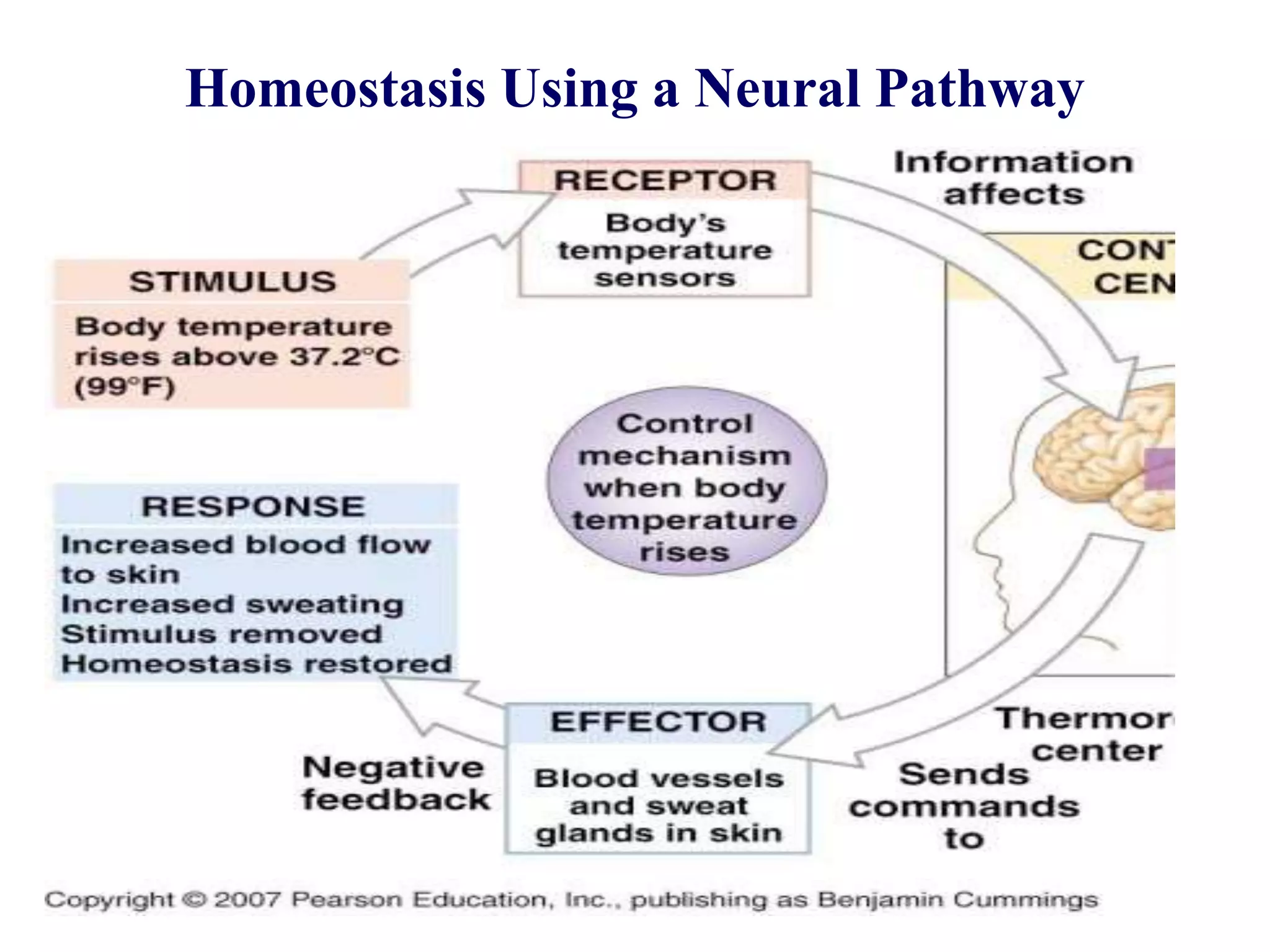
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to regulate its internal environment to maintain a stable and constant condition. It involves various mechanisms to regulate key variables such as temperature, fluid balance, and pH levels. Homeostatic control systems use negative feedback loops to detect changes and counteract them to return conditions back to normal. Positive feedback mechanisms can also be involved to accelerate necessary responses like clotting, but these are tightly regulated to avoid harm. Multiple organ systems work in coordination through neural and hormonal signaling to maintain homeostasis.