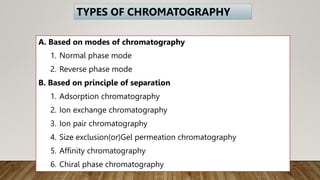
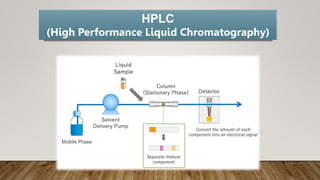
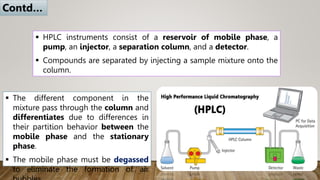
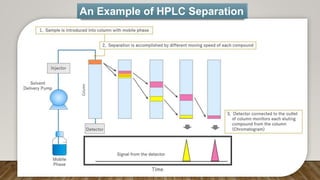
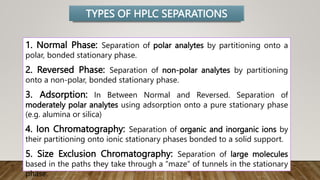
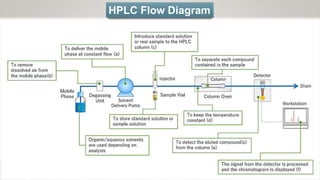
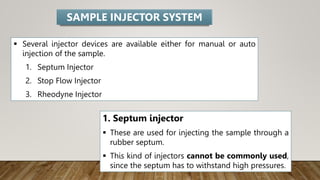
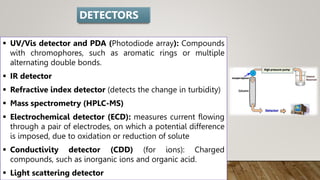
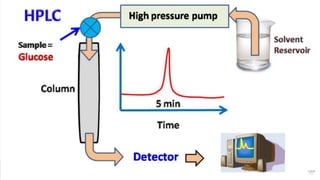
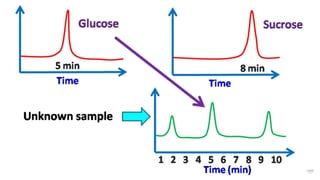
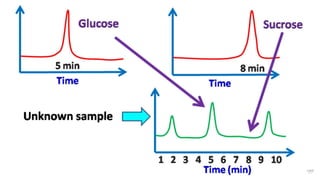
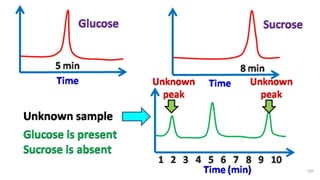
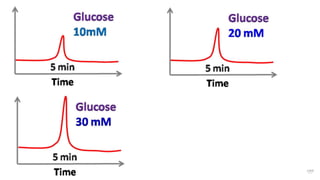
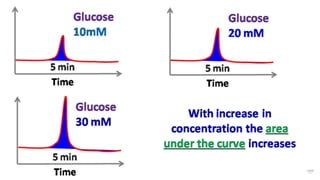
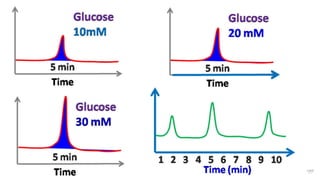
HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) is a separation technique used to separate, identify, and quantify compounds in mixtures. It works by injecting samples into a column with a stationary phase and passing a liquid mobile phase through under high pressure. Compounds are separated based on how they partition between the mobile and stationary phases. HPLC is useful for pharmaceutical analysis, clinical applications, chemical separations, and purification of compounds due to its high resolution, sensitivity, repeatability, and ability to separate both volatile and non-volatile compounds.