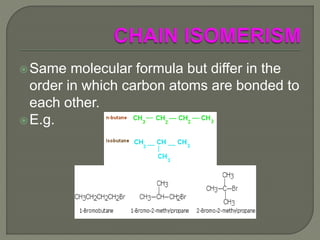
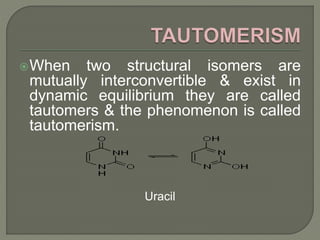
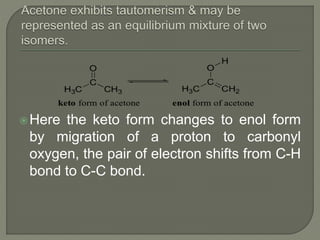
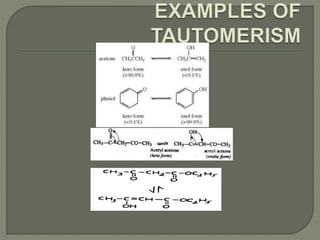
There are two main types of isomers: structural isomers and stereoisomers. Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas due to differences in how atoms are arranged within the molecule. There are five types of structural isomers: chain isomers, position isomers, functional isomers, metamerism, and tautomers. Tautomers are structural isomers that can interconvert and exist in dynamic equilibrium, such as the keto and enol forms of aldehydes and ketones which involve the migration of a proton between carbon and oxygen atoms.