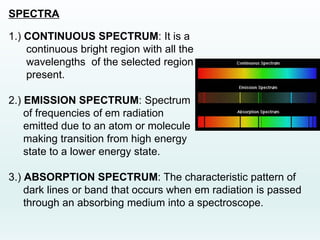
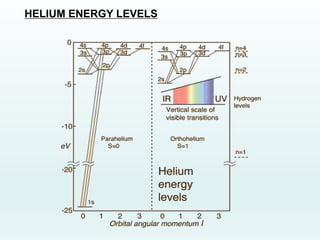
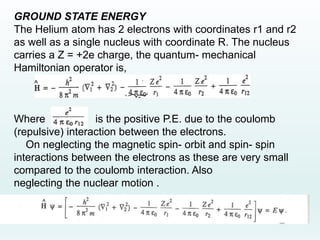
This document discusses the properties of helium atoms. It begins with an introduction describing helium's atomic structure and state at room temperature. It then covers helium's history of discovery, physical properties, emission spectra, allowed energy levels of electrons, and the differences between orthohelium and parahelium states. The document also describes using the variational method to calculate helium's ground state energy more accurately than unperturbed calculations. Finally, it lists some common uses and applications of helium such as in balloons, welding, and lasers.