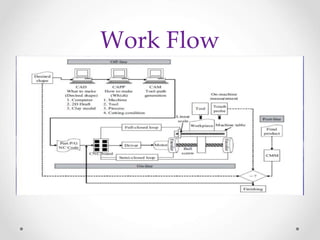
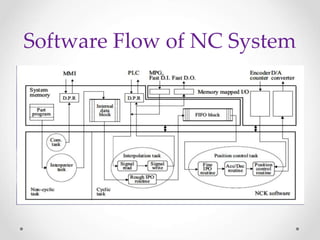
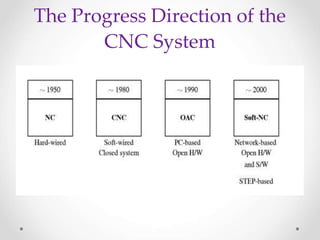
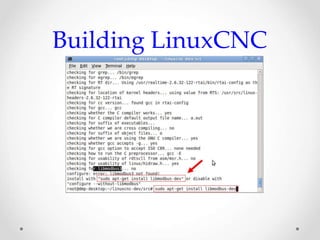
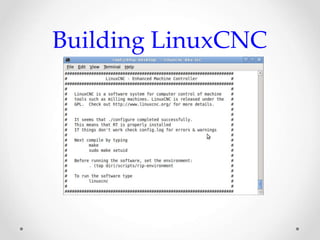
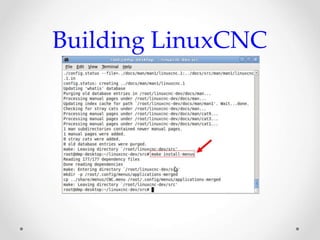
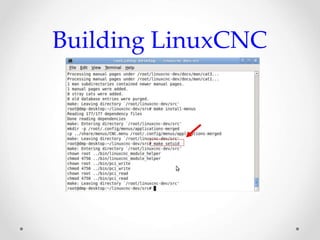
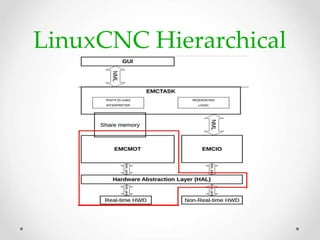
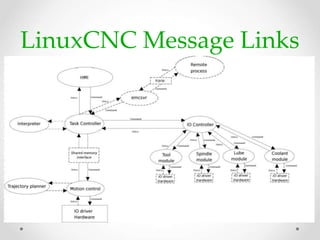
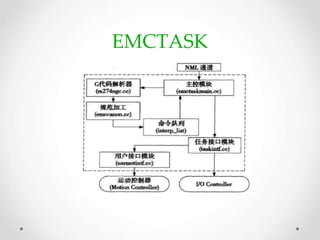
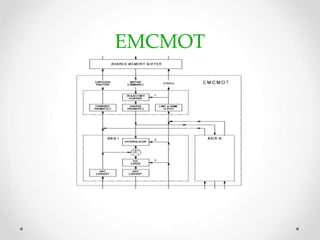
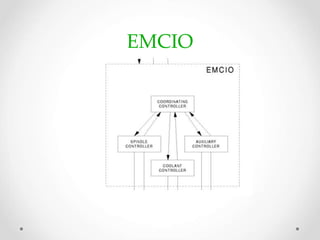
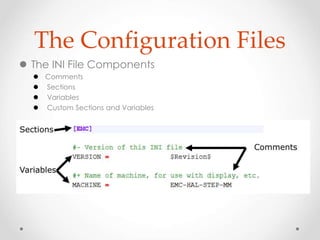
This document provides an overview of LinuxCNC, an open-source CNC controller. It discusses the basic components of a CNC system and the software workflow. It then describes how to install and build LinuxCNC from source code. The key configuration files like INI, HAL, VAR and TBL are introduced. Finally, it explains the hardware abstraction layer (HAL) which provides a way to connect LinuxCNC signals to hardware pins through components, pins, signals and functions. The HAL uses commands like loadrt, addf, loadusr and net to manage the connections.