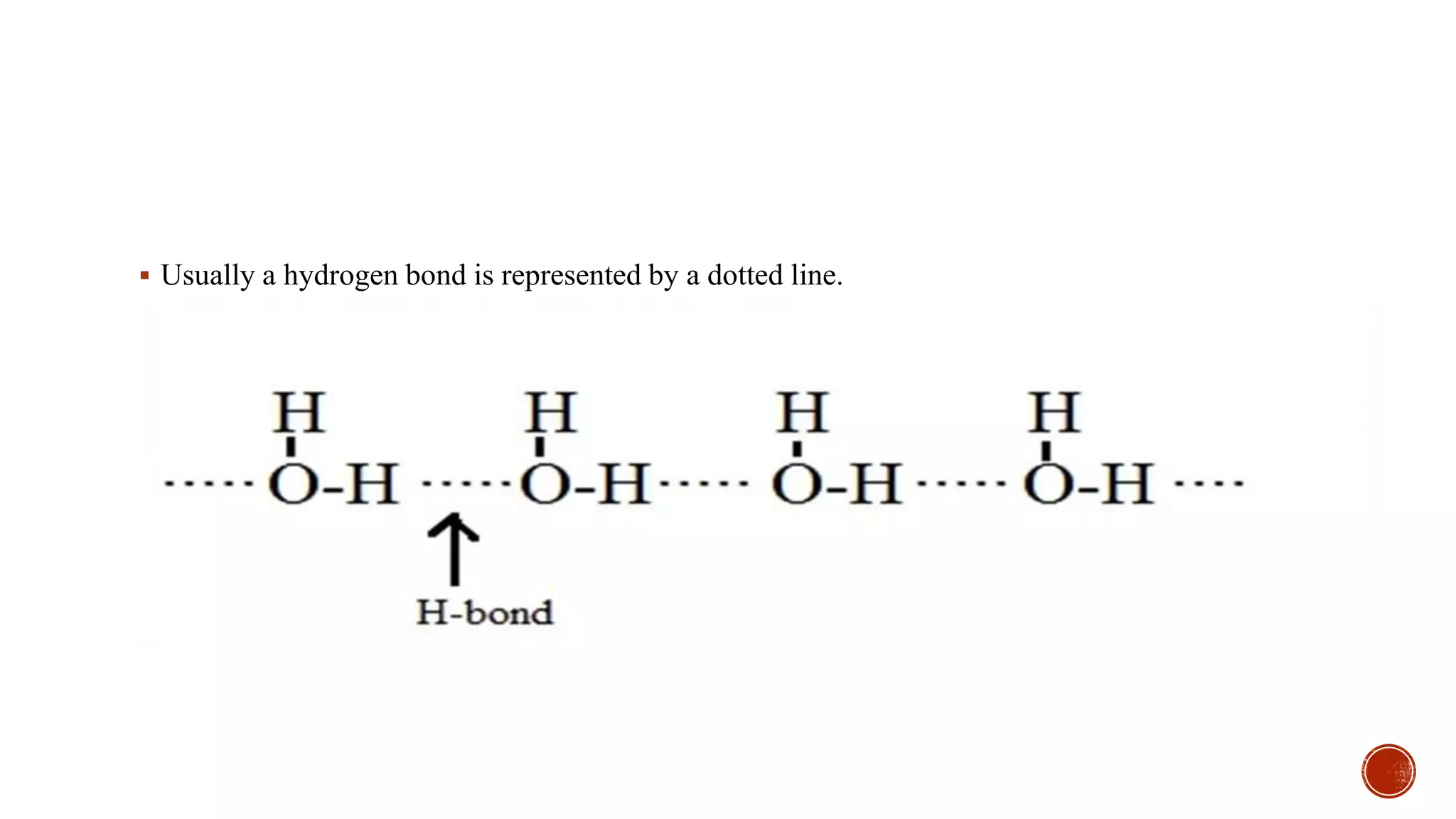
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom like oxygen or nitrogen forms an electrostatic attraction to another electronegative atom. This occurs in compounds containing O-H or N-H bonds like water, alcohols, acids, and amines. The hydrogen bond is weaker than a covalent bond but significantly impacts properties like boiling point and solubility. Compounds with hydrogen bonding have higher boiling points and solubility compared to similar compounds without hydrogen bonding.