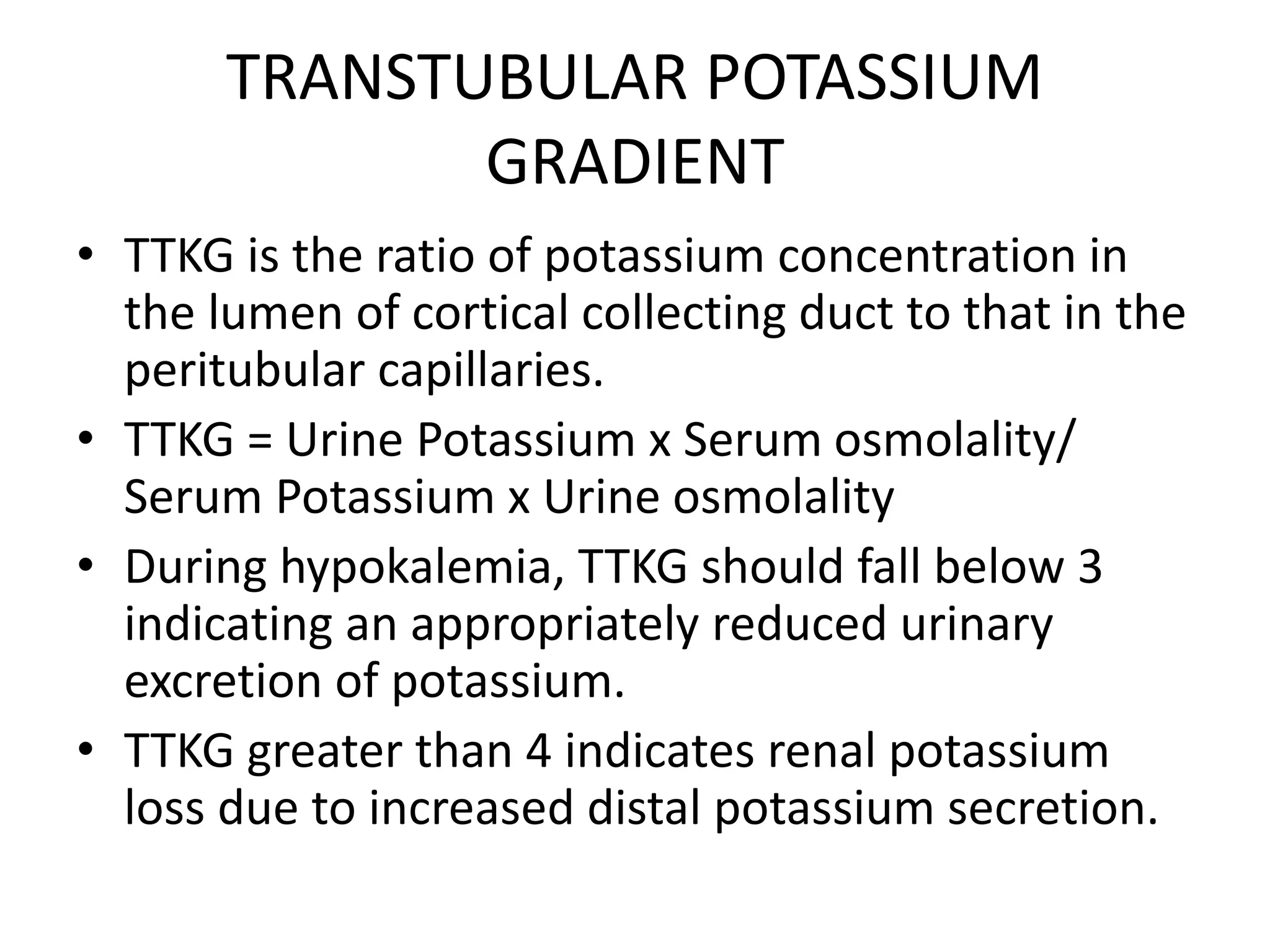
Hypokalemia is an electrolyte disorder characterized by serum potassium levels below 3.5 meq/l, which can lead to serious complications like arrhythmias and paralysis. The document discusses potassium's physiological functions, its distribution in the body, clinical manifestations of hypokalemia, causes, diagnostic approaches, and treatment options. Effective management involves potassium replacement and addressing the underlying causes, with oral treatment preferred unless severe cases necessitate intravenous administration.