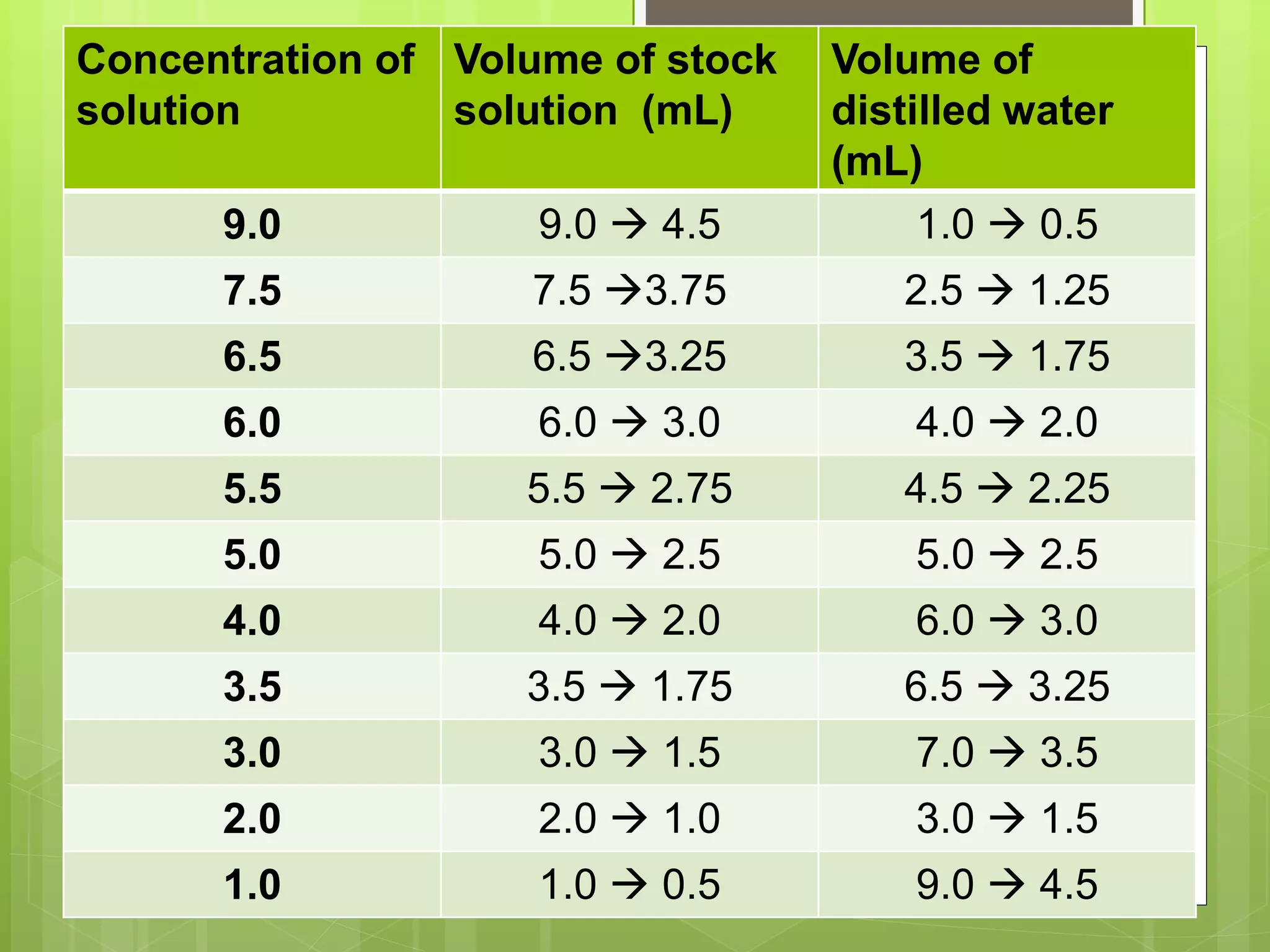
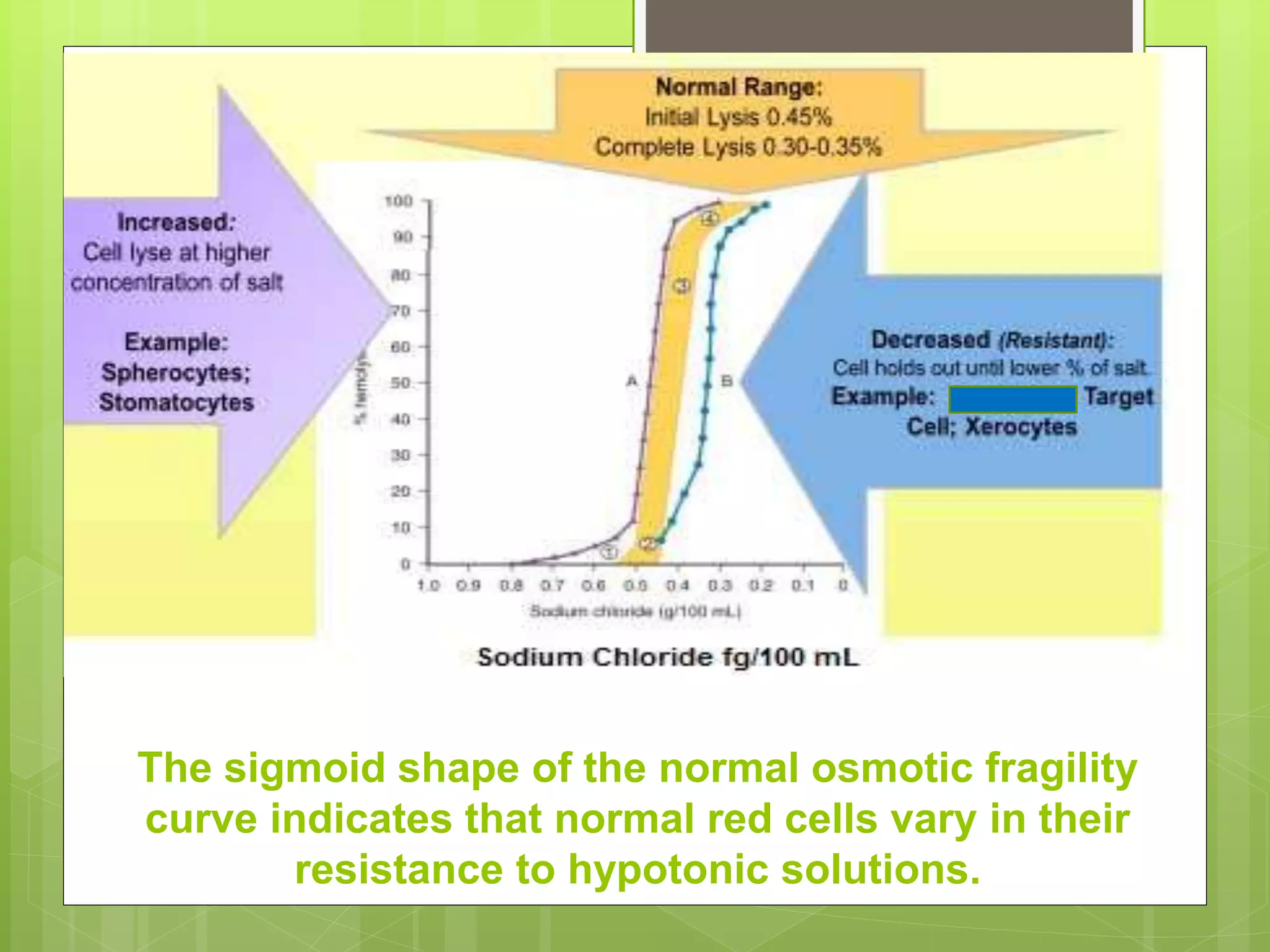
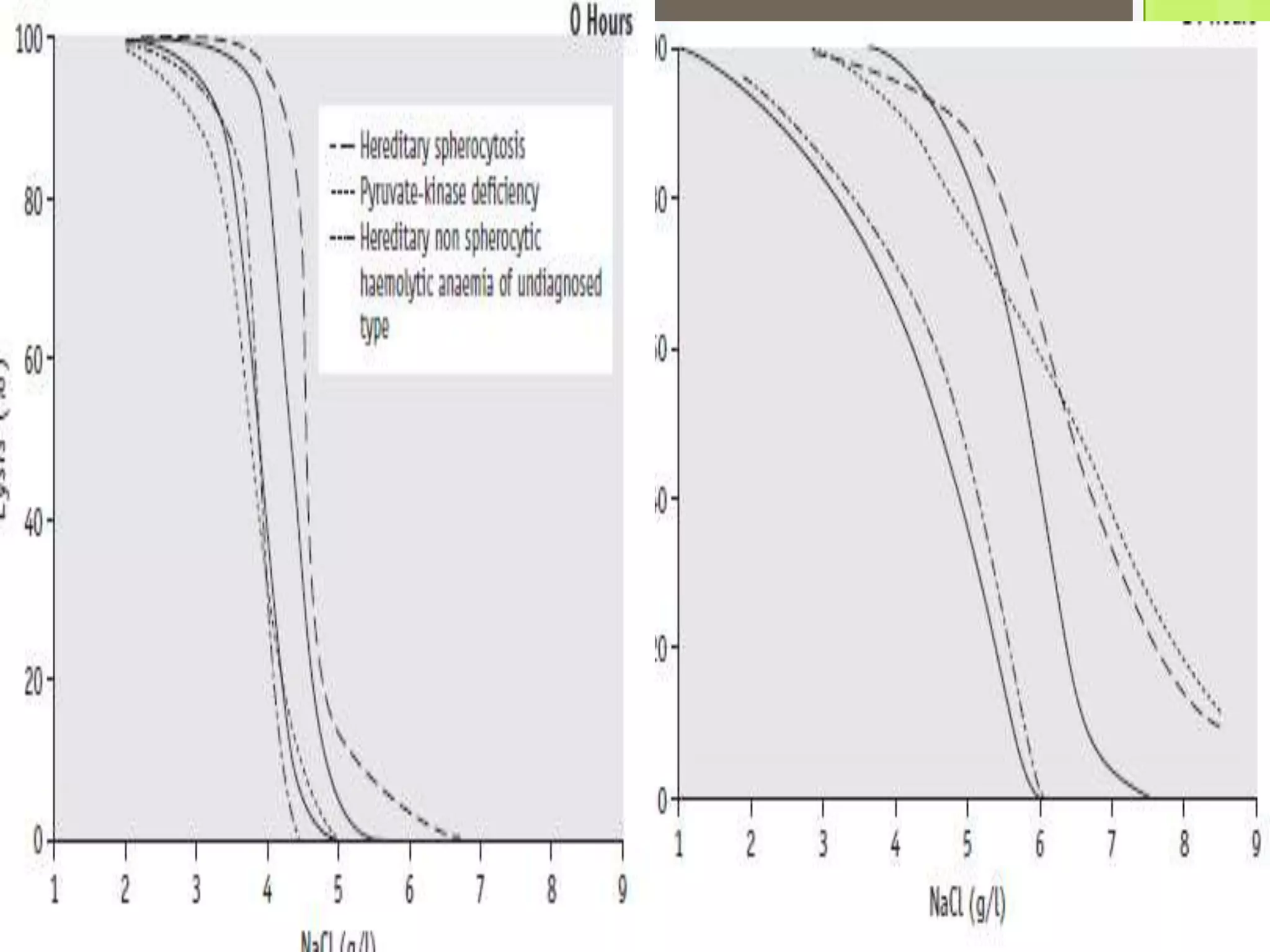
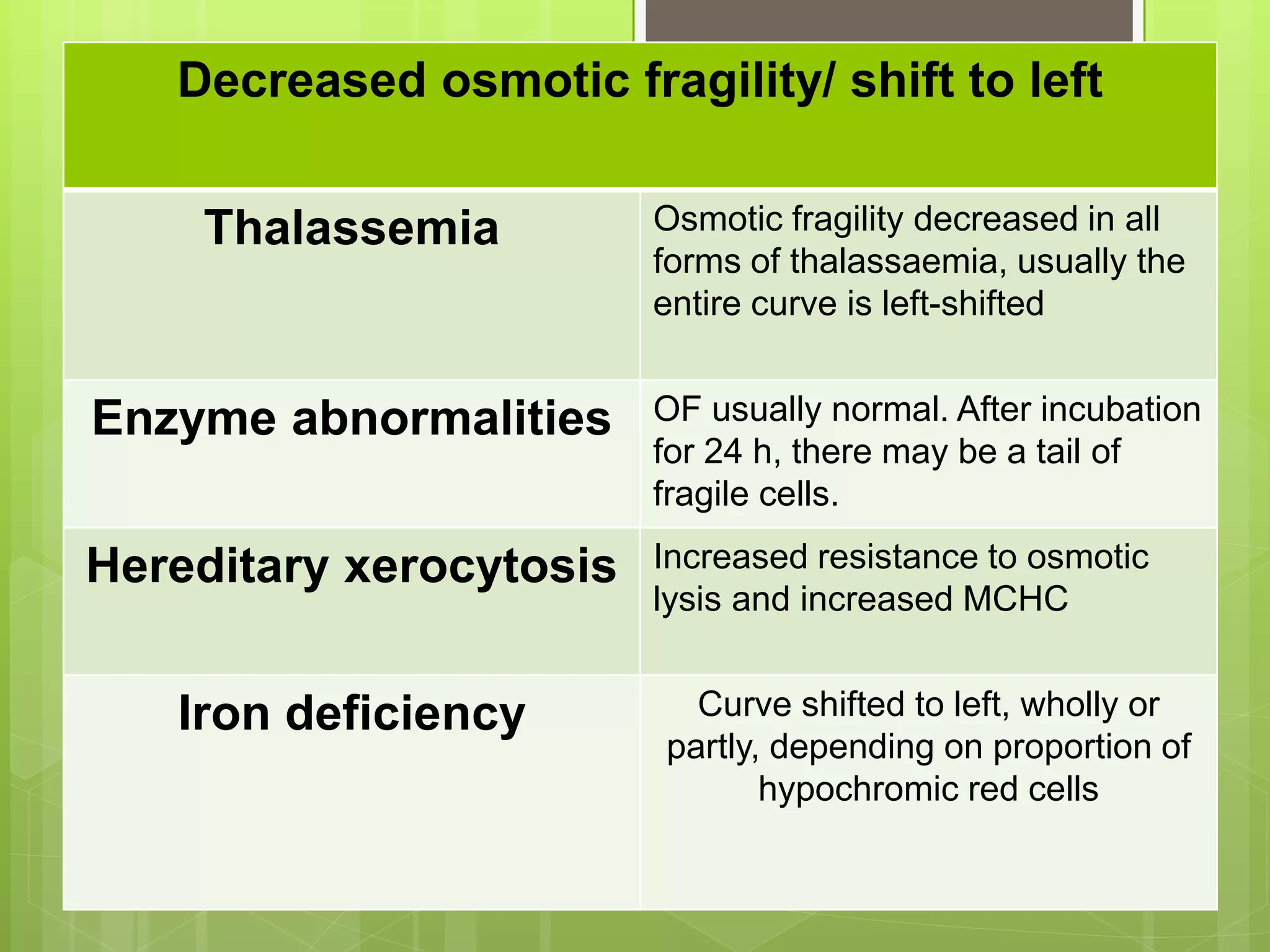
This document describes the osmotic fragility test procedure and its use in evaluating red blood cell disorders. It involves incubating blood samples in serially diluted saline solutions and analyzing hemolysis. Abnormally increased or decreased fragility can indicate conditions like hereditary spherocytosis or iron deficiency anemia respectively. A modified test called NESTROFT is also described, which is useful for screening for beta thalassemia trait in areas without automated analyzers.