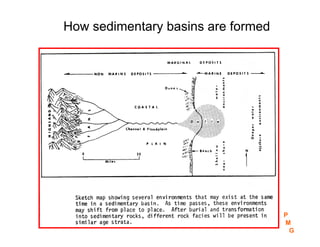
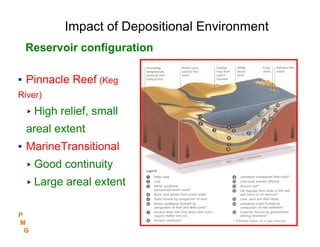
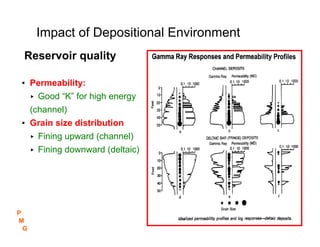
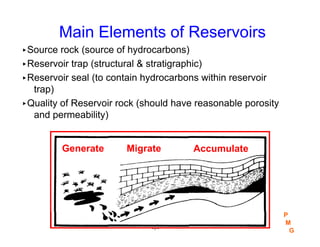
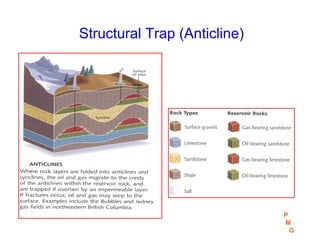
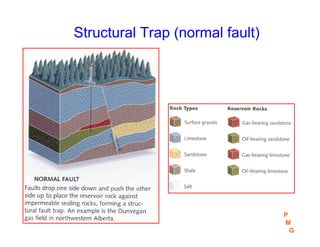
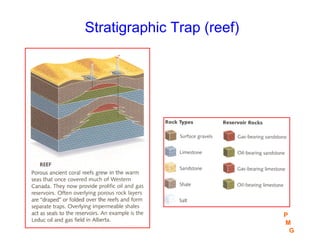
This document discusses key concepts in petroleum geology, including the geologic cycle of erosion, deposition, and uplift that forms sedimentary basins. Depositional environments like marine, deltaic, and fluvial systems impact reservoir properties. Geologic time periods are defined using fossils and dating methods. Potential reservoir rocks include sandstone, limestone, and dolomite formed from sediment. Traps such as anticlines, faults, and pinch outs can accumulate oil and gas within porous and permeable reservoir rocks sealed below impermeable caprock. Geologic maps and cross-sections are used to interpret subsurface structures and stratigraphy.