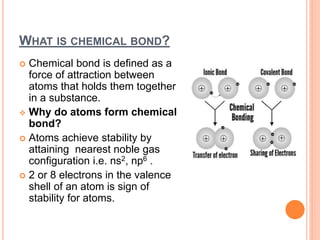
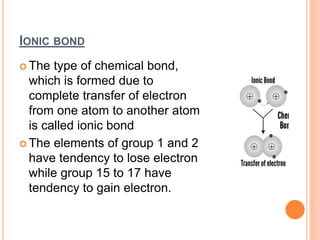
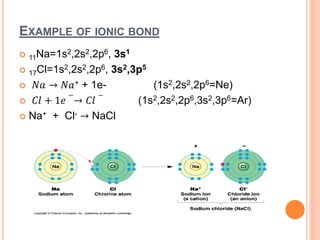
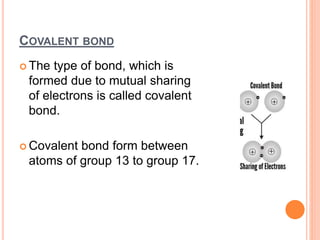
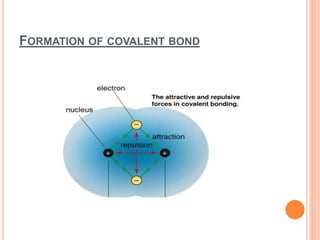
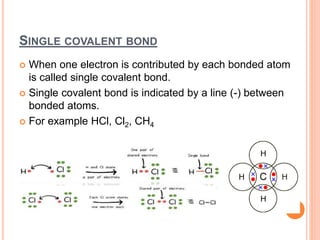
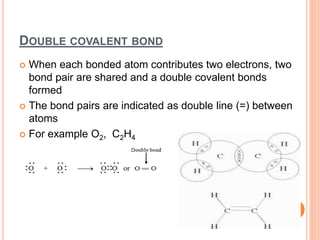
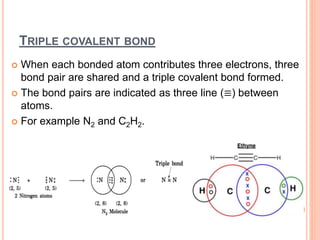
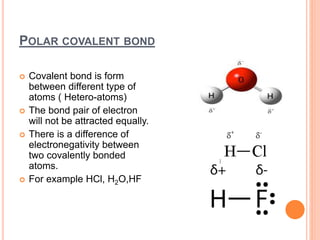
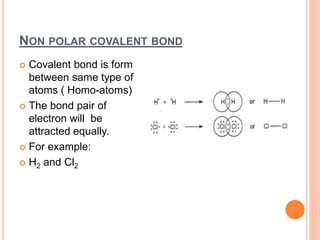
Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve stable electron configurations. They follow the octet rule by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons to acquire eight electrons in their valence shell. There are four main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds form when electrons are completely transferred between atoms, covalent bonds form when electrons are shared between atoms, and polar and nonpolar covalent bonds differ based on whether the electron sharing is equal or unequal. Chemical bonds determine many properties of compounds including their physical state, solubility, and ability to conduct heat and electricity.