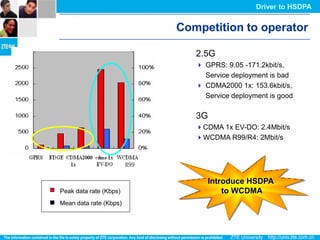
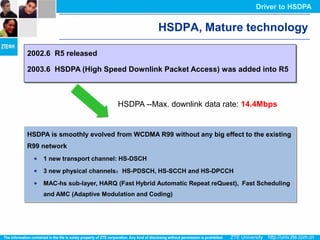
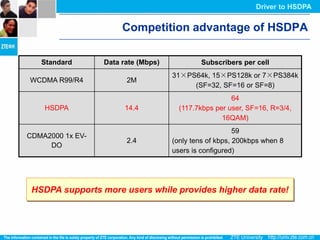
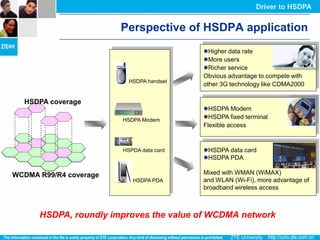
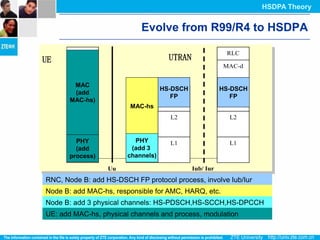
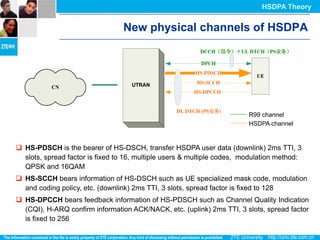
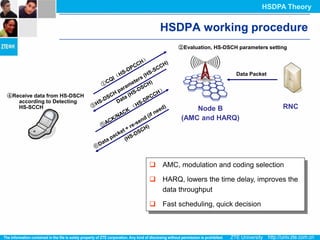
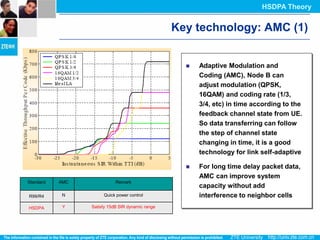
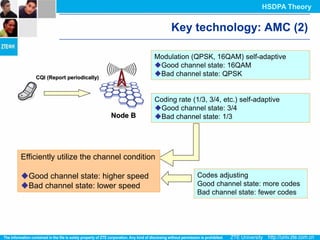
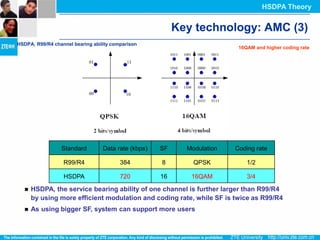
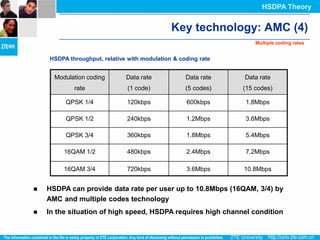
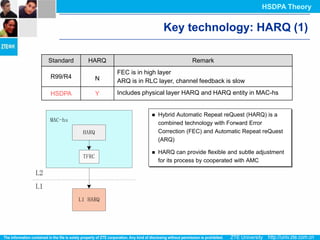
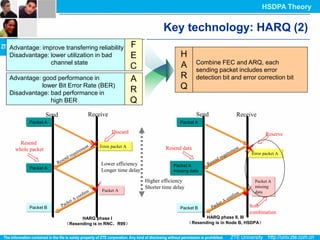
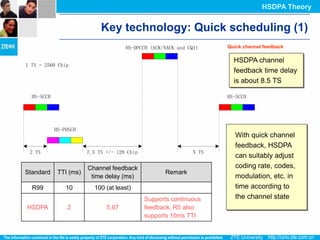
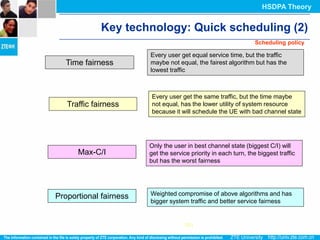
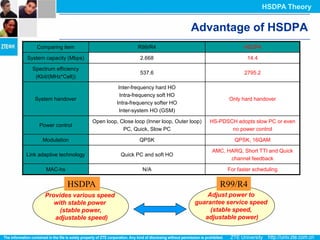
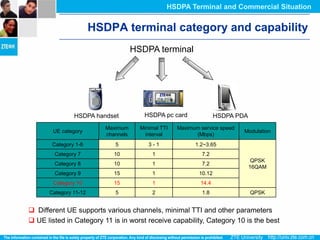
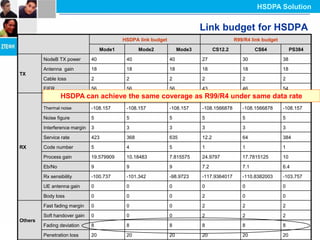
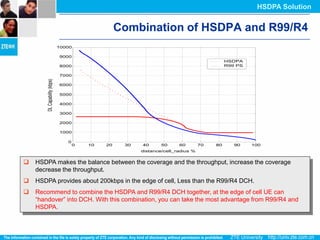
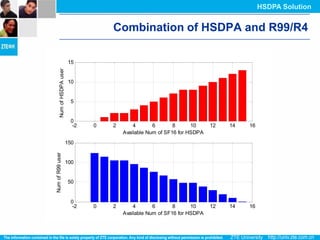
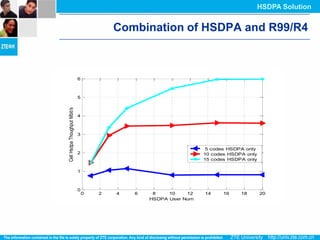
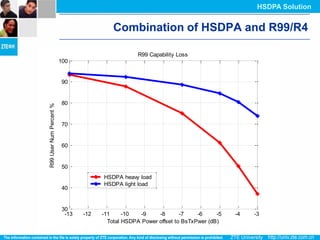
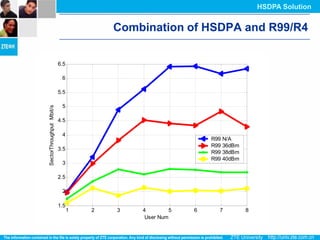
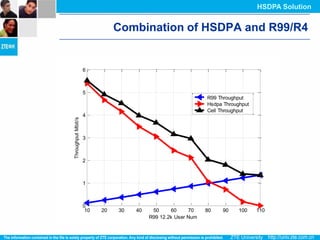
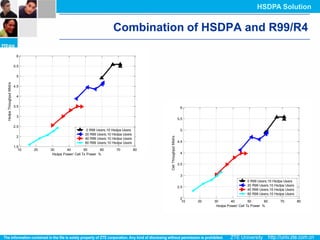
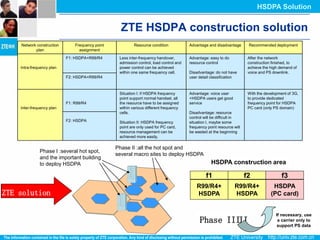
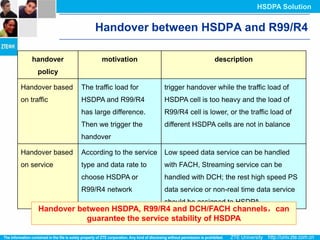
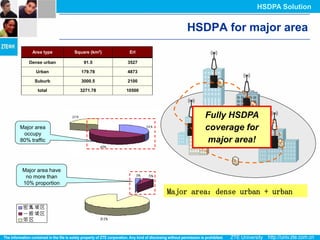
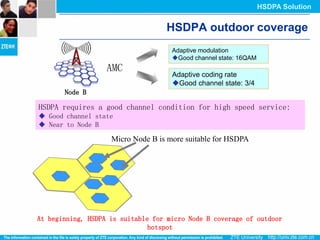
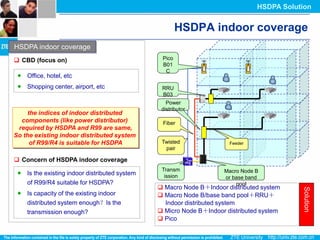
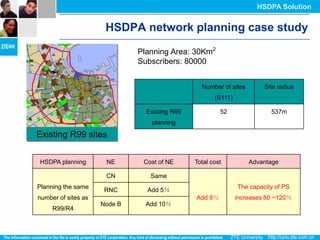
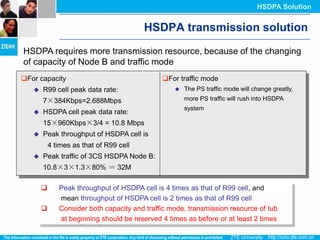
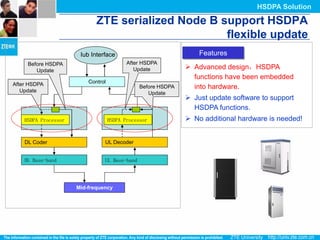
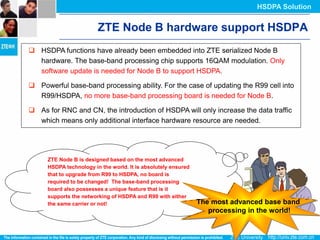
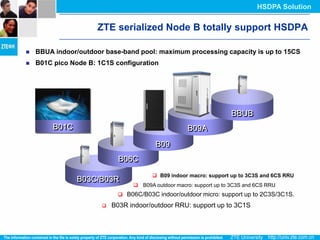
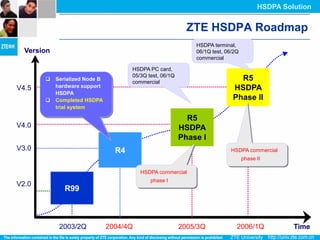
The document discusses the technology behind HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access), which enhances the downlink speed of WCDMA networks. It describes the drivers for adopting HSDPA, including increasing competition from other technologies, and explains the key technologies that enable HSDPA's higher speeds, such as adaptive modulation and coding, hybrid ARQ, and fast scheduling. Finally, it discusses the commercial deployment of HSDPA terminals and networks beginning in 2005.