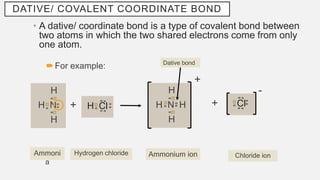
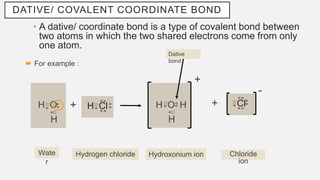
The document discusses various types of chemical bonds, focusing on hydrogen bonds, dative bonds, and metallic bonds. It explains how hydrogen bonds affect properties like melting/boiling points, solubility in water and organic solvents, and electrical conductivity. The text also describes dative bonds and metallic bonding, emphasizing their roles in the behavior of molecular and metallic substances.