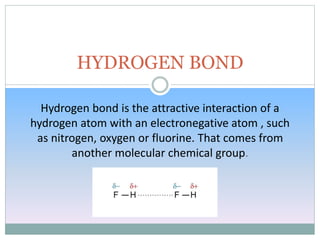
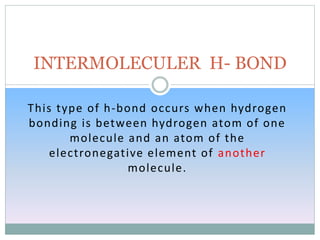
Hydrogen bonding occurs when a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom like nitrogen, oxygen or fluorine interacts with another electronegative atom. This interaction is stronger than van der Waals forces but weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. Hydrogen bonding plays a key role in the structures of water and DNA, enabling water to have high boiling and melting points and DNA to form its double helix structure. There are two types of hydrogen bonds: intermolecular between molecules and intramolecular within the same molecule.