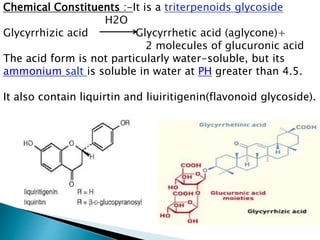
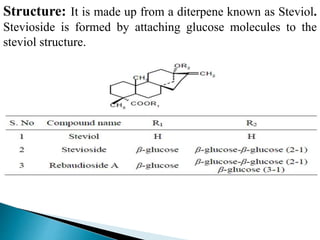
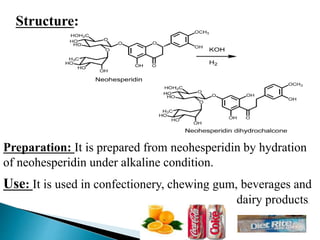
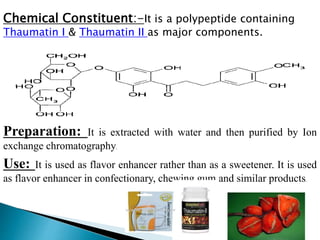
This document discusses different types of sweetening agents that can be used in drug formulations to mask bitter tastes. It describes nutritive sweeteners like sucrose and fructose, as well as non-nutritive sweeteners like saccharin and aspartame. Several natural sweeteners are then outlined in more detail, including glycyrrhizin, stevioside, neoshesperidin dihydrochalcone, thaumatin, and monellin. Their sources, properties, structures, and uses are provided. Finally, sugar and honey - two common nutritive sweeteners - are summarized with information on their preparation and applications.