Chemical bonding (ncert)
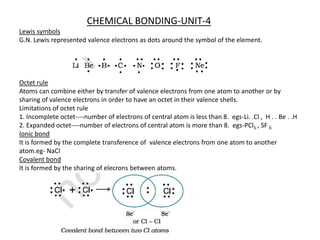
- 1. CHEMICAL BONDING-UNIT-4 Lewis symbols G.N. Lewis represented valence electrons as dots around the symbol of the element. Octet rule Atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. Limitations of octet rule 1. Incomplete octet----number of electrons of central atom is less than 8. egs-Li. .Cl , H . . Be . .H 2. Expanded octet----number of electrons of central atom is more than 8. egs-PCl5 , SF 6 Ionic bond It is formed by the complete transference of valence electrons from one atom to another atom.eg- NaCl Covalent bond It is formed by the sharing of elecrons between atoms.
- 2. VSEPR Theory [ valence shell electron pair repulsion theory ] 1. The shape of a molecule depends on the number of electron pairs around central atom. 2. The valence electrons should be placed as far as possible to acquire maximum stability. 3. The repulsive interactions of electron pairs decrease in the order; lone pair- lone pair > lone pair-bond pair > bond pair – bond pair. 1. Beryllium chloride[BeCl2] Be has 2 valence electrons & these are shared with 2 chlorine atoms to form two Be-Cl bonds.To minimise repulsion, two electron pairs are arranged at angle of 180 0 with linear shape. 2. Boron trifluoride [BF3] Boron has 3 valence electrons &these are shared with 3 fluorine atoms to form three B-F bonds. Thus with three bond pairs, BF3 will adopt trigonal planar geometry with bond angle 120 0 . 3. Methane [CH4] Carbon has 4 valence electrons &these are shared with 4 hydrogen atoms to form four C-H bonds.Thus with four bond pairs, CH4 will adopt tetrahedral shape with bond angle 109 0 281. 4. Ammonia [NH3] Nitrogen atom has 5 valence electrons.Three of these are shared with 3 hydrogen atoms to form three N-H bonds.The remaining two electrons are present as lone pair.Thus in ammonia ,there are three bond pairs & one lone pair. These four electron pairs adopt tetrahedral geometry. But due to bond pair-lone pair repulsion ,bond angle decreases from 109 0 28 1 to 107 0 with pyramidal shape .
- 3. 5. Water [H2O] Oxygen atom has 6 valence electrons. Two of these are shared with two hydrogen atoms to form two O-H bonds . Thus in water molecule, there are two bond pairs & two lone pairs . These four electron pairs adopt tetrahedral geometry. But due to repulsion between bond pairs & lone pairs, bond angle decreases from 109 028 1 to 104.5 0 with bent shape. Valence bond theory [V B theory ] 1. Covalent bonds are formed by overlapping of half filled atomic orbitals in the valence shell. 2. These orbitals must have electrons with opposite spins. 3. Overlapping results in decrease of energy & formation of covalent bond. 4. Greater the overlapping, stronger is the bond. Types of covalent bond Sigma ( σ )bond It is formed by axial [end to end or head on] overlapping. It is a strong bond. It can be formed by overlap of s-s , s-p or p-p orbitals.
- 4. Pi(∏) bond It is formed by sidewise [lateral] overlapping. It is a weak bond.It can be formed by overlap of p-p orbitals.
- 5. Hybridisation It is the process of intermixing of atomic orbitals of different energy to form equal number of hybrid orbitals with same energy &shape. Features of hybridisation 1. The number of hybrid orbitals formed is equal to no. of atomic orbitals hybridised. 2. The hybrid orbitals are equivalent in energy & shape. 3. The type of hybridisation indicates shape of molecules. Conditions for hybridisation 1. The orbitals present in valence shell are hybridised. 2.The orbitals should have almost equal energy. 3. The promotion of electron is not essential condition. 4. Even filled orbitals can take part in hybridisation. Types of hybridisation 1. sp 3hybridisation It involves mixing of one s orbital & three p orbital to form four sp 3 hybrid orbitals. An example is methane[CH 4]. The shape of molecule is tetrahedron with bond angle 109.5 0. The ground state electronic configuration of carbon is 1s 2 2s 2 2px1 2py1 2pz0. The excited state ele. Conf. is 1s 2 2s 1 2px1 2py1 2pz1 .The 2s &three 2p orbitals hybridise to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals.Each of these orbitals overlaps axially with half filled 1s orbital of hydrogen atom forming four C-H sigma bonds.
- 6. In ethane,carbon atoms are in sp3 hybridised state.One H.O. overlaps axially with orbital of other atom to form C-C sigma bond while other three H.O overlaps with orbitals of hydrogen atom to form C-H sigma bonds.
- 9. Sp hybridisation This involves mixing of one s orbital & one p orbital resulting in the formation of two sp hybrid orbitals.It has linear geometry with bond angle 180 0.
- 11. Molecular orbital theory [M O theory ] 1. The electrons in a molecule are present in the molecular orbitals. 2. The atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. 3. Molecular orbital is polycentric. 4. The number of molecular orbital formed is equal to number of combining atomic orbitals. 5. When two atomic orbitals combine, two molecular orbitals ie bonding & antibonding molecular orbitals are formed. 6. The bonding molecular orbital has lower energy &greater stability than antibonding molecular orbital. LCAO method Consider hydrogen molecule with two atoms A & B.Their atomic orbitals may be represented by wave functions Ψ A and Ψ B. The molecular orbital σ formed by addition of atomic orbital is called bonding molecular orbital & molecular orbital σ * formed by subtraction of atomic orbital is called anti bonding molecular orbital.
- 12. Conditions for combination of atomic orbitals- 1.Atomic orbitals must have same energy. 2. Atomic orbitals must have same symmetry. 3. Atomic orbitals must overlap to maximum extent. Energy level diagram for molecular orbitals In diatomic molecules upto N2, the order of increasing energy is
- 13. For diatomic molecules O2 , F2 , Ne2 the order of increasing energy is Bond order It is half the difference between number of electrons in the bonding &antibonding orbitals. b.o =1/2 [Nb – Na ] If b.o is positive ,molecule will be stable. If b.o is negative or zero ,molecule will be unstable. Integral b.o values of 1 , 2 , 3 correspond to single, double or triple bond. b.O increases as bond length decreases. Diamagnetic means electrons are paired & paramagnetic means unpaired electrons are present. Hydrogen bond It is the attractive force which binds hydrogen atom of one molecule with electronegative atom of another molecule.
- 14. Resonance When a molecule can not be represented by a single structure but its characteristic properties can be described by two or more different structures, the actual molecule is said to be resonance hybrid of these structures. Resonance stabilises a molecule.
- 15. Polarity of bonds As a result of polarisation,molecule possess dipole moment which is product of charge & distance between charges. In the case of polyatomic molecule, dipole moment depends on bond dipoles &spatial arrangement of bonds.
- 17. Fajan’s rule The covalent character of ionic bond increases with small size of cation ,large size of anion and large charge on cation & anion.