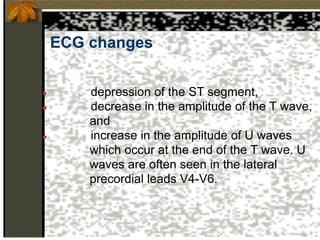
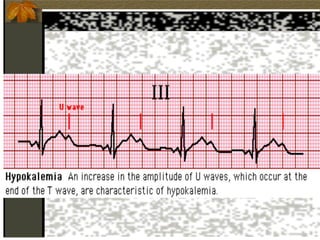
1. Hypokalemia is defined as a serum potassium level below 3.5 mEq/L. It can cause weakness, paralysis, and ECG changes. Treatment involves oral or IV potassium supplementation as well as treating the underlying cause.
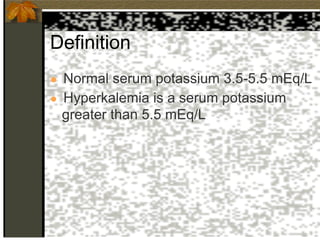
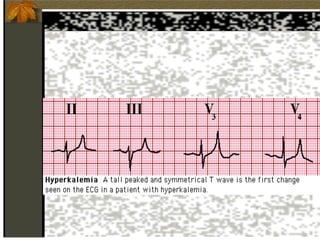
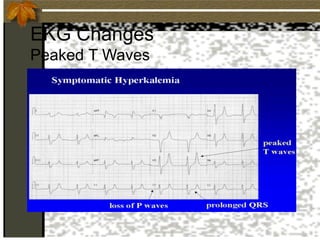
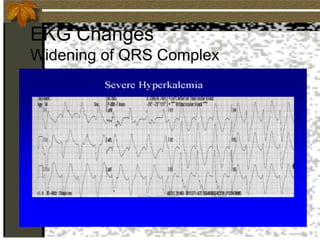
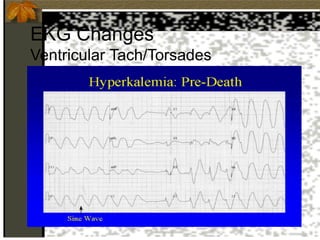
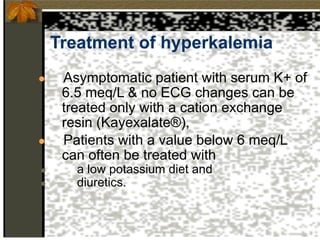
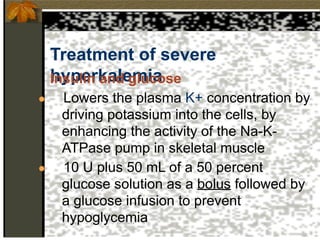
2. Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium above 5.5 mEq/L. It can cause muscle weakness, arrhythmias, and ECG changes like peaked T waves. Treatment focuses on stabilizing the heart with calcium, driving potassium into cells with insulin/glucose or beta-agonists, and removing potassium from the body with cation exchange resins or dialysis.
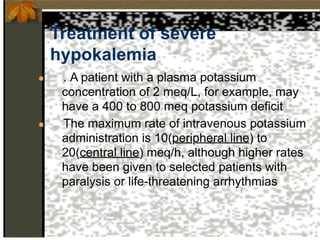
3. Severe cases may require higher doses administered more quickly via