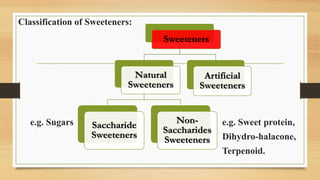
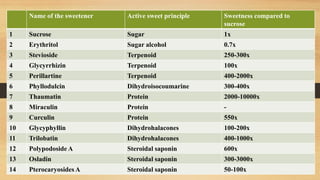
This document discusses various natural sweeteners, including their source, characteristics, and uses. It categorizes sweeteners as nutritive or non-nutritive and outlines various naturally derived sweeteners such as stevia, glycyrrhizin, neohesperidin dihydrochalcone, thaumatin, monellins, honey, agave nectar, and xylitol. It provides details on their extraction sources and chemical properties and compares their sweetness and health effects to traditional sugars.