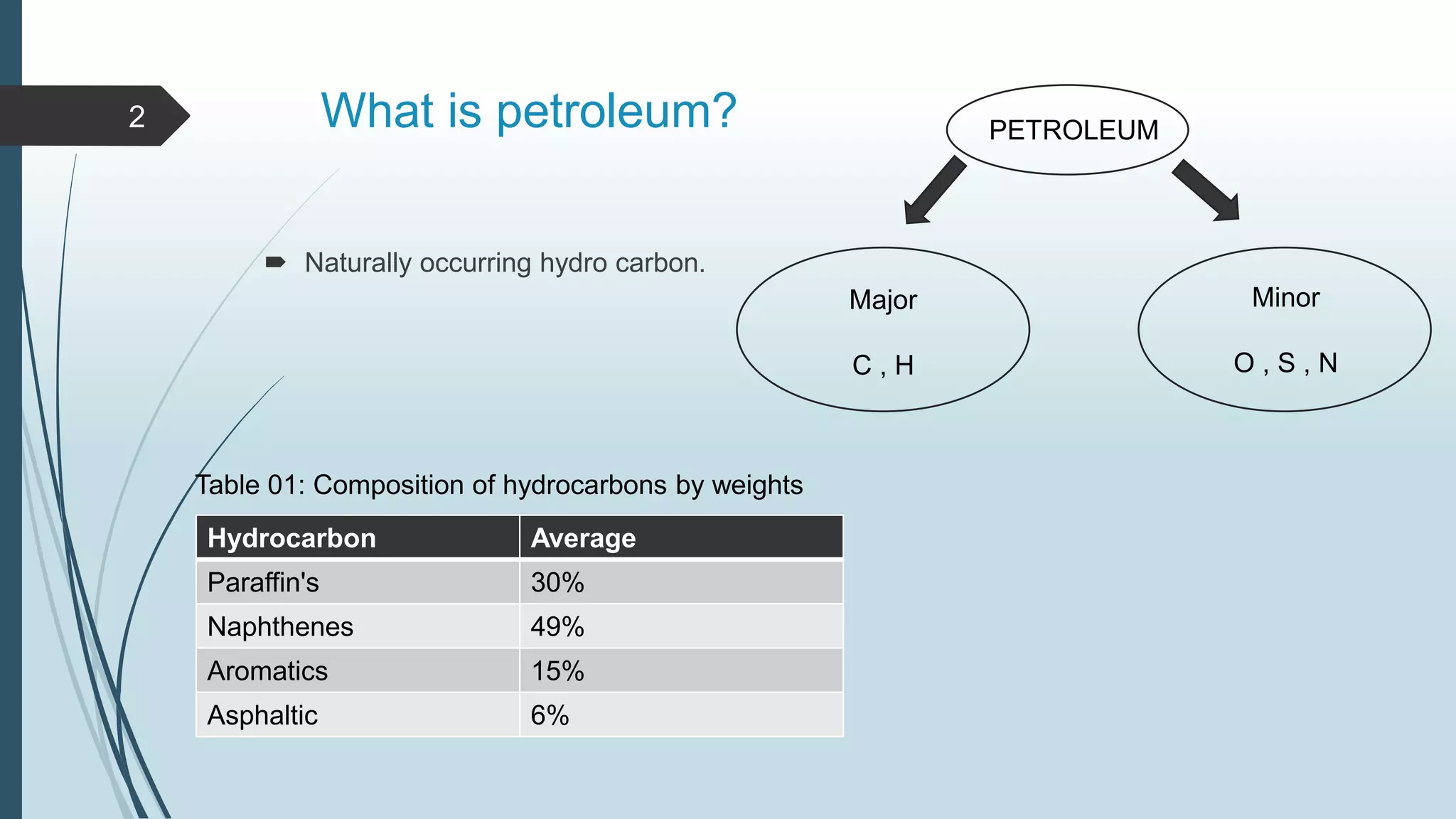
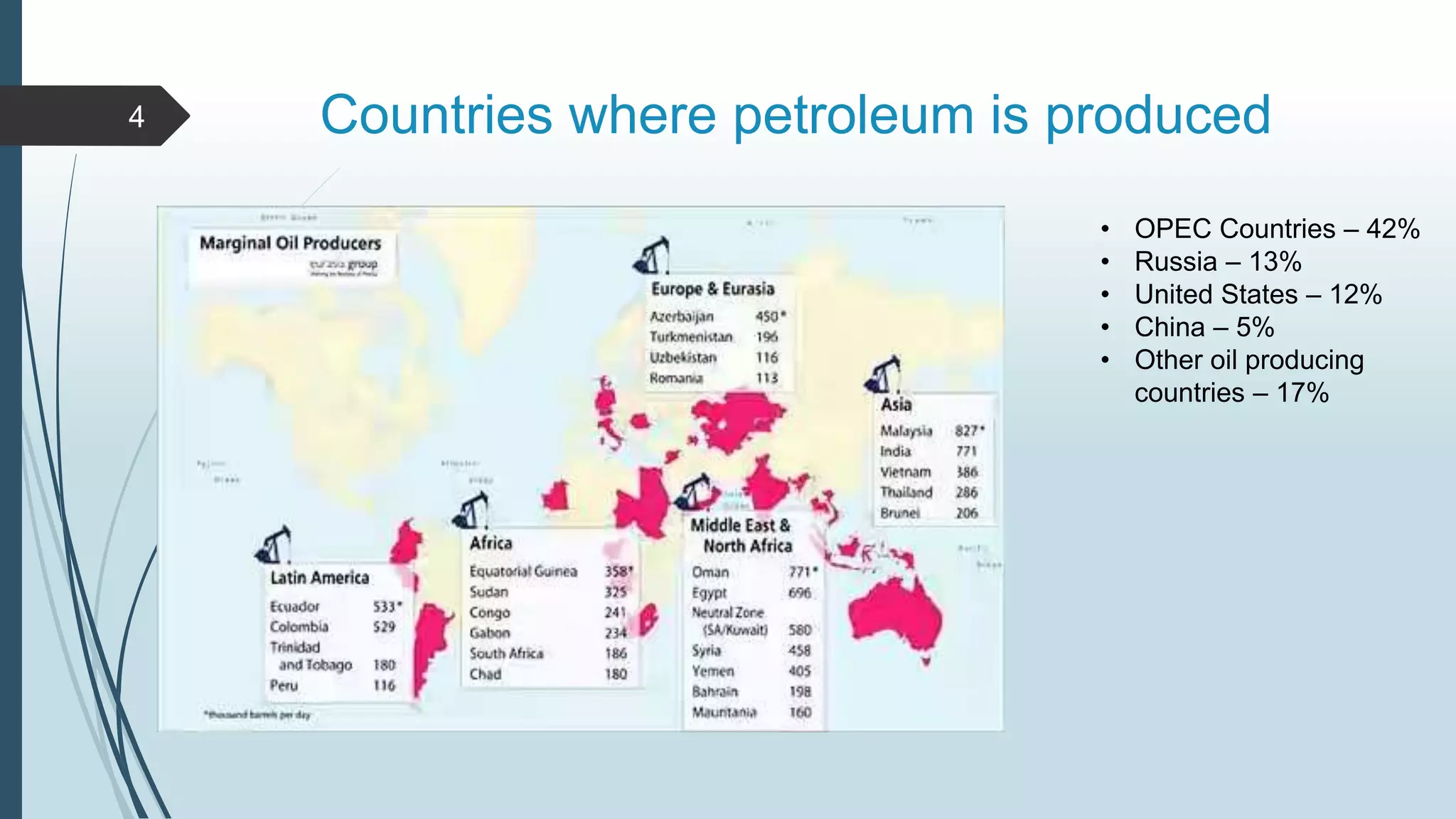
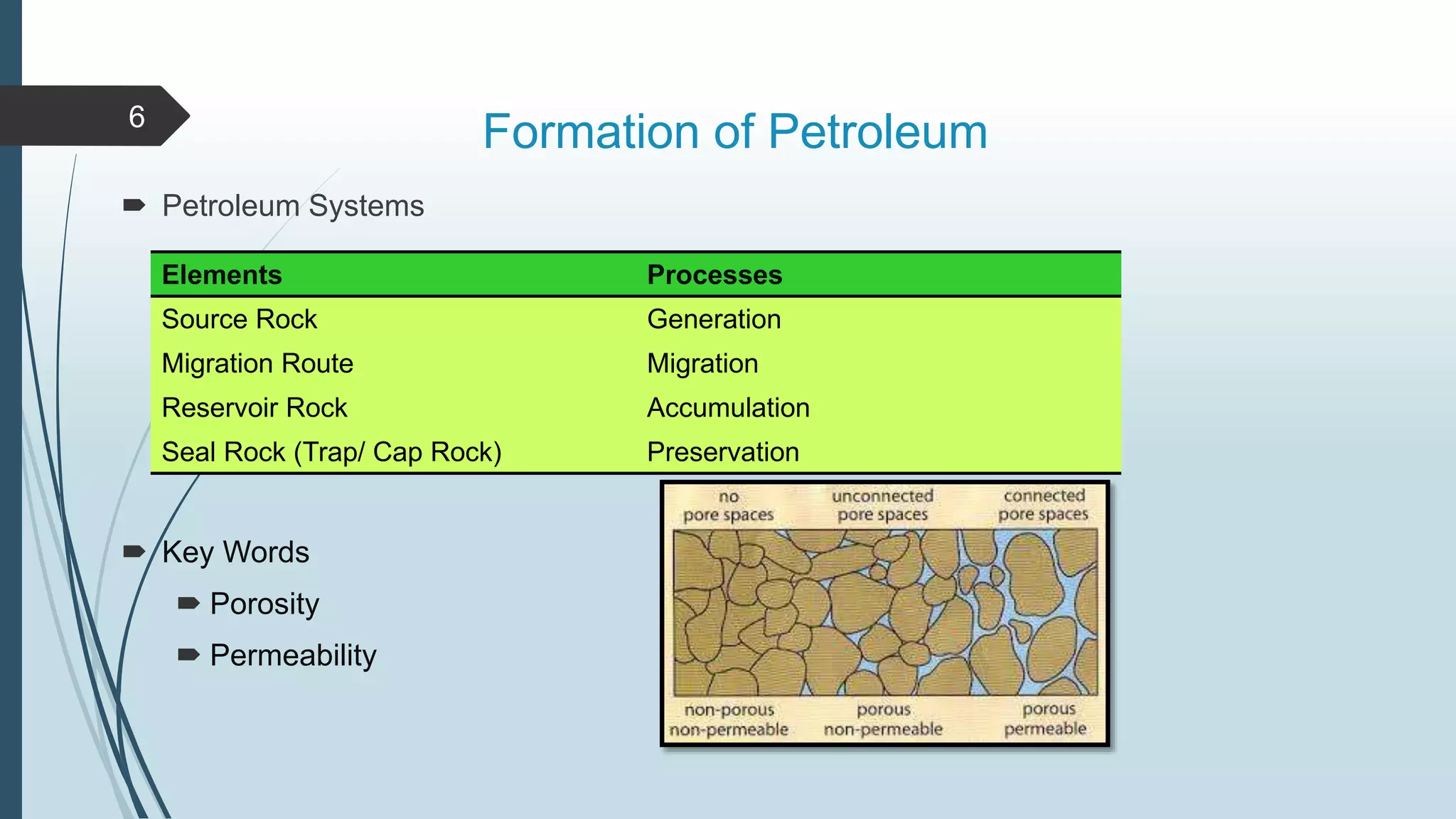
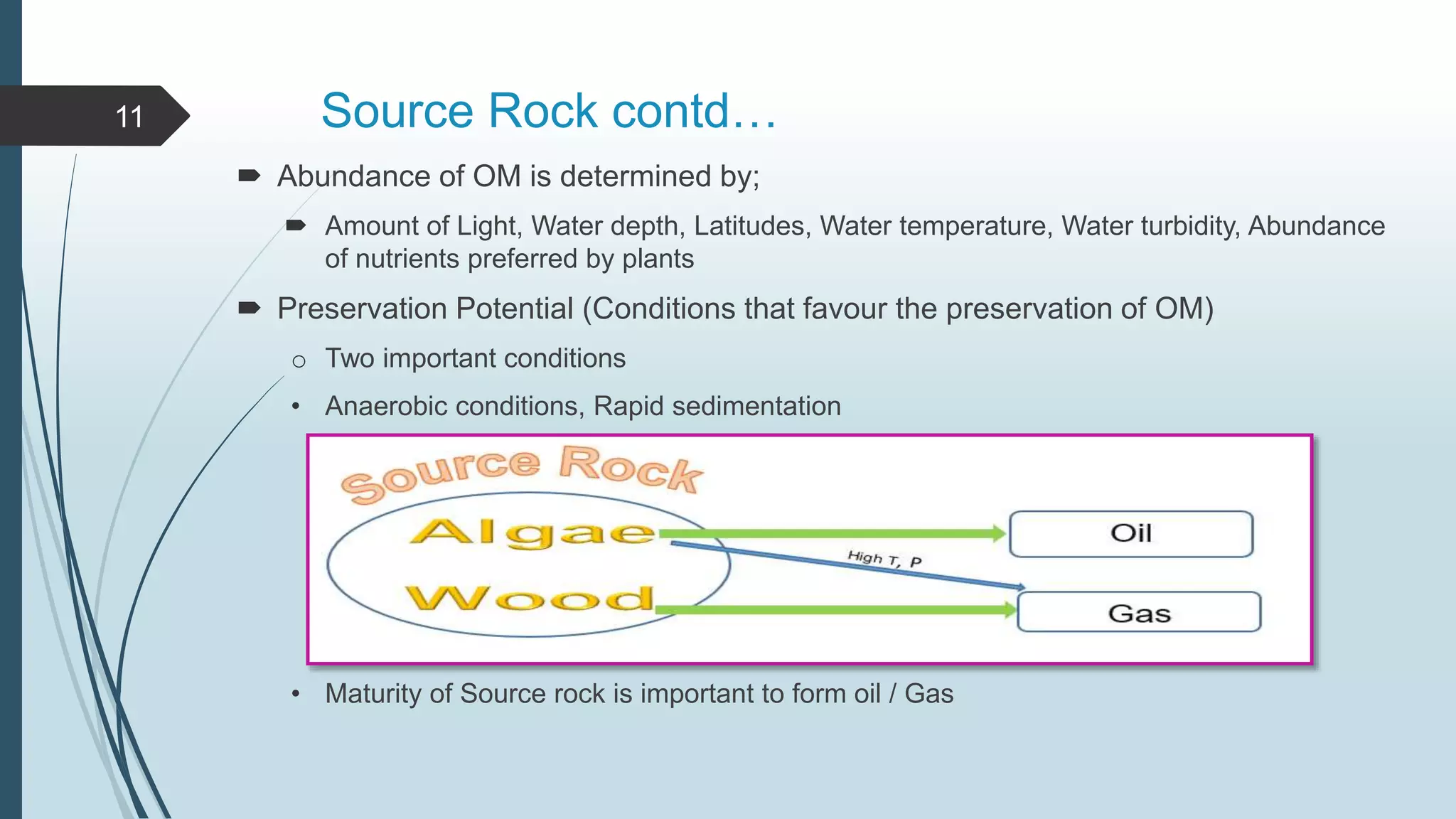
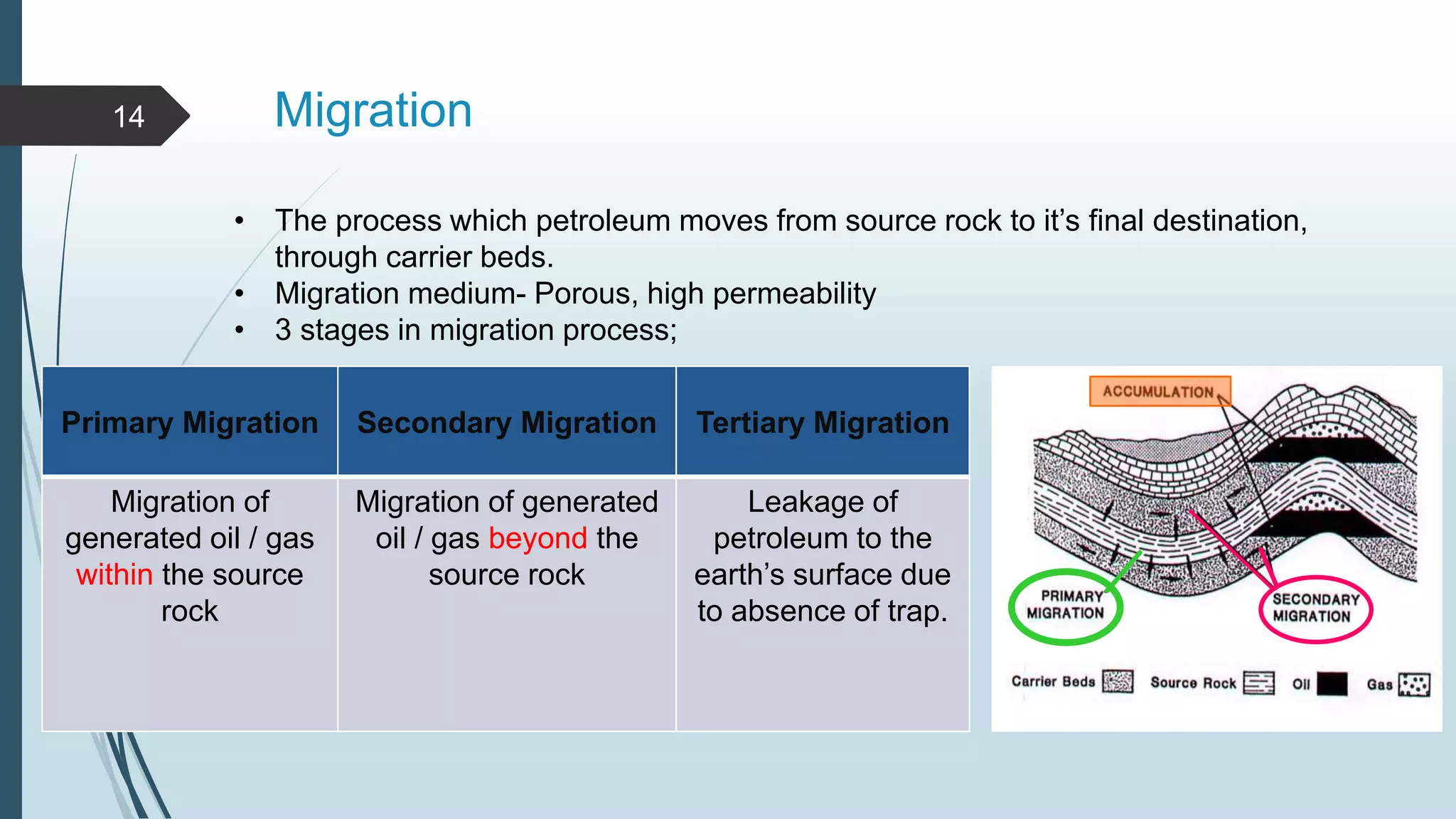
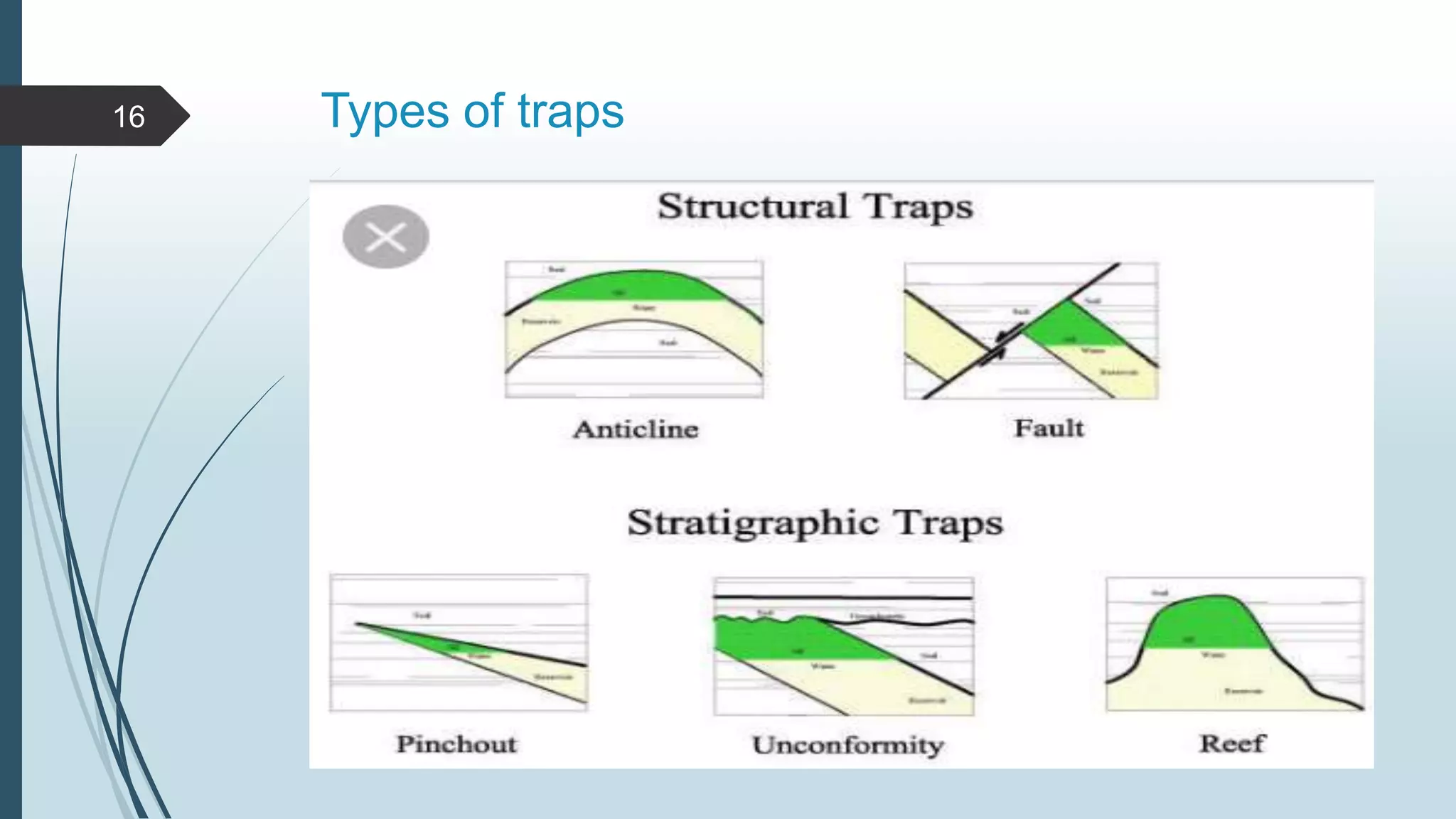
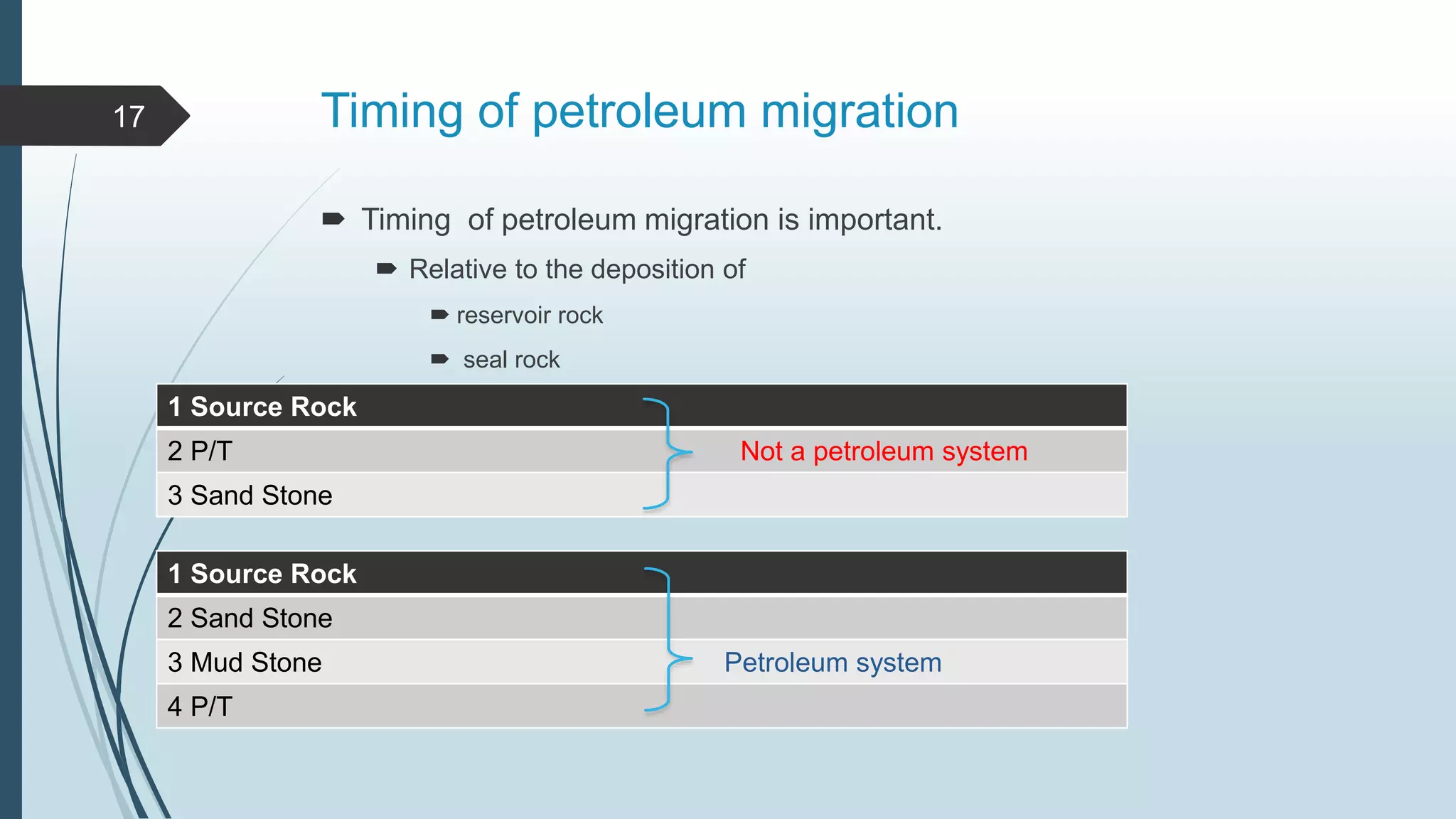
Petroleum, or oil, is a naturally occurring hydrocarbon that is formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. It is composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, along with smaller amounts of other elements. There are different types of hydrocarbons that make up petroleum, with paraffin being the most common at 30%. Petroleum is formed through a process called diagenesis where organic matter buried deep underground is exposed to high temperatures and pressures over long periods of time. As it forms, petroleum may migrate upward through porous and permeable reservoir rocks until it is trapped by an impermeable cap rock in a structure known as an oil trap. The main reservoir rocks that can store petroleum are sandstone and