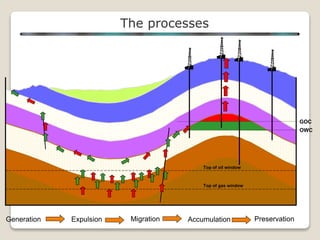
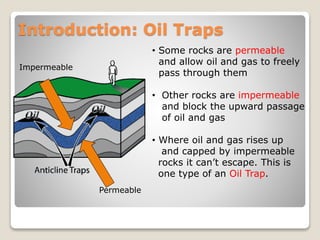
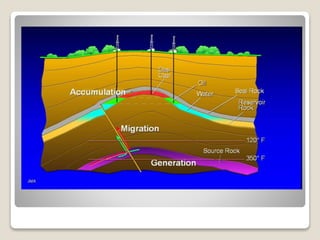
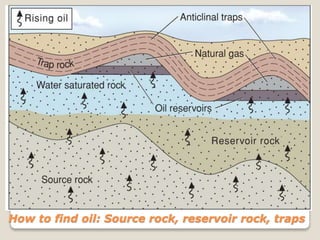
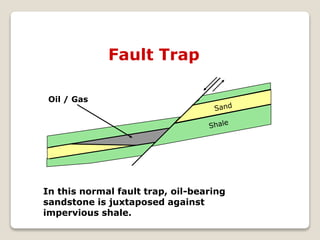
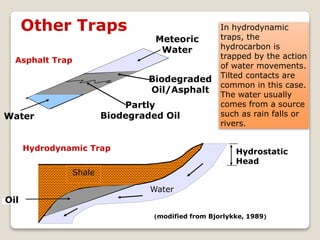
This document discusses the key geological elements of a petroleum system including source rocks, reservoir rocks, seals, migration routes, and traps. It explains that source rocks contain organic matter that generates hydrocarbons through diagenesis, catagenesis and metagenesis as the rocks are buried deeper. Reservoir rocks have pore spaces that can absorb hydrocarbons, while seal rocks are impermeable layers that trap hydrocarbons between them and the reservoir rock. Traps form where hydrocarbons are blocked from further migrating, such as in structural traps like folds and faults or stratigraphic traps caused by changes in rock layers.