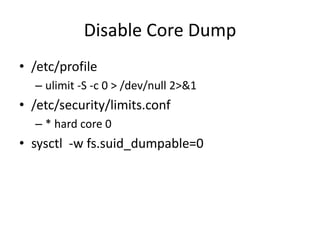
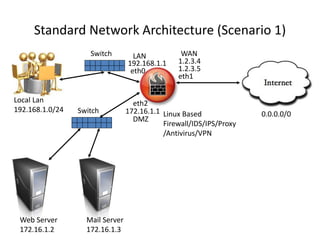
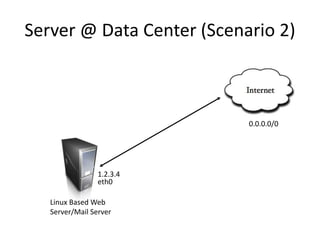
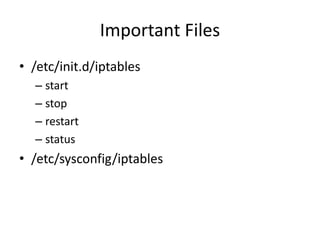
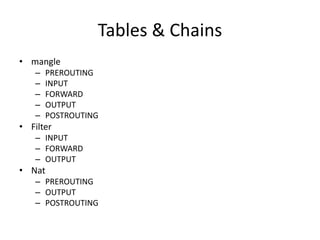
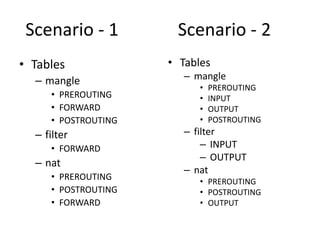
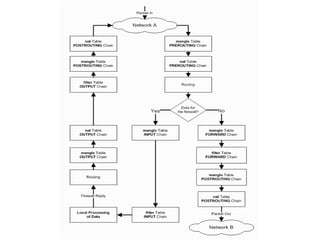
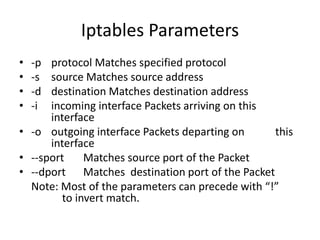
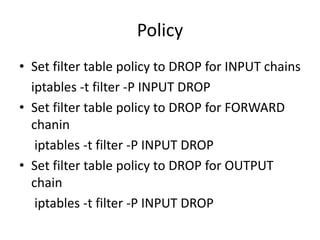
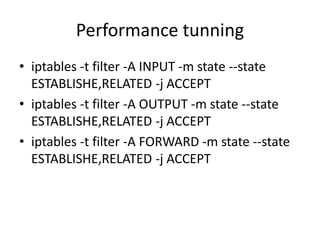
The document provides a comprehensive guide on transforming a Linux box into a security gateway, covering topics such as system hardening, firewall configuration, and various security concepts including VPNs and IDS/IPS. It details essential configurations, modifications to kernel parameters, and the use of iptables for managing network traffic. Additionally, it outlines practical examples and commands for implementing security rules and optimizing performance.