This document provides an overview of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). It discusses the principle, types, instrumentation, parameters, advantages, disadvantages and applications of HPLC. The key points are:
- HPLC was developed in the 1970s to improve separation efficiency by using high pressure to force the mobile phase through the column faster.
- There are various types of HPLC based on the mode of chromatography (normal vs reverse phase), principle of separation, elution technique, scale of operation, and type of analysis.
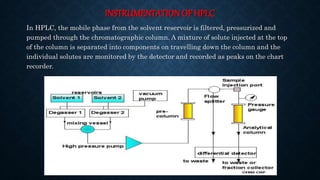
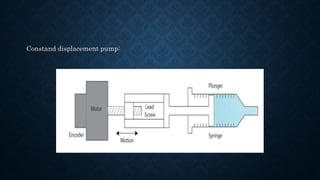
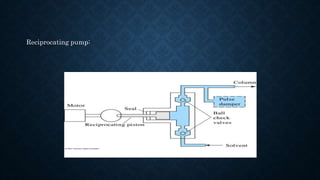
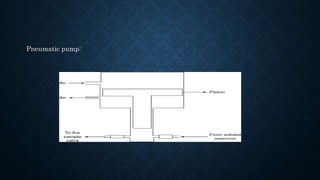
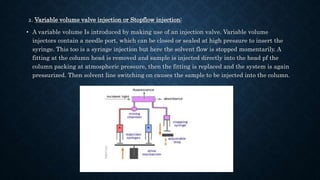
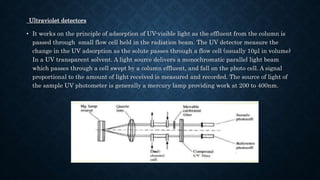
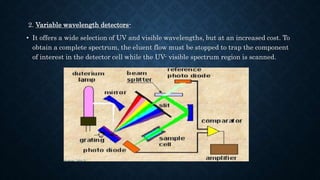
- The basic instrumentation includes solvent reservoirs, pumps, an injection system, columns, detectors and recorders. Common pumps are syringe pumps, reciprocating pumps and pneumatic pumps.