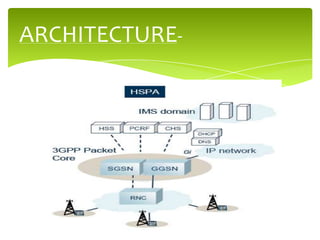
HSPA is a mobile telecommunications protocol that extends 3G networks by improving data transmission rates. It consists of HSDPA for faster downloads and HSUPA for faster uploads. HSPA was designed for non-real time data and increases peak rates to 14Mbps down and 5.8Mbps up. It achieves these improvements through technologies like shorter transmission time intervals, link adaptation, advanced modulation schemes, and MIMO antennas. The architecture introduces new channels like HS-DSCH for user data and HS-SCCH for control information. Subsequent evolutions like HSPA+ and DC-HSDPA have further increased speeds through higher order modulation and dual-cell connections.