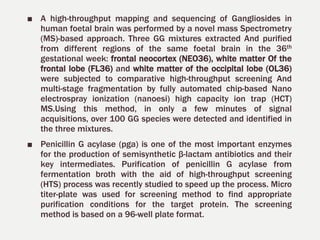
1. High throughput screening (HTS) is a process for screening large numbers of biological compounds against selected targets using automated equipment. It aims to accelerate the drug discovery process.
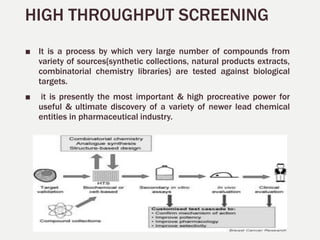
2. The key steps in HTS include target identification, reagent preparation, assay development, screening compound libraries, data analysis and management. HTS assays can be biochemical, cellular, or involve measuring second messengers.
3. HTS has various applications in natural product drug discovery, including identifying inhibitors of human thrombin from plant extracts. Euphane triterpenes isolated from Lantana camara leaves showed potent thrombin inhibitory activity.






















![Strategies Adopted for Identification Process of Plants
for Targeted Sets
S.No Research Group Adopted Methodology Comments
1 Ethnobotanical Network Worked intimately with indigenous
colleagues and traditional doctors in
different countries.
Low output of actual plant
samples for evaluation in
laboratory. High output of valuable
information(s) of their usage.
2 Pharmaceutical Companies Make use of information(s) reported in
Books, Journals etc.
Chinese Traditional Medicines;
Indian Traditional Medicines
3 Natural Products Alert
[NAPRALERT],
Database
The system is maintained at the University
of Illinois at Chicago (USA)
Contains huge number of
references related to
• Ethnobotanical reports
• Reports of biological activity in
scientific literature, and
• Phytochemical data.
4 Chemical Information
Databases]
Dictionary of Natural Products
[Chapman and Hall, New York
Database contains information on
more than 100,000 natural plant
products, including the plant
species from where the chemical
compound actually originates.
5 Literature Survey To generate semi-purified plant extracts or
chemical group of specific interest, or
extracts that are enriched in the chemical
entities
Plants having an ethnomedical
application the extracts may be
prepared using recommended
traditional medicine](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highthroughputscreening-220822051651-7dcef693/85/HIGH-THROUGHPUT-SCREENING-pptx-26-320.jpg)