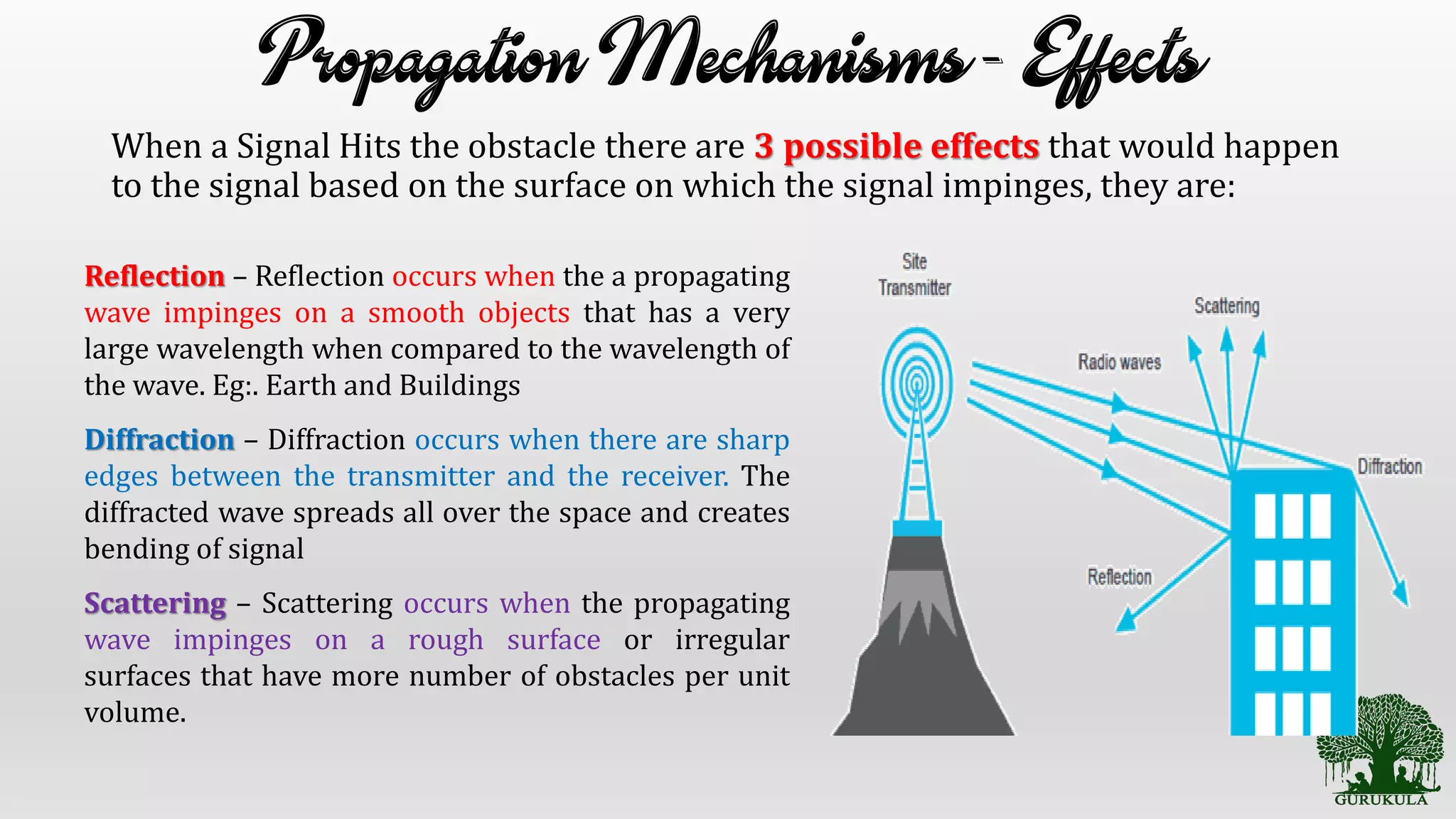
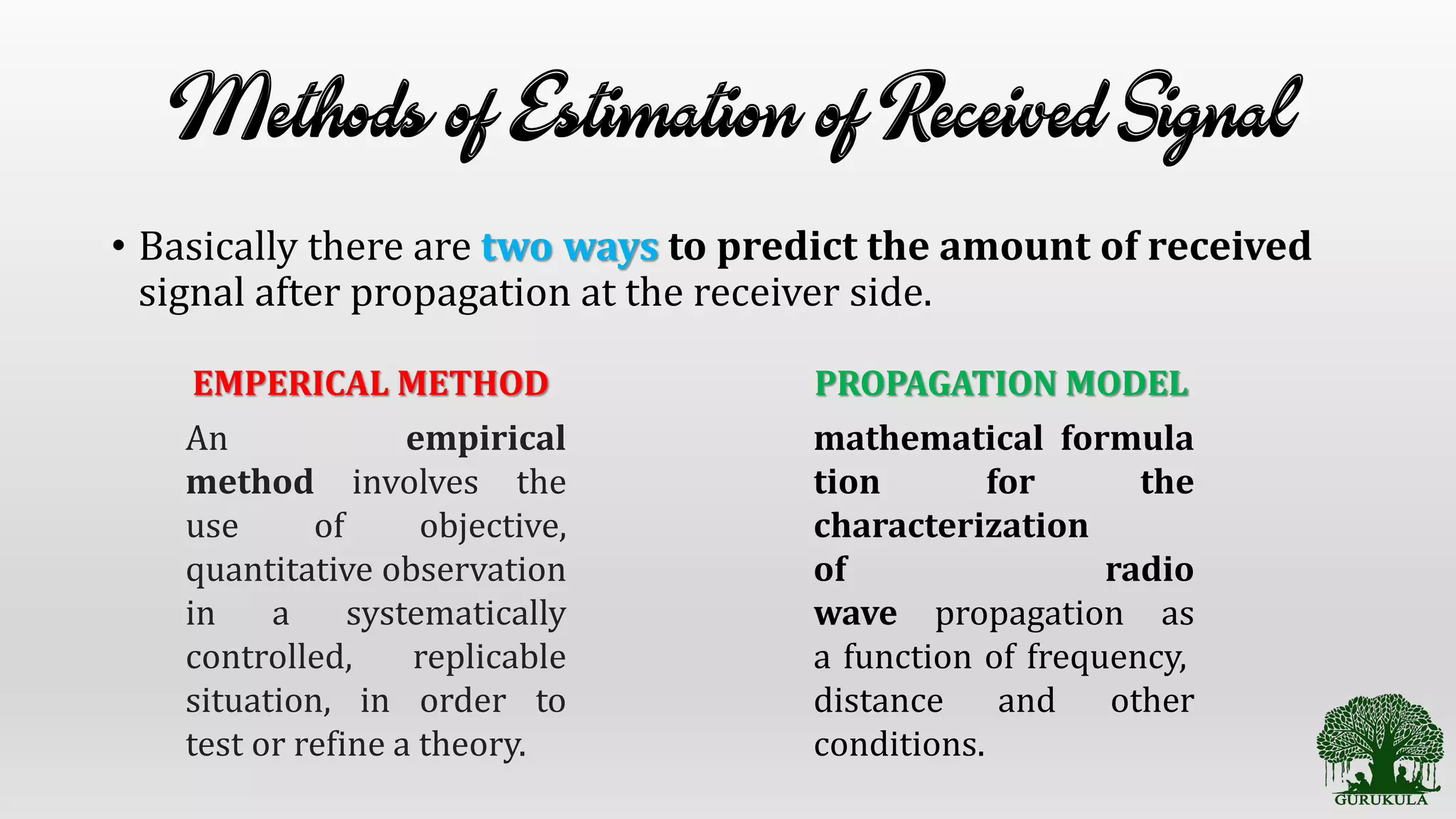
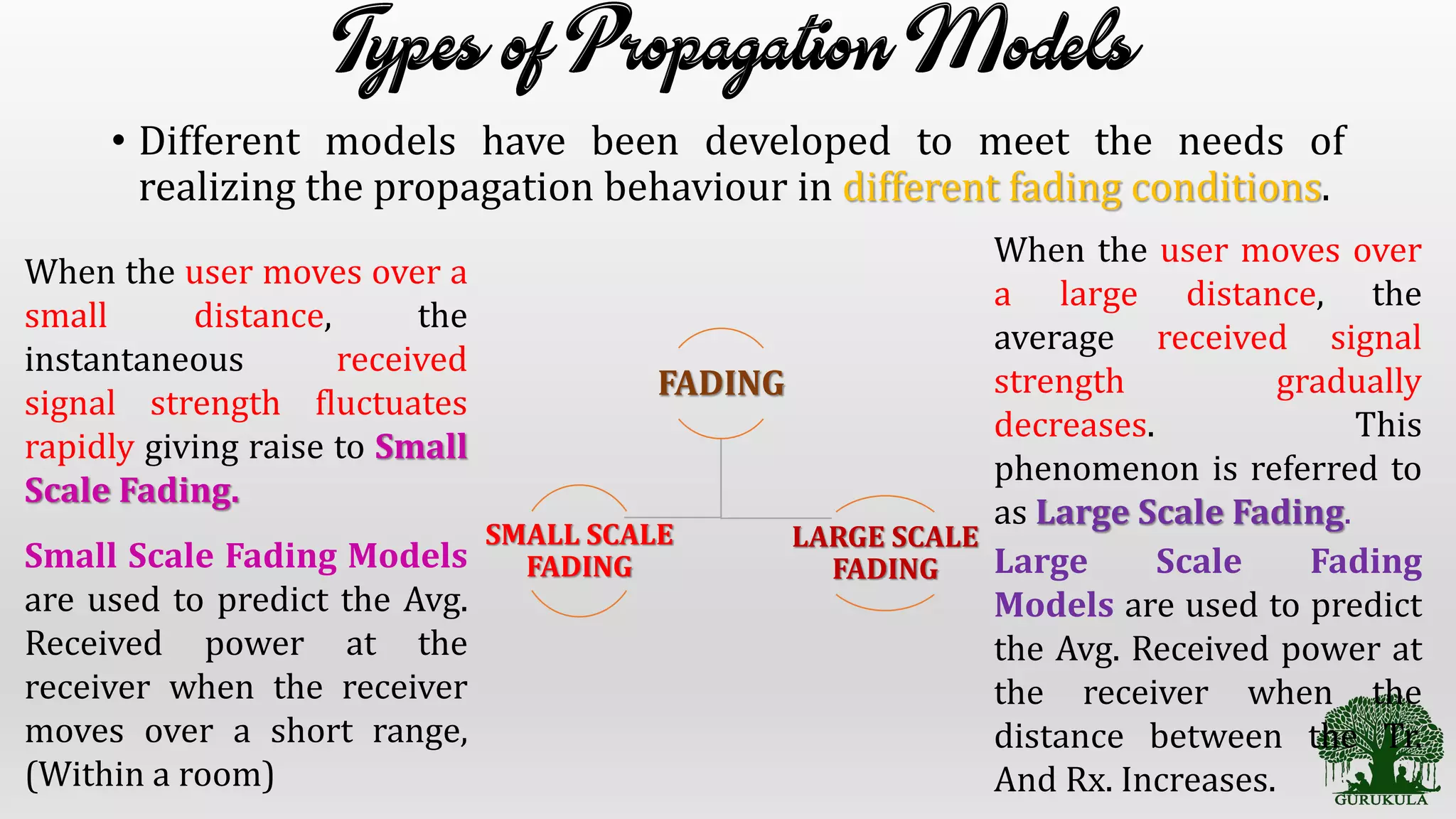
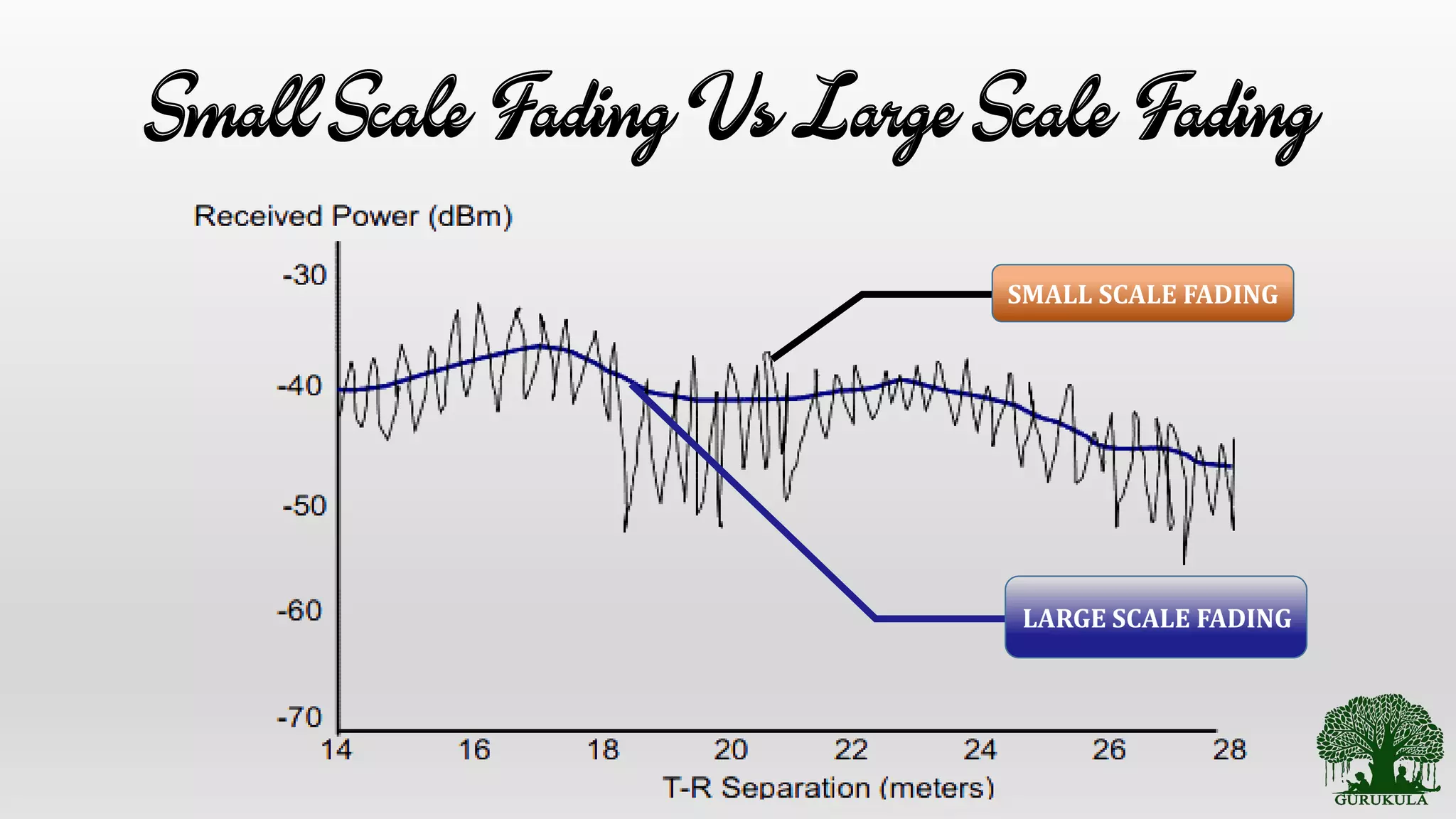
This document discusses wireless communication propagation mechanisms and propagation models. It explains that when a signal hits an obstacle, it can be reflected, diffracted, or scattered depending on the surface properties. Propagation models are used to predict the average received signal power and design wireless systems by characterizing radio wave propagation based on factors like frequency and distance. Small-scale fading models predict power fluctuations over short ranges, while large-scale models predict average power decreases over large distances between transmitter and receiver.