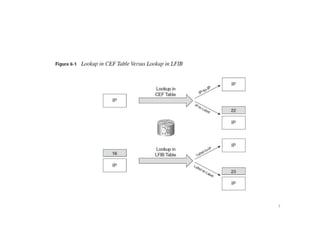
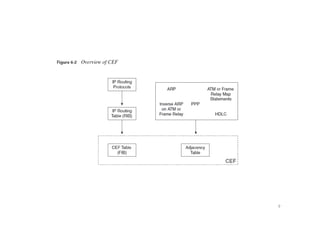
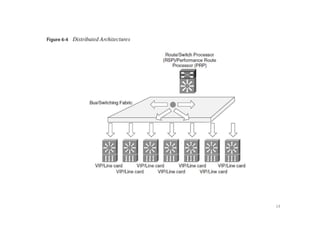
Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF) is Cisco IOS's default packet forwarding method. CEF builds the forwarding table in advance based on the routing table, rather than building it on demand like fast switching. CEF is needed in MPLS networks because labeled packets are switched based on the label and IP packets are switched using the CEF table. CEF has two main components - the Forwarding Information Base (FIB) which makes forwarding decisions, and the adjacency table which provides Layer 2 rewrite information. Distributed CEF allows packet forwarding load to be distributed across distributed CPUs in routers for high performance.